AWS Certified Data Engineer – Associate DEA-C01 Exam Learning Path
- Just cleared the AWS Certified Data Engineer – Associate DEA-C01 exam with a score of 930/1000.
- AWS Certified Data Engineer – Associate DEA-C01 exam is the latest AWS exam released on 12th March 2024.
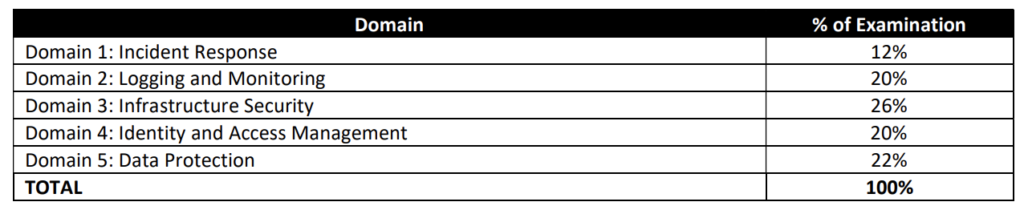
AWS Certified Data Engineer – Associate DEA-C01 Exam Content
- Data Engineer exam validates skills and knowledge in core data-related AWS services, ability to ingest and transform data, orchestrate data pipelines while applying programming concepts, design data models, manage data life cycles, and ensure data quality.
-
Exam also validates a candidate’s ability to complete the following tasks:
- Ingest and transform data, and orchestrate data pipelines while applying programming concepts.
- Choose an optimal data store, design data models, catalog data schemas, and manage data lifecycles.
- Operationalize, maintain, and monitor data pipelines. Analyze data and ensure data quality.
- Implement appropriate authentication, authorization, data encryption, privacy, and governance. Enable logging
Refer AWS Certified Data Engineer – Associate DEA-C01 Exam Guide
AWS Certified Data Engineer – Associate DEA-C01 Exam Summary
- DEA-C01 exam consists of 65 questions in 130 minutes, and the time is more than sufficient if you are well-prepared.
- DEA-C01 exam includes two types of questions, multiple-choice and multiple-response.
- DEA-C01 has a scaled score between 100 and 1,000. The scaled score needed to pass the exam is 720.
- Associate exams currently cost $ 150 + tax.
- You can get an additional 30 minutes if English is your second language by requesting Exam Accommodations. It might not be needed for Associate exams but is helpful for Professional and Specialty ones.
- AWS exams can be taken either remotely or online, I prefer to take them online as it provides a lot of flexibility. Just make sure you have a proper place to take the exam with no disturbance and nothing around you.
- Also, if you are taking the AWS Online exam for the first time try to join at least 30 minutes before the actual time as I have had issues with both PSI and Pearson with long wait times.
AWS Certified Data Engineer – Associate DEA-C01 Exam Resources
- Online Courses
- Stephane Maarek – AWS Certified Data Engineer Associate 2024 – Hands On!
- Whizlabs – AWS Certified Data Engineer Associate Course
- Practice tests
- Signed up with AWS for the Free Tier account which provides a lot of Services to be tried for free with certain limits which are more than enough to get things going. Be sure to decommission services beyond the free limits, preventing any surprises 🙂
- Read the FAQs at least for the important topics, as they cover important points and are good for quick review
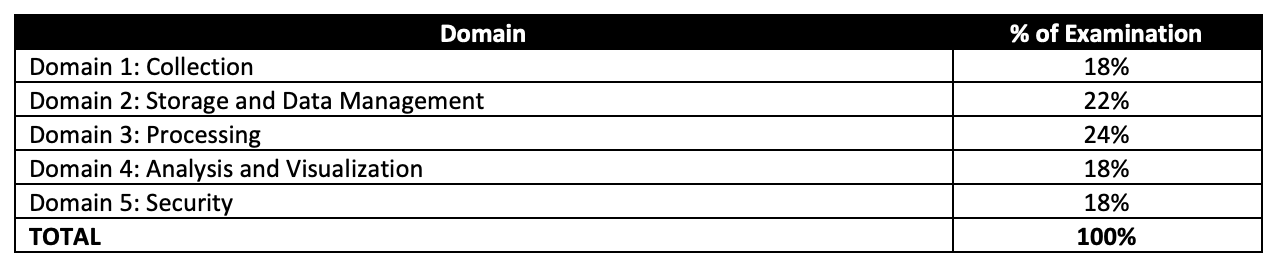
AWS Certified Data Engineer – Associate DEA-C01 Exam Topics
- DEA-C01 Exam covers the data engineering aspects in terms of data ingestion, transformation, orchestration, designing data models, managing data life cycles, and ensuring data quality.
Analytics
- Ensure you know and cover all the services in-depth, as 80% of the exam focuses on topics like Glue, Athena, Kinesis, and Redshift.
- AWS Analytics Services Cheat Sheet
- Glue
- DEA-C01 covers Glue in great detail.
- AWS Glue is a fully managed, ETL service that automates the time-consuming steps of data preparation for analytics.
- supports server-side encryption for data at rest and SSL for data in motion.
- Glue ETL engine to Extract, Transform, and Load data that can automatically generate Scala or Python code.
- Glue Data Catalog is a central repository and persistent metadata store to store structural and operational metadata for all the data assets. It works with Apache Hive as its metastore.
- Glue Crawlers scan various data stores to automatically infer schemas and partition structures to populate the Data Catalog with corresponding table definitions and statistics.
- Glue Job Bookmark tracks data that has already been processed during a previous run of an ETL job by persisting state information from the job run.
- Glue Streaming ETL enables performing ETL operations on streaming data using continuously running jobs.
- Glue provides a flexible scheduler that handles dependency resolution, job monitoring, and retries.
- Glue Studio offers a graphical interface for authoring AWS Glue jobs to process data allowing you to define the flow of the data sources, transformations, and targets in the visual interface and generating Apache Spark code on your behalf.
- Glue Data Quality helps reduce manual data quality efforts by automatically measuring and monitoring the quality of data in data lakes and pipelines.
- Glue DataBrew helps prepare, visualize, clean, and normalize data directly from the data lake, data warehouses, and databases, including S3, Redshift, Aurora, and RDS.
- Glue Flex execution option helps to reduce the costs of pre-production, test, and non-urgent data integration workloads by up to 34% and is ideal for customer workloads that don’t require fast jobs start times.
- Glue
FindMatchestransform helps identify duplicate or matching records in the dataset, even when the records do not have a common unique identifier and no fields match exactly.
- Kinesis
- Understand Kinesis Data Streams and Kinesis Data Firehose in-depth.
- Know Kinesis Data Streams vs Kinesis Firehose
- Know Kinesis Data Streams is open-ended for both producer and consumer. It supports KCL and works with Spark.
- Know Kinesis Firehose is open-ended for producers only. Data is stored in S3, Redshift, and OpenSearch.
- Kinesis Firehose works in batches with minimum 60secs intervals and in near-real time.
- Kinesis Firehose supports out-of-the-box transformation and custom transformation using Lambda
- Kinesis supports encryption at rest using server-side encryption
- Kinesis supports Interface VPC endpoint to keep traffic between the VPC and Kinesis Data Streams from leaving the Amazon network and doesn’t require an internet gateway, NAT device, VPN connection, or Direct Connect connection.
- Kinesis Producer Library supports batching
- Kinesis Data Analytics OR Managed Service for Apache Flink
- helps transform and analyze streaming data in real time using Apache Flink.
- supports anomaly detection using Random Cut Forest ML
- supports reference data stored in S3.
- Redshift
- Redshift is also covered in depth.
- Redshift Advanced include
- Redshift Distribution Style determines how data is distributed across compute nodes and helps minimize the impact of the redistribution step by locating the data where it needs to be before the query is executed.
- Redshift Enhanced VPC routing forces all COPY and UNLOAD traffic between the cluster and the data repositories through the VPC.
- Workload management (WLM) enables users to flexibly manage priorities within workloads so that short, fast-running queries won’t get stuck in queues behind long-running queries.
- Redshift Spectrum
- helps query structured and semistructured data from files in S3 without having to load the data into Redshift tables.
- cannot access data from Glacier.
- Federated Query feature allows querying and analyzing data across operational databases, data warehouses, and data lakes.
- Short query acceleration (SQA) prioritizes selected short-running queries ahead of longer-running queries.
- Concurrency Scaling helps support thousands of concurrent users and concurrent queries, with consistently fast query performance.
- Redshift Serverless is a serverless option of Redshift that makes it more efficient to run and scale analytics in seconds without the need to set up and manage data warehouse infrastructure.
- Streaming ingestion provides low-latency, high-speed ingestion of stream data from Kinesis Data Streams and Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka into a Redshift provisioned or Redshift Serverless materialized view.
- Redshift data sharing can securely share access to live data across Redshift clusters, workgroups, AWS accounts, and AWS Regions without manually moving or copying the data.
- Redshift Data API provides a secure HTTP endpoint and integration with AWS SDKs to help access Redshift data with web services–based applications, including AWS Lambda, SageMaker notebooks, and AWS Cloud9.
- Redshift Best Practices w.r.t selection of Distribution style, Sort key, importing/exporting data
- COPY command which allows parallelism, and performs better than multiple COPY commands
- COPY command can use manifest files to load data
- COPY command handles encrypted data
- COPY command which allows parallelism, and performs better than multiple COPY commands
- Redshift Resizing cluster options (elastic resize did not support node type changes before, but does now)
- Redshift supports encryption at rest and in transit
- Redshift supports encrypting an unencrypted cluster using KMS. However, you can’t enable hardware security module (HSM) encryption by modifying the cluster. Instead, create a new, HSM-encrypted cluster and migrate your data to the new cluster.
- Know Redshift views to control access to data.
- Athena
- is a serverless, interactive analytics service built on open-source frameworks, supporting open-table and file formats.
- provides a simplified, flexible way to analyze data in an S3 data lake and 30 data sources, including on-premises data sources or other cloud systems using SQL or Python without loading the data.
- integrates with QuickSight for visualizing the data or creating dashboards.
- uses a managed Glue Data Catalog to store information and schemas about the databases and tables for the data stored in S3.
- Workgroups can be used to separate users, teams, applications, or workloads, to set limits on the amount of data each query or the entire workgroup can process, and to track costs.
- Athena best practices
- Data partitioning,
- Partition projection, and
- Columnar file formats like ORC or Parquet as they support compression and are splittable.
- Elastic Map Reduce
- Understand EMRFS
- Use Consistent view to make sure S3 objects referred by different applications are in sync. Although, it is not needed now.
- Know EMR Best Practices (hint: start with many small nodes instead of few large nodes)
- Know EMR Encryption options
- supports SSE-S3, SS3-KMS, CSE-KMS, and CSE-Custom encryption for EMRFS
- supports LUKS encryption for local disks
- supports TLS for data in transit encryption
- supports EBS encryption
- Hive metastore can be externally hosted using RDS, Aurora, and AWS Glue Data Catalog
- Understand EMRFS
- OpenSearch
- OpenSearch is a search service that supports indexing, full-text search, faceting, etc.
- OpenSearch can be used for analysis and supports visualization using OpenSearch Dashboards which can be real-time.
- OpenSearch Service Storage tiers support Hot, UltraWarm, and Cold and the data can be transitioned using Index State management.
- QuickSight
- Know Supported Data Sources
- QuickSight provides IP addresses that need to be whitelisted for QuickSight to access the data store.
- QuickSight provides direct integration with Microsoft AD
- QuickSight supports row-level security using dataset rules to control access to data at row granularity based on permissions associated with the user interacting with the data.
- QuickSight supports ML insights as well
- QuickSight supports users defined via IAM or email signup.
- AWS Lake Formation
- is an integrated data lake service that helps to discover, ingest, clean, catalog, transform, and secure data and make it available for analysis.
- automatically manages access to the registered data in S3 through services including AWS Glue, Athena, Redshift, QuickSight, and EMR
- provides central access control for the data, including table-and-column-level access controls, and encryption for data at rest.
- Simple Storage Service – S3 as a storage service
- S3 storage classes with lifecycle policies based on usage to provide cost-effective storage solutions.
- S3 Event Notifications integrates with SNS and Lambda for real-time data processing
- Data Pipeline for data transfer helps automate and schedule regular data movement and data processing activities in AWS.
- Step Functions help build distributed applications, automate processes, orchestrate microservices, and create data and ML pipelines.
- AppFlow is a fully managed integration service to securely exchange data between software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications, such as Salesforce, and AWS services, such as Simple Storage Service (S3) and Redshift.
Security, Identity & Compliance
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Understand IAM Roles
- Key Management Service (KMS) provides key management for encryption at rest.
- Integrates with S3, Redshift, Kinesis
- S3 Integration with SSE, SSE-C, SSE-KMS
- AWS Secrets Manager
- helps protect secrets needed to access applications, services, and IT resources.
- Amazon Macie is a security service that uses machine learning to automatically discover, classify, and protect sensitive data in S3.
Management & Governance Tools
- Understand AWS CloudWatch for Logs and Metrics.
- CloudWatch Logs Subscription Filters can be used to route data to Kinesis Data Streams, Kinesis Data Firehose, and Lambda.
On the Exam Day
- Make sure you are relaxed and get some good night’s sleep. The exam is not tough if you are well-prepared.
- If you are taking the AWS Online exam
- Try to join at least 30 minutes before the actual time as I have had issues with both PSI and Pearson with long wait times.
- The online verification process does take some time and usually, there are glitches.
- Remember, you would not be allowed to take the take if you are late by more than 30 minutes.
- Make sure you have your desk clear, no hand-watches, or external monitors, keep your phones away, and nobody can enter the room.
Finally, All the Best 🙂