SageMaker Built-in Algorithms
- SageMaker provides a suite of built-in algorithms, pre-trained models, and pre-built solution templates to help data scientists and ML practitioners get started on training and deploying ML models quickly.
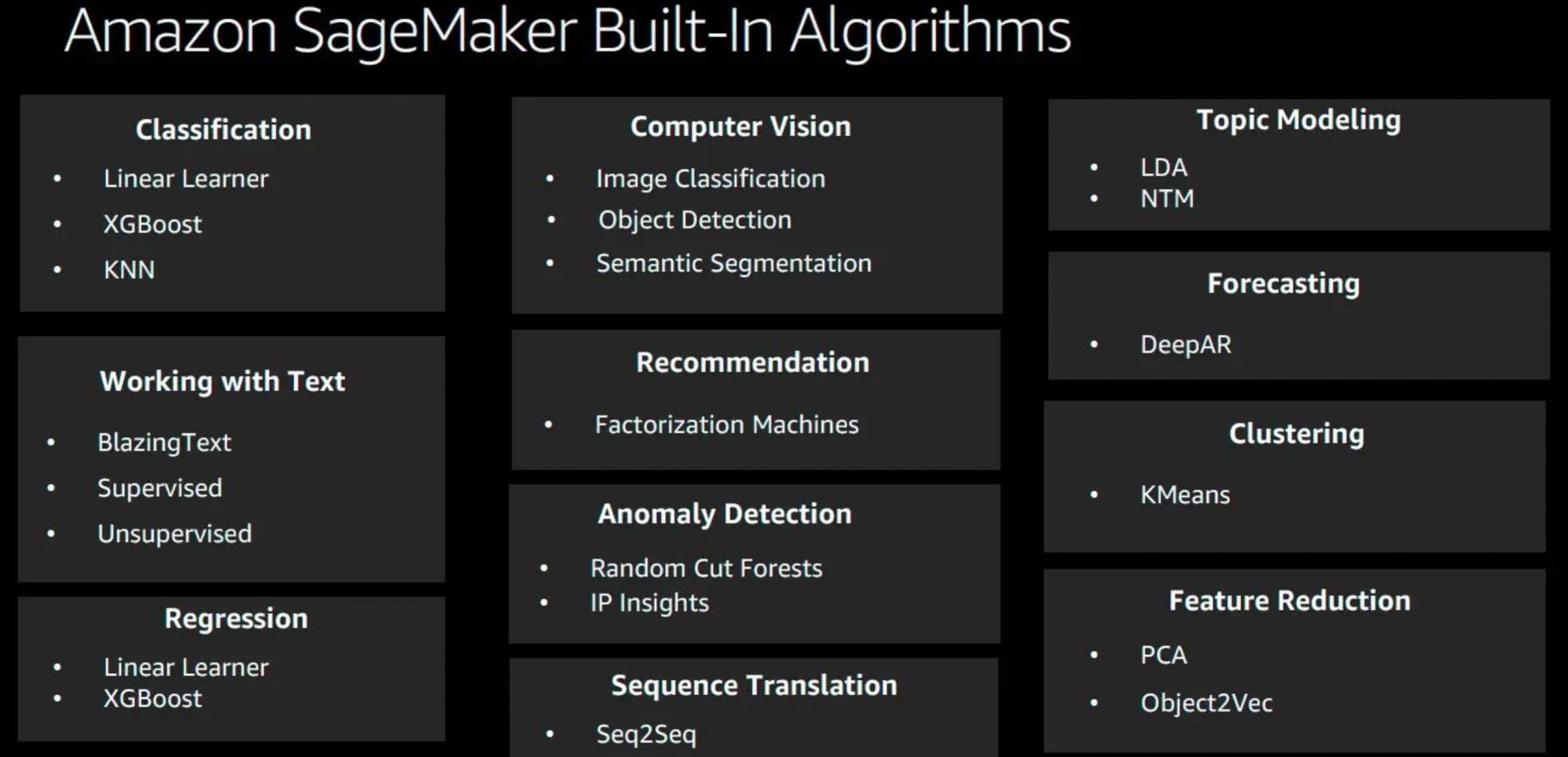
Text-based
BlazingText algorithm
- provides highly optimized implementations of the Word2vec and text classification algorithms.
- Word2vec algorithm
- useful for many downstream natural language processing (NLP) tasks, such as sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, machine translation, etc.
- maps words to high-quality distributed vectors, whose representation is called word embeddings
- word embeddings capture the semantic relationships between words.
- Text classification
- is an important task for applications performing web searches, information retrieval, ranking, and document classification
- provides the Skip-gram and continuous bag-of-words (CBOW) training architectures
Forecasting
DeepAR
- is a supervised learning algorithm for forecasting scalar (one-dimensional) time series using recurrent neural networks (RNN).
- use the trained model to generate forecasts for new time series that are similar to the ones it has been trained on.
Recommendation
Factorization Machine
- is a general-purpose supervised learning algorithm used for both classification and regression tasks.
- extension of a linear model designed to capture interactions between features within high dimensional sparse datasets economically, such as click prediction and item recommendation.
Clustering
K-means algorithm
- is an unsupervised learning algorithm for clustering
- attempts to find discrete groupings within data, where members of a group are as similar as possible to one another and as different as possible from members of other groups
Classification
K-nearest neighbors (k-NN) algorithm
- is an index-based algorithm.
- uses a non-parametric method for classification or regression.
- For classification problems, the algorithm queries the k points that are closest to the sample point and returns the most frequently used label of their class as the predicted label.
- For regression problems, the algorithm queries the k closest points to the sample point and returns the average of their feature values as the predicted value.
Linear Learner
- are supervised learning algorithms used for solving either classification or regression problems
XGBoost (eXtreme Gradient Boosting)
- is a popular and efficient open-source implementation of the gradient boosted trees algorithm.
- Gradient boosting is a supervised learning algorithm that attempts to accurately predict a target variable by combining an ensemble of estimates from a set of simpler, weaker models
Topic Modelling
Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA)
- is an unsupervised learning algorithm that attempts to describe a set of observations as a mixture of distinct categories.
- used to discover a user-specified number of topics shared by documents within a text corpus.
Neural Topic Model (NTM)
- is an unsupervised learning algorithm that is used to organize a corpus of documents into topics that contain word groupings based on their statistical distribution
- Topic modeling can be used to classify or summarize documents based on the topics detected or to retrieve information or recommend content based on topic similarities.
Feature Reduction
Object2Vec
- is a general-purpose neural embedding algorithm that is highly customizable
- can learn low-dimensional dense embeddings of high-dimensional objects.
Principal Component Analysis – PCA
- is an unsupervised ML algorithm that attempts to reduce the dimensionality (number of features) within a dataset while still retaining as much information as possible.
Anomaly Detection
Random Cut Forest (RCF)
- is an unsupervised algorithm for detecting anomalous data points within a data set.
IP Insights
- is an unsupervised learning algorithm that learns the usage patterns for IPv4 addresses.
- designed to capture associations between IPv4 addresses and various entities, such as user IDs or account numbers
Sequence Translation
Sequence to Sequence – seq2seq
- is a supervised learning algorithm where the input is a sequence of tokens (for example, text, audio), and the output generated is another sequence of tokens.
- key uses cases are machine translation (input a sentence from one language and predict what that sentence would be in another language), text summarization (input a longer string of words and predict a shorter string of words that is a summary), speech-to-text (audio clips converted into output sentences in tokens)
Computer Vision – CV
Image classification
- a supervised learning algorithm that supports multi-label classification
- takes an image as input and outputs one or more labels
- uses a convolutional neural network (ResNet) that can be trained from scratch or trained using transfer learning when a large number of training images are not available.
- recommended input format is Apache MXNet RecordIO. Also supports raw images in .jpg or .png format.
Object Detection
- detects and classifies objects in images using a single deep neural network.
- is a supervised learning algorithm that takes images as input and identifies all instances of objects within the image scene.
Semantic Segmentation
- provides a fine-grained, pixel-level approach to developing computer vision applications.
- tags every pixel in an image with a class label from a predefined set of classes and is critical to an increasing number of CV applications, such as self-driving vehicles, medical imaging diagnostics, and robot sensing.
- also provides information about the shapes of the objects contained in the image. The segmentation output is represented as a grayscale image, called a segmentation mask.
AWS Certification Exam Practice Questions
- Questions are collected from Internet and the answers are marked as per my knowledge and understanding (which might differ with yours).
- AWS services are updated everyday and both the answers and questions might be outdated soon, so research accordingly.
- AWS exam questions are not updated to keep up the pace with AWS updates, so even if the underlying feature has changed the question might not be updated
- Open to further feedback, discussion and correction.
- An Analytics team is leading an organization and wants to use anomaly detection to identify potential risks. What Amazon SageMaker machine learning algorithms are best suited for identifying anomalies?
- Semantic segmentation
- K-nearest neighbors
- Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA)
- Random Cut Forest (RCF)
- A ML specialist team works for a marketing consulting firm wants to
apply different marketing strategies per segment of their customer base. Online retailer purchase history from the last 5 years is available, it has been decided to segment the customers based on their purchase history. Which type of machine learning algorithm would give you segmentation based on purchase history in the most expeditious manner?
- K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
- K-Means
- Semantic Segmentation
- Neural Topic Model (NTM)
- A ML specialist team is looking to improve the quality of searches for their library of documents that are uploaded in PDF, Rich Text Format, or ASCII text. It is looking to use machine learning to automate the identification of key topics for each of the documents. What machine learning resources are best suited for this problem? (Select TWO)
- BlazingText algorithm
- Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) algorithm
- Topic Finder (TF) algorithm
- Neural Topic Model (NTM) algorithm
- A manufacturing company has a large set of labeled historical sales data. The company would like to predict how many units of a particular part should be produced each quarter. Which machine learning approach should be used to solve this problem?
- BlazingText algorithm
- Random Cut Forest (RCF)
- Principal component analysis (PCA)
- Linear regression
- An agency collects census information with responses for approximately 500 questions from each citizen. Which algorithm would help reduce the number for features?
- Factorization machines (FM) algorithm
- Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) algorithm
- Principal component analysis (PCA) algorithm
- Random Cut Forest (RCF) algorithm
- A store wants to understand some characteristics of visitors to the store. The store has security video recordings from the past several years. The store wants to group visitors by hair style and hair color. Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST amount of effort?
- Object detection algorithm
- Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) algorithm
- Random Cut Forest (RCF) algorithm
- Semantic segmentation algorithm
References
SageMaker_Build-in_Algortithms

