AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C03 Exam Learning Path
- I just cleared the AWS Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C03 exam with a score of 914/1000.
- AWS Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C03 exam is the latest AWS exam released on 30th August 2022 and has replaced the previous AWS Solutions Architect – SAA-C02 certification exam.
AWS Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C03 Exam Content
- It basically validates the ability to effectively demonstrate knowledge of how to design, architect, and deploy secure, cost-effective, and robust applications on AWS technologies
-
The exam also validates a candidate’s ability to complete the following tasks:
-
Design solutions that incorporate AWS services to meet current business requirements and future projected needs
-
Design architectures that are secure, resilient, high-performing, and cost-optimized
-
Review existing solutions and determine improvements
-
Refer AWS Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C03 Exam Guide
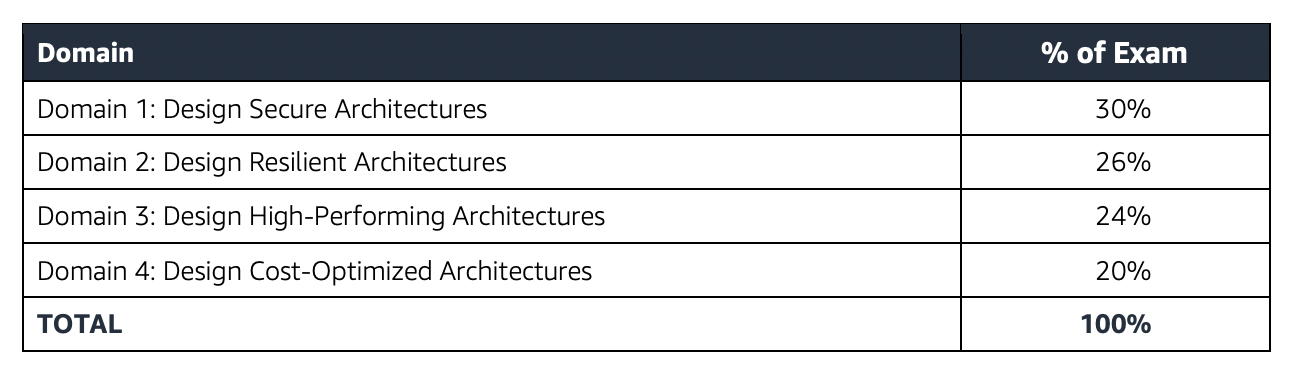
AWS Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C03 Exam Summary
- SAA-C03 exam consists of 65 questions in 130 minutes, and the time is more than sufficient if you are well-prepared.
- SAA-C03 exam includes two types of questions, multiple-choice and multiple-response.
- SAA-C03 has a scaled score between 100 and 1,000. The scaled score needed to pass the exam is 720.
- Associate exams currently cost $ 150 + tax.
- You can get an additional 30 minutes if English is your second language by requesting Exam Accommodations. It might not be needed for Associate exams but is helpful for Professional and Specialty ones.
- AWS exams can be taken either remotely or online, I prefer to take them online as it provides a lot of flexibility. Just make sure you have a proper place to take the exam with no disturbance and nothing around you.
- Also, if you are taking the AWS Online exam for the first time try to join at least 30 minutes before the actual time as I have had issues with both PSI and Pearson with long wait times.
AWS Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C03 Exam Resources
- Online Courses
- Stephane Maarek – Ultimate AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate SAA-C03
- Adrian Cantrill – AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate (SAA-C03)
- Adrian Cantrill – All Associate Bundle
- DolfinEd – AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate – SAA-C03 (E-Study & Lab Guides Included)
- DolfinEd – AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate (On-line, Instructor-Led – Private Group Bootcamp)
- Whizlabs – AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate Course
- Coursera Exam Prep: AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate
- Practice tests
- Braincert AWS Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C03 Practice Exams, which are updated for SAA-C03
- Stephane Maarek – AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate Practice Exams
- Whizlabs – AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate Practice Tests
- Signed up with AWS for the Free Tier account which provides a lot of Services to be tried for free with certain limits which are more than enough to get things going. Be sure to decommission services beyond the free limits, preventing any surprises 🙂
- Also, use QwikLabs for introductory courses which are free
- Read the FAQs at least for the important topics, as they cover important points and are good for quick review
AWS Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C03 Exam Topics
- SAA-C03 Exam covers the design and architecture aspects in deep, so you must be able to visualize the architecture, even draw them out or prepare a mental picture just to understand how it would work and how different services relate.
- SAA-C03 exam concepts cover solutions that fall within AWS Well-Architected framework to cover scalable, highly available, cost-effective, performant, and resilient pillars.
- If you had been preparing for the SAA-C02, SAA-C03 is pretty much similar to SAA-C02 except for the addition of some new services Aurora Serverless, AWS Global Accelerator, FSx for Windows, and FSx for Lustre.
Networking
- Virtual Private Network – VPC
- Create a VPC from scratch with public, private, and dedicated subnets with proper route tables, security groups, and NACLs.
- Understand what a CIDR is and address patterns.
- Subnets are public or private depending on whether they can route traffic directly through an Internet gateway
- Understand how communication happens between the Internet, Public subnets, Private subnets, NAT, Bastion, etc.
- Bastion (also referred to as a Jump server) can be used to securely access instances in the private subnets.
- Create two-tier architecture with application in public and database in private subnets
- Create three-tier architecture with web servers in public, application, and database servers in private. (hint: focus on security group configuration with least privilege)
- Security Groups and NACLs
- Security Groups are Stateful vs NACLs are stateless.
- Also, only NACLs provide the ability to deny or block IPs
- NAT Gateway or Instances
- help enables instances in a private subnet to connect to the Internet.
- Understand the difference between NAT Gateway & NAT Instance.
- NAT Gateway is AWS-managed and is scalable and highly available.
- VPC endpoints
- enable the creation of a private connection between VPC to supported AWS services and VPC endpoint services powered by PrivateLink using its private IP address without needing an Internet or NAT Gateway.
- VPC Gateway Endpoints supports S3 and DynamoDB.
- VPC Interface Endpoints OR Private Links supports others
- VPN and Direct Connect for on-premises to AWS connectivity
- VPN provides a quick, cost-effective, secure channel, however, routes through the internet and does not provide consistent throughput
- Direct Connect provides consistent, dedicated throughput without Internet, however, requires time to set up and is not cost-effective.
- Understand Data Migration techniques at a high level
- VPN and Direct Connect for continuous, frequent data transfers.
- Snow Family is ideal for one-time, cost-effective huge data transfer.
- Choose a technique depending on the available bandwidth, data transfer needed, time available, encryption, one-time or continuous.
- CloudFront
- fully managed, fast CDN service that speeds up the distribution of static, dynamic web, or streaming content to end-users
- S3 frontend by CloudFront provides low latency, performant experience for global users.
- provides static and dynamic caching for both AWS and on-premises origin.
- Global Accelerator
- optimizes the path to applications to keep packet loss, jitter, and latency consistently low.
- helps improve the performance by lowering first-byte latency
- provides 2 static IP address
- Know CloudFront vs Global Accelerator
- Route 53
- highly available and scalable DNS web service.
- Health checks and failover routing helps provide resilient and active-passive solutions
- Route 53 Routing Policies and their use cases (hint: focus on weighted, latency, geolocation, failover routing)
- Elastic Load Balancer
- Focus on ALB and NLB
- Differences between ALB vs NLB
- ALB is layer 7 vs NLB is layer 4
- ALB provides content-based, host-based, path-based routing
- ALB provides dynamic port mapping which allows the same tasks to be hosted on the ECS node
- NLB provides low latency, the ability to scale rapidly, and a static IP address
- ALB works with WAF while NLB does not.
- Gateway Load Balancer – GWLB
- helps deploy, scale, and manage virtual appliances like firewalls, IDS/IPS, and deep packet inspection systems.
Security
- Identity Access Management – IAM
- IAM role
- provides permissions that are not associated with a particular user, group, or service and are intended to be assumable by anyone who needs it.
- can be used for EC2 application access and Cross-account access
- IAM identity providers and federation and use cases – Although did not see much in SAA-C03
- IAM role
- Key Management Services – KMS encryption service
- for key management and envelope encryption
- S3 Integration with SSE, SSE-C, SSE-KMS
- KMS Multi-region keys are AWS KMS keys in different AWS Regions that can be used interchangeably – as though having the same key in multiple Regions.
- AWS WAF
- integrates with CloudFront, and ALB to provide protection against Cross-site scripting (XSS), and SQL injection attacks.
- provides IP blocking and geo-protection, rate limiting, etc.
- AWS Shield
- managed DDoS protection service
- integrates with CloudFront, ALB, and Route 53
- Advanced provides additional detection and mitigation against large and sophisticated DDoS attacks, near real-time visibility into attacks
- AWS GuardDuty
- managed threat detection service and provides Malware protection
- AWS Inspector
- is a vulnerability management service that continuously scans the AWS workloads for vulnerabilities
- AWS Secrets Manager
- helps protect secrets needed to access applications, services, and IT resources.
- supports rotations of secrets, which Systems Manager Parameter Stores does not support.
- Disaster Recovery whitepaper
- Be sure you know the different recovery types with impact on RTO/RPO.
Storage
- Understand various storage options S3, EBS, Instance store, EFS, Glacier, FSx, and what are the use cases and anti-patterns for each
- Instance Store
- is physically attached to the EC2 instance and provides the lowest latency and highest IOPS
- Elastic Block Storage – EBS
- EBS volume types and their use cases in terms of IOPS and throughput. SSD for IOPS and HDD for throughput
- EBS Snapshots
- Backups are automated, snapshots are manual
- Can be used to encrypt an unencrypted EBS volume
- Multi-Attach EBS feature allows attaching an EBS volume to multiple instances within the same AZ only.
- EBS fast snapshot restore feature helps ensure that the EBS volumes created from a snapshot are fully-initialized at creation and instantly deliver all of their provisioned performance.
- Simple Storage Service – S3
- S3 storage classes with lifecycle policies
- Understand the difference between SA Standard vs SA IA vs SA IA One Zone in terms of cost and durability
- S3 Data Protection
- S3 Client-side encryption encrypts data before storing it in S3
- S3 features including
- S3 provides cost-effective static website hosting. However, it does not support HTTPS endpoint. Can be integrated with CloudFront for HTTPS, caching, performance, and low-latency access.
- S3 versioning provides protection against accidental overwrites and deletions. Used with MFA Delete feature.
- S3 Pre-Signed URLs for both upload and download provide access without needing AWS credentials.
- S3 CORS allows cross-domain calls
- S3 Transfer Acceleration enables fast, easy, and secure transfers of files over long distances between your client and an S3 bucket.
- S3 Event Notifications to trigger events on various S3 events like objects added or deleted. Supports SQS, SNS, and Lambda functions.
- Integrates with Amazon Macie to detect PII data
- Replication that supports the same and cross-region replication required versioning to be enabled.
- Integrates with Athena to analyze data in S3 using standard SQL.
- S3 storage classes with lifecycle policies
- Glacier
- as archival storage with various retrieval patterns
- Glacier Instant Retrieval allows retrieval in milliseconds.
- Glacier Expedited retrieval allows object retrieval within mins.
- Storage gateway and its different types.
- Cached Volume Gateway provides access to frequently accessed data while using AWS as the actual storage
- Stored Volume gateway uses AWS as a backup, while the data is being stored on-premises as well
- File Gateway supports SMB protocol
- FSx is easy and cost-effective to launch and run popular file systems.
- FSx provides two file systems to choose from:
- Amazon FSx for Windows File Server
- works with both Linux and Windows
- provides Windows File System features including integration with Active Directory.
- Amazon FSx for Lustre
- for high-performance workloads
- works with only Linux
- Elastic File System – EFS
- simple, fully managed, scalable, serverless, and cost-optimized file storage for use with AWS Cloud and on-premises resources.
- provides shared volume across multiple EC2 instances, while EBS can be attached to a single instance within the same AZ or EBS Multi-Attach can be attached to multiple instances within the same AZ
- supports the NFS protocol, and is compatible with Linux-based AMIs
- supports cross-region replication, storage classes for cost.
- AWS Transfer Family
- secure transfer service that helps transfer files into and out of AWS storage services using FTP, SFTP and FTPS protocol.
- Difference between EBS vs S3 vs EFS
- Difference between EBS vs Instance Store
- Would recommend referring Storage Options whitepaper, although a bit dated 90% still holds right
Compute
- Elastic Cloud Compute – EC2
- Auto Scaling and ELB
- Auto Scaling provides the ability to ensure a correct number of EC2 instances are always running to handle the load of the application
- Elastic Load Balancer allows the incoming traffic to be distributed automatically across multiple healthy EC2 instances
- Autoscaling & ELB
- work together to provide High Availability and Scalability.
- Span both ELB and Auto Scaling across Multi-AZs to provide High Availability
- Do not span across regions. Use Route 53 or Global Accelerator to route traffic across regions.
- EC2 Instance Purchase Types – Reserved, Scheduled Reserved, On-demand, and Spot and their use cases
- Reserved instances provide cost benefits for long terms requirements over On-demand instances for continuous persistent load
- Scheduled Reserved Instances for load with fixed scheduled and time interval
- Spot instances provide cost benefits for temporary, fault-tolerant, spiky load
- EC2 Placement Groups
- Cluster placement groups provide low latency and high throughput communication
- Spread placement group provides high availability
- Lambda and serverless architecture, its features, and use cases.
- Lambda integrated with API Gateway to provide a serverless, highly scalable, cost-effective architecture
- Elastic Container Service – ECS with its ability to deploy containers and microservices architecture.
- ECS role for tasks can be provided through taskRoleArn
- ALB provides dynamic port mapping to allow multiple same tasks on the same node.
- Elastic Kubernetes Service – EKS
- managed Kubernetes service to run Kubernetes in the AWS cloud and on-premises data centers
- ideal for migration of an existing workload on Kubernetes
- Elastic Beanstalk at a high level, what it provides, and its ability to get an application running quickly.
Databases
- Understand relational and NoSQL data storage options which include RDS, DynamoDB, and Aurora with their use cases
- Relational Database Service – RDS
- Read Replicas vs Multi-AZ
- Read Replicas for scalability, Multi-AZ for High Availability
- Multi-AZ are regional only
- Read Replicas can span across regions and can be used for disaster recovery
- Understand Automated Backups, underlying volume types (which are the same as EBS volume types)
- Read Replicas vs Multi-AZ
- Aurora
- provides multiple read replicas and replicates 6 copies of data across AZs
- Aurora Serverless
- provides a highly scalable cost-effective database solution
- automatically starts up, shuts down, and scales capacity up or down based on the application’s needs.
- supports only MySQL and PostgreSQL
- DynamoDB
- provides low latency performance, a key-value store
- is not a relational database
- DynamoDB DAX provides caching for DynamoDB
- DynamoDB TTL helps expire data in DynamoDB without any cost or consuming any write throughput.
- ElastiCache use cases, mainly for caching performance
Integration Tools
- Simple Queue Service
- as message queuing service and SNS as pub/sub notification service
- as a decoupling service and provide resiliency
- SQS features like visibility, and long poll vs short poll
- provide scaling for the Auto Scaling group based on the SQS size.
- SQS Standard vs SQS FIFO difference
- FIFO provides exactly-once delivery but with low throughput
- Simple Notification Service – SNS
- is a web service that coordinates and manages the delivery or sending of messages to subscribing endpoints or clients
- Fanout pattern can be used to push messages to multiple subscribers
Analytics
- Redshift as a business intelligence tool
- Kinesis
- for real-time data capture and analytics.
- Integrates with Lambda functions to perform transformations
- AWS Glue
- fully-managed, ETL service that automates the time-consuming steps of data preparation for analytics
Management Tools
- CloudWatch
- monitoring to provide operational transparency
- is extendable with custom metrics
- CloudWatch -> (Subscription filter) -> Kinesis Data Firehose -> S3
- CloudTrail
- helps enable governance, compliance, and operational and risk auditing of the AWS account.
- helps to get a history of AWS API calls and related events for the AWS account.
- CloudFormation
- easy way to create and manage a collection of related AWS resources, and provision and update them in an orderly and predictable fashion.
- AWS Config
- fully managed service that provides AWS resource inventory, configuration history, and configuration change notifications to enable security, compliance, and governance.
AWS Whitepapers & Cheatsheets
- Architecting for the AWS Cloud: Best Practices
- AWS Well-Architected Framework whitepaper
- AWS Storage & Content Delivery Services Cheatsheet
- AWS Compute Services Cheat Sheet
- AWS Database Services Cheat Sheet
On the Exam Day
- Make sure you are relaxed and get some good night’s sleep. The exam is not tough if you are well-prepared.
- If you are taking the AWS Online exam
- Try to join at least 30 minutes before the actual time as I have had issues with both PSI and Pearson with long wait times.
- The online verification process does take some time and usually, there are glitches.
- Remember, you would not be allowed to take the take if you are late by more than 30 minutes.
- Make sure you have your desk clear, no hand-watches, or external monitors, keep your phones away, and nobody can enter the room.
Finally, All the Best 🙂
