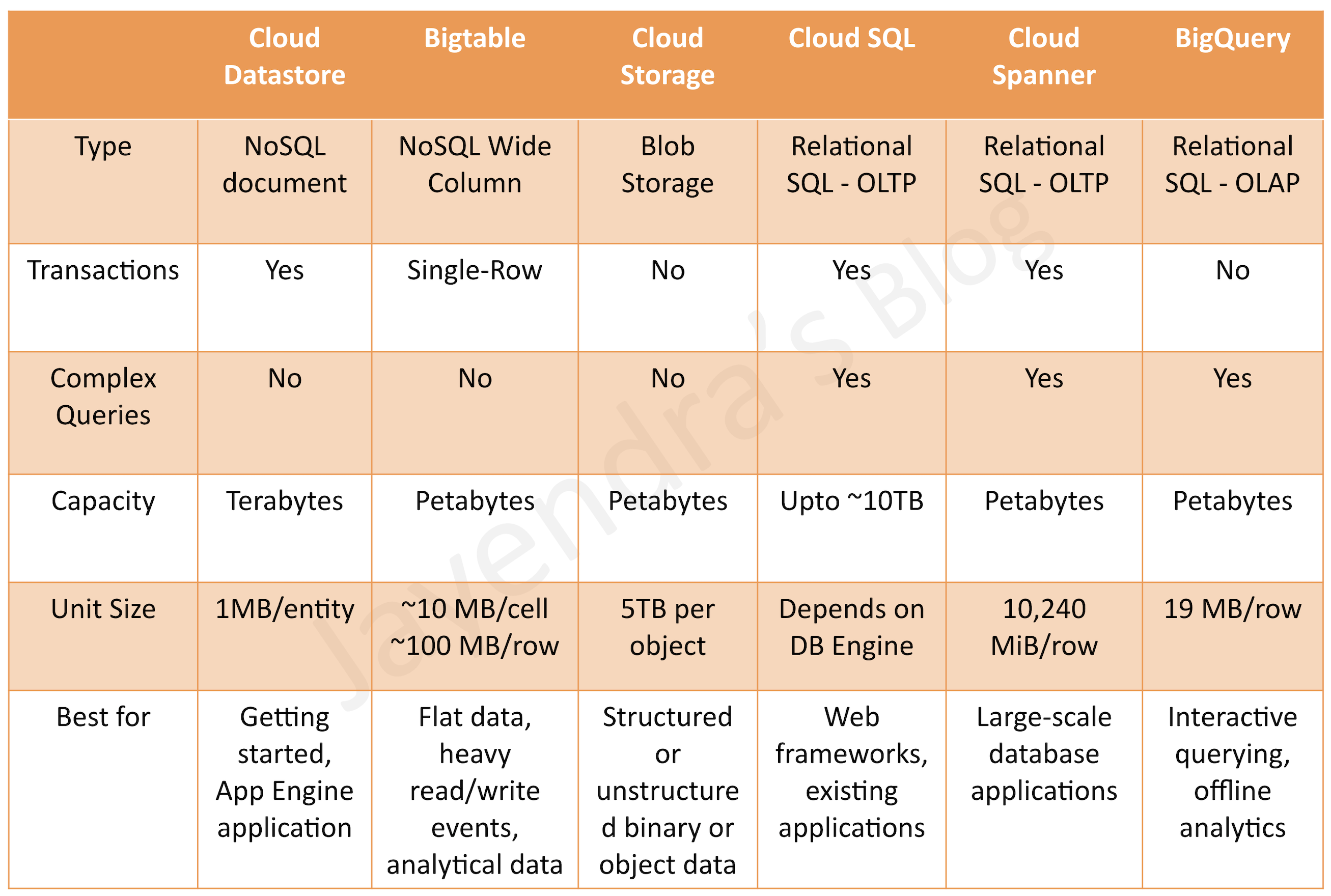
GCP Storage Options
GCP provides various storage options and the selection can be based on
- Structured vs Unstructured
- Relational (SQL) vs Non-Relational (NoSQL)
- Transactional (OLTP) vs Analytical (OLAP)
- Fully Managed vs Requires Provisioning
- Global vs Regional
- Horizontal vs Vertical scaling
Cloud Firestore
- Cloud Firestore is a fully managed, highly scalable, serverless, non-relational NoSQL document database
- fully managed with no-ops and no planned downtime and no need to provision database instances (vs Bigtable)
- uses a distributed architecture to automatically manage scaling.
- queries scale with the size of the result set, not the size of the data set
- supports ACID Atomic transactions – all or nothing (vs Bigtable)
- provides High availability of reads and writes – runs in Google data centers, which use redundancy to minimize impact from points of failure.
- provides massive scalability with high performance – uses a distributed architecture to automatically manage scaling.
- scales from zero to terabytes with flexible storage and querying of data
- provides SQL-like query language
- supports strong consistency
- supports data encryption at rest and in transit
- provides terabytes of capacity with a maximum unit size of 1 MB per entity (vs Bigtable)
- Consider using Cloud Firestore if you need to store semi-structured objects, or if require support for transactions and SQL-like queries.
Cloud Bigtable
- Bigtable provides a scalable, fully managed, non-relational NoSQL wide-column analytical big data database service suitable for both low-latency single-point lookups and precalculated analytics.
- supports large quantities (>1 TB) of semi-structured or structured data (vs Datastore)
- supports high throughput or rapidly changing data (vs BigQuery)
- managed, but needs provisioning of nodes and can be expensive (vs Datastore and BigQuery)
- does not support transactions or strong relational semantics (vs Datastore)
- does not support SQL queries (vs BigQuery and Datastore)
- Not Transactional and does not support ACID
- provides eventual consistency
- ideal for time-series or natural semantic ordering data
- can run asynchronous batch or real-time processing on the data
- can run machine learning algorithms on the data
- provides petabytes of capacity with a maximum unit size of 10 MB per cell and 100 MB per row.
- Usage Patterns
- Low-latency read/write access
- High-throughput data processing
- Time series support
- Anti Patterns
- Not an ideal storage option for future analysis – Use BigQuery instead
- Not an ideal storage option for transactional data – Use relational database or Datastore
- Common Use cases
- IoT, finance, adtech
- Personalization, recommendations
- Monitoring
- Geospatial datasets
- Graphs
- Consider using Cloud Bigtable, if you need high-performance datastore to perform analytics on a large number of structured objects
Cloud Storage
- Cloud Storage provides durable and highly available object storage.
- fully managed, simple administration, cost-effective, and scalable service that does not require capacity management
- supports unstructured data storage like binary or raw objects
- provides high performance, internet-scale
- supports data encryption at rest and in transit
- Consider using Cloud Storage, if you need to store immutable blobs larger than 10 MB, such as large images or movies. This storage service provides petabytes of capacity with a maximum unit size of 5 TB per object.
- Usage Patterns
- Images, pictures, and videos
- Objects and blobs
- Unstructured data
- Long term storage for archival or compliance
- Anti Patterns
- Common Use cases
- Storing and streaming multimedia
- Storage for custom data analytics pipelines
- Archive, backup, and disaster recovery
Cloud SQL
- provides fully managed, relational SQL databases
- offers MySQL, PostgreSQL, MSSQL databases as a service
- manages OS & Software installation, patches and updates, backups and configuring replications, failover however needs to select and provision machines (vs Cloud Spanner)
- single region only – although it now supports cross-region read replicas (vs Cloud Spanner)
- Scaling
- provides vertical scalability (Max. storage of 10TB)
- storage can be increased without incurring any downtime
- provides an option to increase the storage automatically
- storage CANNOT be decreased
- supports Horizontal scaling for read-only using read replicas (vs Cloud Spanner)
- performance is linked to the disk size
- Security
- data is encrypted when stored in database tables, temporary files, and backups.
- external connections can be encrypted by using SSL, or by using the Cloud SQL Proxy.
- High Availability
- fault-tolerance across zones can be achieved by configuring the instance for high availability by adding a failover replica
- failover is automatic
- can be created from primary instance only
- replication from the primary instance to failover replica is semi-synchronous.
- failover replica must be in the same region as the primary instance, but in a different zone
- only one instance for every primary instance allowed
- supports managed backups and backups are created on primary instance only
- supports automatic replication
- Backups
- Automated backups can be configured and are stored for 7 days
- Manual backups (snapshots) can be created and are not deleted automatically
- Point-in-time recovery
- requires binary logging enabled.
- every update to the database is written to an independent log, which involves a small reduction in write performance.
- performance of the read operations is unaffected by binary logging, regardless of the size of the binary log files.
- Usage Patterns
- direct lift and shift for MySQL, PostgreSQL, MSSQL database only
- relational database service with strong consistency
- OLTP workloads
- Anti Patterns
- need data storage more than 10TB, use Cloud Spanner
- need global availability with low latency, use Cloud Spanner
- not a direct replacement for Oracle use installation on GCE
- Common Use cases
- Websites, blogs, and content management systems (CMS)
- Business intelligence (BI) applications
- ERP, CRM, and eCommerce applications
- Geospatial applications
- Consider using Cloud SQL for full relational SQL support for OTLP and lift and shift of MySQL, PostgreSQL databases
Cloud Spanner
- Cloud Spanner provides fully managed, relational SQL databases with joins and secondary indexes
- provides cross-region, global, horizontal scalability, and availability
- supports strong consistency, including strongly consistent secondary indexes
- provides high availability through synchronous and built-in data replication.
- provides strong global consistency
- supports database sizes exceeding ~2 TB (vs Cloud SQL)
- does not provide direct lift and shift for relational databases (vs Cloud SQL)
- expensive as compared to Cloud SQL
- Consider using Cloud Spanner for full relational SQL support, with horizontal scalability spanning petabytes for OTLP
BigQuery
- provides fully managed, no-ops, OLAP, enterprise data warehouse (EDW) with SQL and fast ad-hoc queries.
- provides high capacity, data warehousing analytics solution
- ideal for big data exploration and processing
- not ideal for operational or transactional databases
- provides SQL interface
- A scalable, fully managed
- Usage Patterns
- OLAP workloads up to petabyte-scale
- Big data exploration and processing
- Reporting via business intelligence (BI) tools
- Anti Patterns
- Not an ideal storage option for transactional data or OLTP – Use Cloud SQL or Cloud Spanner instead
- Low-latency read/write access – Use Bigtable instead
- Common Use cases
- Analytical reporting on large data
- Data science and advanced analyses
- Big data processing using SQL
Memorystore
- provides scalable, secure, and highly available in-memory service for Redis and Memcached.
- fully managed as provisioning, replication, failover, and patching are all automated, which drastically reduces the time spent doing DevOps.
- provides 100% compatibility with open source Redis and Memcached
- is protected from the internet using VPC networks and private IP and comes with IAM integration
- Usage Patterns
- Lift and shift migration of applications
- Low latency data caching and retrieval
- Anti Patterns
- Relational or NoSQL database
- Analytics solution
- Common Use cases
- User session management
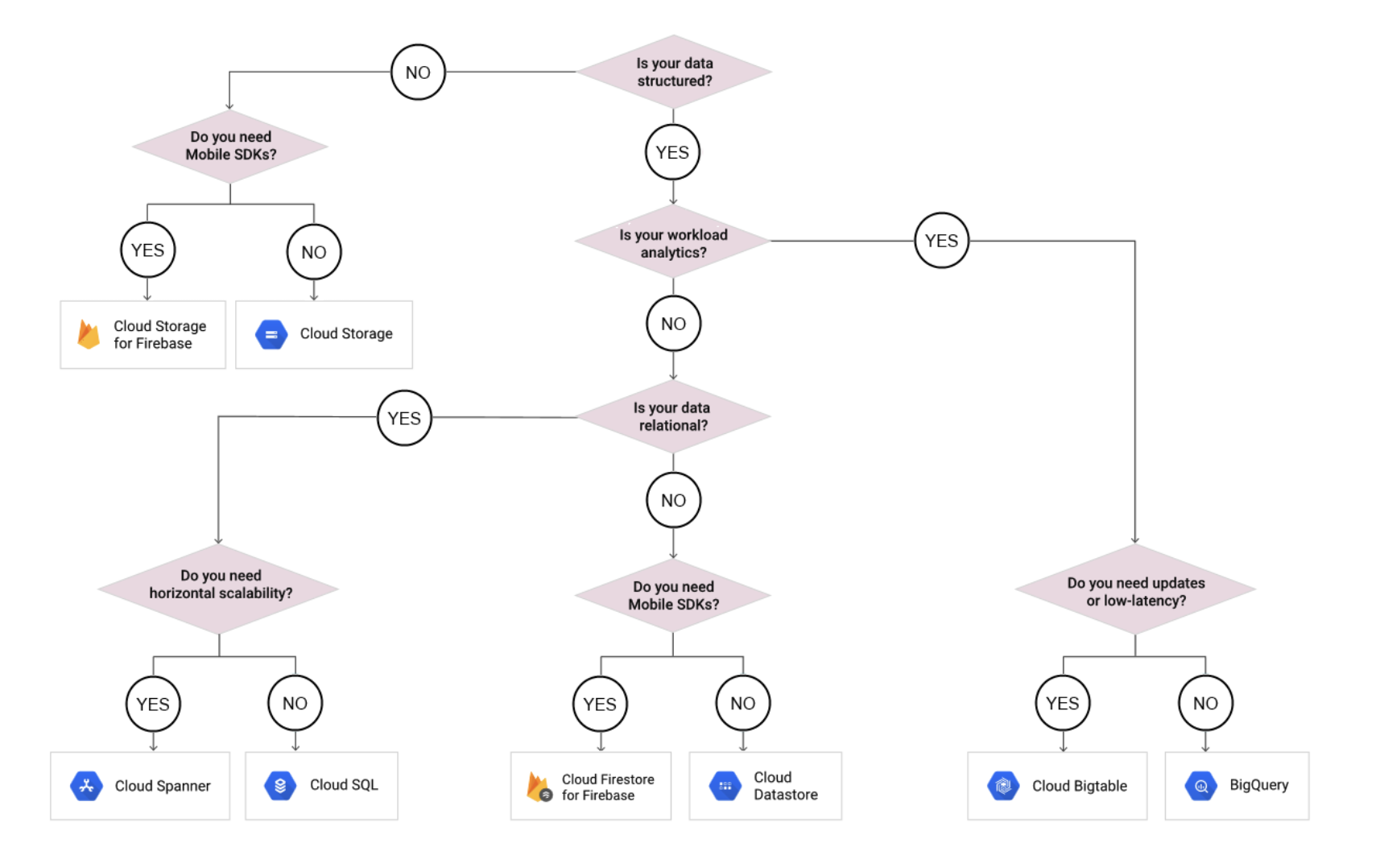
GCP Storage Options Decision Tree
GCP Certification Exam Practice Questions
- Questions are collected from Internet and the answers are marked as per my knowledge and understanding (which might differ with yours).
- GCP services are updated everyday and both the answers and questions might be outdated soon, so research accordingly.
- GCP exam questions are not updated to keep up the pace with GCP updates, so even if the underlying feature has changed the question might not be updated
- Open to further feedback, discussion and correction.
- Your application is hosted across multiple regions and consists of both relational database data and static images. Your database has over 10 TB of data. You want to use a single storage repository for each data type across all regions. Which two products would you choose for this task? (Choose two)
- Cloud Bigtable
- Cloud Spanner
- Cloud SQL
- Cloud Storage
- You are building an application that stores relational data from users. Users across the globe will use this application. Your CTO is concerned about the scaling requirements because the size of the user base is unknown. You need to implement a database solution that can scale with your user growth with minimum configuration changes. Which storage solution should you use?
- Cloud SQL
- Cloud Spanner
- Cloud Firestore
- Cloud Datastore
- Your company processes high volumes of IoT data that are time-stamped. The total data volume can be several petabytes. The data needs to be written and changed at a high speed. You want to use the most performant storage option for your data. Which product should you use?
- Cloud Datastore
- Cloud Storage
- Cloud Bigtable
- BigQuery
- Your App Engine application needs to store stateful data in a proper storage service. Your data is non-relational database data. You do not expect the database size to grow beyond 10 GB and you need to have the ability to scale down to zero to avoid unnecessary costs. Which storage service should you use?
- Cloud Bigtable
- Cloud Dataproc
- Cloud SQL
- Cloud Datastore
- A financial organization wishes to develop a global application to store transactions happening from different part of the world. The storage system must provide low latency transaction support and horizontal scaling. Which GCP service is appropriate for this use case?
- Bigtable
- Datastore
- Cloud Storage
- Cloud Spanner
- You work for a mid-sized enterprise that needs to move its operational system transaction data from an on-premises database to GCP. The database is about 20 TB in size. Which database should you choose?
- Cloud SQL
- Cloud Bigtable
- Cloud Spanner
- Cloud Datastore
I like your site – which much effort you put the main aspects for each gcp service together. It’s a great overview for people who are preparing for the exam.
Btw. there is an error “Consider using cloud sql” in the Cloud Spanner block
Thanks Lui, corrected the same.