AWS Certified Security – Specialty (SCS-C01) Exam Learning Path
I recently re-certified AWS Certified Security – Specialty (SCS-C01) after first clearing the same in 2019 and the format, and domains are pretty much the same however has been enhanced to cover all the latest services.
AWS Certified Security – Specialty (SCS-C01) Exam Content
- The AWS Certified Security – Specialty (SCS-C01) exam focuses on the AWS Security and Compliance concepts. It basically validates
- An understanding of specialized data classifications and AWS data protection mechanisms.
- An understanding of data-encryption methods and AWS mechanisms to implement them.
- An understanding of secure Internet protocols and AWS mechanisms to implement them.
- A working knowledge of AWS security services and features of services to provide a secure production environment.
- Competency gained from two or more years of production deployment experience using AWS security services and features.
- The ability to make tradeoff decisions with regard to cost, security, and deployment complexity given a set of application requirements. An understanding of security operations and risks
Refer to AWS Certified Security – Speciality Exam Guide
AWS Certified Security – Specialty (SCS-C01) Exam Summary
-
Specialty exams are tough, lengthy, and tiresome. Most of the questions and answers options have a lot of prose and a lot of reading that needs to be done, so be sure you are prepared and manage your time well.
- SCS-C01 exam has 65 questions to be solved in 170 minutes which gives you roughly 2 1/2 minutes to attempt each question.
- SCS-C01 exam includes two types of questions, multiple-choice and multiple-response.
- SCS-C01 has a scaled score between 100 and 1,000. The scaled score needed to pass the exam is 750.
- Associate exams currently cost $ 300 + tax.
- You can get an additional 30 minutes if English is your second language by requesting Exam Accommodations. It might not be needed for Associate exams but is helpful for Professional and Specialty ones.
- As always, mark the questions for review and move on and come back to them after you are done with all.
- As always, having a rough architecture or mental picture of the setup helps focus on the areas that you need to improve. Trust me, you will be able to eliminate 2 answers for sure and then need to focus on only the other two. Read the other 2 answers to check the difference area and that would help you reach the right answer or at least have a 50% chance of getting it right.
- AWS exams can be taken either remotely or online, I prefer to take them online as it provides a lot of flexibility. Just make sure you have a proper place to take the exam with no disturbance and nothing around you.
- Also, if you are taking the AWS Online exam for the first time try to join at least 30 minutes before the actual time as I have had issues with both PSI and Pearson with long wait times.
AWS Certified Security – Specialty (SCS-C01) Exam Resources
- Online Courses
- Stephae Maarek – AWS Certified Security Specialty
- Adrian Cantrill – AWS Certified Security – Specialty
- Whizlabs – AWS Certified Security Specialty Course
- DolfinEd – AWS Certified Security Specialty
- Practice tests
- Braincert AWS Certified Security – Specialty Practice Exams
- Stephane Maarek – AWS Certified Security – Specialty Practice Exams
- Whizlabs – AWS Certified Security Specialty Practice Test
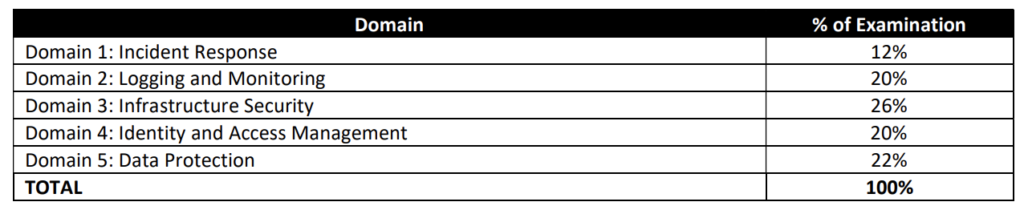
AWS Certified Security – Specialty (SCS-C01) Exam Topics
- AWS Certified Security – Specialty (SCS-C01) exam focuses a lot on Security & Compliance concepts involving Data Encryption at rest or in transit, Data protection, Auditing, Compliance and regulatory requirements, and automated remediation.
Security, Identity & Compliance
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- IAM Roles to grant the service, users temporary access to AWS services.
- IAM Role can be used to give cross-account access and usually involves creating a role within the trusting account with a trust and permission policy and granting the user in the trusted account permissions to assume the trusting account role.
- Identity Providers & Federation to grant external user identity (SAML or Open ID compatible IdPs) permissions to AWS resources without having to be created within the AWS account.
- IAM Policies help define who has access & what actions can they perform.
- IAM Roles to grant the service, users temporary access to AWS services.
- Deep dive into Key Management Service (KMS). There would be quite a few questions on this.
- is a managed encryption service that allows the creation and control of encryption keys to enable data encryption.
- uses Envelope Encryption which uses a master key to encrypt the data key, which is then used to encrypt the data.
- Understand how KMS works
- Understand IAM Policies, Key Policies, Grants to grant access.
- Key policies are the primary way to control access to KMS keys. Unless the key policy explicitly allows it, you cannot use IAM policies to allow access to a KMS key.
- are regional, however, supports multi-region keys, which are KMS keys in different AWS Regions that can be used interchangeably – as though you had the same key in multiple Regions.
- KMS Multi-region keys
- are AWS KMS keys in different AWS Regions that can be used interchangeably – as though having the same key in multiple Regions.
- are not global and each multi-region key needs to be replicated and managed independently.
- Understand the difference between CMK with generated and imported key material esp. in rotating keys
- KMS usage with VPC Endpoint which ensures the communication between the VPC and KMS is conducted entirely within the AWS network.
- KMS ViaService condition
- Cloud HSM
- is a cloud-based hardware security module (HSM) that enables you to easily generate and use your own encryption keys on the AWS Cloud
- AWS Certificate Manager (ACM)
- helps provision, manage, and deploy public and private SSL/TLS certificates for use with AWS services
- to use an ACM Certificate with CloudFront, the certificate must be imported into the US East (N. Virginia) region.
- is regional and you need to request certificates in all regions and associate individually in all regions.
- does not support EC2 instances and private keys cannot be exported.
- AWS Secrets Manager
- protects secrets needed to access applications, services, etc.
- enables you to easily rotate, manage, and retrieve database credentials, API keys, and other secrets throughout their lifecycle
- supports automatic rotation of credentials for RDS, DocumentDB, etc.
- Secrets Manager vs Systems Manager Parameter Store
- Secrets Manager supports automatic rotation while SSM Parameter Store does not
- Parameter Store is cost-effective as compared to Secrets Manager.
- AWS GuardDuty
- is a threat detection service that continuously monitors the AWS accounts and workloads for malicious activity and delivers detailed security findings for visibility and remediation.
- supports CloudTrail S3 data events and management event logs, DNS logs, EKS audit logs, and VPC flow logs.
- AWS Inspector
- is an automated security assessment service that helps improve the security and compliance of applications deployed on AWS.
- Amazon Macie
- is a security service that uses machine learning to automatically discover, classify, and protect sensitive data in S3.
- AWS Artifact is a central resource for compliance-related information that provides on-demand access to AWS’ security and compliance reports and select online agreements
- AWS Shield & Shield Advanced
- for DDoS protection and integrates with Route 53, CloudFront, ALB, and Global Accelerator.
- AWS WAF
- protects from common attack techniques like SQL injection and XSS, Conditions based include IP addresses, HTTP headers, HTTP body, and URI strings.
- integrates with CloudFront, ALB, and API Gateway.
- supports Web ACLs and can block traffic based on IPs, Rate limits, and specific countries as well
- allows IP match set rule to allow/deny specific IP addresses and rate-based rule to limit the number of requests.
- logs can be sent to the CloudWatch Logs log group, an S3 bucket, or Kinesis Data Firehose.
- AWS Security Hub is a cloud security posture management service that performs security best practice checks, aggregates alerts, and enables automated remediation.
- AWS Network Firewall is a stateful, fully managed, network firewall and intrusion detection and prevention service (IDS/IPS) for VPCs.
- AWS Resource Access Manager helps you securely share your resources across AWS accounts, within your organization or organizational units (OUs), and with IAM roles and users for supported resource types.
- AWS Signer is a fully managed code-signing service to ensure the trust and integrity of your code.
- AWS Audit Manager to map your compliance requirements to AWS usage data with prebuilt and custom frameworks and automated evidence collection.
- AWS Cognito esp. User Pools
- Firewall Manager helps centrally configure and manage firewall rules across the accounts and applications in AWS Organizations which includes a variety of protections, including WAF, Shield Advanced, VPC security groups, Network Firewall, and Route 53 Resolver DNS Firewall.
Networking & Content Delivery
- Virtual Private Connect – VPC
- Security Groups, NACLs
- NACLs are stateless, Security groups are stateful
- NACLs at subnet level, Security groups at the instance level
- NACLs need to open ephemeral ports for response traffic.
- VPC Gateway Endpoints to provide access to S3 and DynamoDB
- VPC Interface Endpoints or PrivateLink provide access to a variety of services like SQS, Kinesis, or Private APIs exposed through NLB.
- VPC Peering
- to enable communication between VPCs within the same or different regions.
- Route tables need to be configured on either VPC for them to be able to communicate.
- does not allow cross-region security group reference.
- VPC Flow Logs help capture information about the IP traffic going to and from network interfaces in the VPC
- NAT Gateway provides managed NAT service that provides better availability, higher bandwidth, and requires less administrative effort.
- Security Groups, NACLs
- Virtual Private Network – VPN & Direct Connect to establish connectivity a secured, low latency access between an on-premises data center and VPC.
- IPSec VPN over Direct Connect to provide secure connectivity.
- CloudFront
- integrates with S3 to improve latency, and performance.
- provides multiple security features
- supports encryption at rest and end-to-end encryption
- Viewer Protocol Policy and Origin Protocol Policy to enforce HTTPS – can be configured to require that viewers use HTTPS to request the files so that connections are encrypted when CloudFront communicates with viewers.
- Integrates with ACM and requires certs to be in the us-east-1 region
- Underlying origin can be applied certs from ACM or issued by the third party.
- CloudFront Origin Shield
- helps improve the cache hit ratio and reduce the load on the origin.
- requests from other regional caches would hit the Origin shield rather than the Origin.
- should be placed at the regional cache and not in the edge cache
- should be deployed to the region closer to the origin server
- CloudFront provides Encryption at Rest
- uses SSDs which are encrypted for edge location points of presence (POPs), and encrypted EBS volumes for Regional Edge Caches (RECs).
- Function code and configuration are always stored in an encrypted format on the encrypted SSDs on the edge location POPs, and in other storage locations used by CloudFront.
- Restricting access to content
- Configure HTTPS connections
- Use signed URLs or cookies to restrict access for selected users
- Restrict access to content in S3 buckets using origin access identity – OAI, to prevent users from using the direct URL of the file.
- Restrict direct to load balancer using custom headers, to prevent users from using the direct load balancer URLs.
- Set up field-level encryption for specific content fields
- Use AWS WAF web ACLs to create a web access control list (web ACL) to restrict access to your content.
- Use Geo-restriction, also known as geoblocking, to prevent users in specific geographic locations from accessing content served through a CloudFront distribution.
- Route 53
- is a highly available and scalable DNS web service.
- Resolver Query logging
- logs the queries that originate in specified VPCs, on-premises resources that use inbound resolver or ones using outbound resolver as well as the responses to those DNS queries.
- can be logged to CloudWatch logs, S3, and Kinesis Data Firehose
- Route 53 DNSSEC secures DNS traffic, and helps protect a domain from DNS spoofing man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Elastic Load Balancer
- End to End encryption
- can be done NLB with TCP listener as pass through and terminating SSL on the EC2 instances
- can be done with ALB with SSL termination and using HTTPS between ALB and EC2 instances
- End to End encryption
- Gateway Load Balancer – GWLB
- helps deploy, scale, and manage virtual appliances, such as firewalls, IDS/IPS systems, and deep packet inspection systems.
Management & Governance Tools
- CloudWatch
- CloudWatch logs
- CloudWatch Subscription Filters and their integration with other services.
- CloudWatch Events or EventBridge for more real-time alerts as compared to CloudTrail.
- CloudTrail for audit and governance
- CloudTrail can be enabled for all regions at one go and supports log file integrity validation
- With Organizations, the trail can be configured to log CloudTrail from all accounts to a central account.
- AWS Config
- AWS Config rules can be used to alert for any changes and Config can be used to check the history of changes. AWS Config can also help check approved AMIs compliance
- allows you to remediate noncompliant resources using AWS Systems Manager Automation documents.
- AWS Config -> EventBridge -> Lambda/SNS
- CloudTrail vs Config
- CloudTrail provides the WHO and Config provides the WHAT.
- Systems Manager
- Parameter Store provides secure, scalable, centralized, hierarchical storage for configuration data and secret management. Does not support secrets rotation. Use Secrets Manager instead
- Systems Manager Patch Manager helps select and deploy the operating system and software patches automatically across large groups of EC2 or on-premises instances
- Systems Manager Run Command provides safe, secure remote management of your instances at scale without logging into the servers, replacing the need for bastion hosts, SSH, or remote PowerShell
- Session Manager provides secure and auditable instance management without the need to open inbound ports, maintain bastion hosts, or manage SSH keys.
- AWS Organizations
- is an account management service that enables consolidating multiple AWS accounts into an organization that can be managed centrally.
- can configure Organization Trail to centrally log all CloudTrail logs.
- Service Control Policies
- acts as guardrails and specify the services and actions that users and roles can use in the accounts that the SCP affects.
- are similar to IAM permission policies except that they don’t grant any permissions.
- AWS Trusted Advisor
- inspects the AWS environment to make recommendations for system performance, saving money, availability, and closing security gaps
- CloudFormation
- Deletion Policy to prevent, retain, or backup RDS, EBS Volumes
- Stack policy can prevent stack resources from being unintentionally updated or deleted during a stack update. Stack Policy only applies for Stack updates and not stack deletion.
- Control Tower
- to setup, govern, and secure a multi-account environment
- strongly recommended guardrails cover EBS encryption
Storage & Databases
- Simple Storage Service – S3
- Undertstand S3 Security in detail
- S3 Encryption supports both data at rest and data in transit encryption.
- Data in transit encryption can be provided by enabling communication via SSL or using client-side encryption
- Data at rest encryption can be provided using Server Side or Client Side encryption
- Enforce S3 Encryption at Rest using default encryption of bucket policies
- Enforce S3 encryption in transit using
secureTransportin the S3 bucket policy
- S3 permissions can be handled using
- IAM User Policies
- Resource-based policies which include Bucket policies, Bucket ACL, and Object ACL
- S3 Access Points
- S3 Object Lock helps to store objects using a WORM model and can help prevent objects from being deleted or overwritten for a fixed amount of time or indefinitely.
- S3 Block Public Access provides controls across an entire AWS Account or at the individual S3 bucket level to ensure that objects never have public access, now and in the future.
- S3 Access Points simplify data access for any AWS service or customer application that stores data in S3.
- S3 Versioning with MFA Delete can be enabled on a bucket to ensure that data in the bucket cannot be accidentally overwritten or deleted.
- S3 Access Analyzer monitors the access policies, ensuring that the policies provide only the intended access to your S3 resources.
- Glacier Vault Lock
- EBS Encryption
- Relational Database Services – RDS
- is a web service that makes it easier to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the cloud.
- supports the same encryption at rest methods as EBS
- does not support enabling encryption after creation. Need to create a snapshot, copy the snapshot to an encrypted snapshot and restore it as an encrypted DB.
Compute
- EC2 access using IAM Role, Lambda using the Execution role & ECS using the Task role.
- EC2 Instance Metadata Service version 2 and enforcement of the same.
Integration Tools
- Know how CloudWatch integration with SNS and Lambda can help in notification (Topics are not required to be in detail)
Whitepapers and articles
- AWS Certification – Security Services – Cheat Sheet
- AWS Certification – Identity Services – Cheat Sheet
- AWS Security Incident Response Guide
- AWS DDoS Resiliency Best Practices
- Well-Architected – Security Pillar
On the Exam Day
- Make sure you are relaxed and get some good night’s sleep. The exam is not tough if you are well-prepared.
- If you are taking the AWS Online exam
- Try to join at least 30 minutes before the actual time as I have had issues with both PSI and Pearson with long wait times.
- The online verification process does take some time and usually, there are glitches.
- Remember, you would not be allowed to take the take if you are late by more than 30 minutes.
- Make sure you have your desk clear, no hand-watches, or external monitors, keep your phones away, and nobody can enter the room.
Finally, All the Best 🙂