AWS CloudFormation
- AWS CloudFormation gives developers and systems administrators an easy way to create and manage a collection of related AWS resources, provision and update them in an orderly and predictable fashion.
- CloudFormation consists of
- Template
- is an architectural diagram and provides logical resources
- a JSON or YAML-format, text-based file that describes all the AWS resources needed to deploy and run the application.
- Stack
- is the end result of that diagram and provisions physical resources mapped to the logical resources.
- is the set of AWS resources that are created and managed as a single unit when CloudFormation instantiates a template.
- Template
- CloudFormation template can be used to set up the resources consistently and repeatedly over and over across multiple regions.
- Resources can be updated, deleted, and modified in a controlled and predictable way, in effect applying version control to the infrastructure as done for software code
- AWS CloudFormation Template consists of elements:-
- List of AWS resources and their configuration values
- An optional template file format version number
- An optional list of template parameters (input values supplied at stack creation time)
- An optional list of output values like public IP address using the
Fn:GetAttfunction - An optional list of data tables used to lookup static configuration values for e.g., AMI names per AZ
- CloudFormation supports Chef & Puppet Integration to deploy and configure right down the application layer
- CloudFormation provides a set of application bootstrapping scripts that enable you to install packages, files, and services on the EC2 instances by simply describing them in the CloudFormation template
- By default, automatic rollback on error feature is enabled, which will cause all the AWS resources that CloudFormation created successfully for a stack up to the point where an error occurred to be deleted.
- In case of automatic rollback, charges would still be applied for the resources, the time they were up and running
- CloudFormation provides a WaitCondition resource that acts as a barrier, blocking the creation of other resources until a completion signal is received from an external source e.g. application or management system
- CloudFormation allows deletion policies to be defined for resources in the template for e.g. resources to be retained or snapshots can be created before deletion useful for preserving S3 buckets when the stack is deleted
AWS CloudFormation Concepts
AWS CloudFormation, you work with templates and stacks
Templates
- act as blueprints for building AWS resources.
- is a JSON or YAML formatted text file, saved with any extension, such as .json, .yaml, .template, or .txt.
- have additional capabilities to build complex sets of resources and reuse those templates in multiple contexts for e.g. using input parameters to create generic and reusable templates
- Name used for a resource within the template is a logical name but when CloudFormation creates the resource, it generates a physical name that is based on the combination of the logical name, the stack name, and a unique ID
Stacks
- Stacks manage related resources as a single unit,
- Collection of resources can be created, updated, and deleted by creating, updating, and deleting stacks.
- All the resources in a stack are defined by the stack’s AWS CloudFormation template
- CloudFormation makes underlying service calls to AWS to provision and configure the resources in the stack and can perform only actions that the users have permission to do.
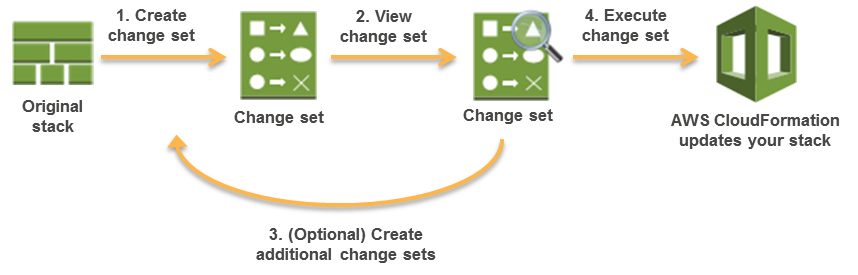
Change Sets
- Change Sets presents a summary or preview of the proposed changes that CloudFormation will make when a stack is updated.
- Change Sets help check how the changes might impact running resources, especially critical resources, before implementing them.
- CloudFormation makes the changes to the stack only when the change set is executed, allowing you to decide whether to proceed with the proposed changes or explore other changes by creating another change set.
- Change sets don’t indicate whether AWS CloudFormation will successfully update a stack for e.g. if account limits are hit or the user does not have permission.
Custom Resources
- Custom resources help write custom provisioning logic in templates that CloudFormation runs anytime the stacks are created, updated, or deleted.
- Custom resources help include resources that aren’t available as AWS CloudFormation resource types and can still be managed in a single stack.
- AWS recommends using CloudFormation Registry instead.
Nested Stacks
- Nested stacks are stacks created as part of other stacks.
- A nested stack can be created within another stack by using the
AWS::CloudFormation::Stackresource. - Nested stacks can be used to define common, repeated patterns and components and create dedicated templates which then can be called from other stacks.
- Root stack is the top-level stack to which all the nested stacks ultimately belong. Nested stacks can themselves contain other nested stacks, resulting in a hierarchy of stacks.
- In addition, each nested stack has an immediate parent stack. For the first level of nested stacks, the root stack is also the parent stack.
- Certain stack operations, such as stack updates, should be initiated from the root stack rather than performed directly on nested stacks themselves.
Drift Detection
- Drift detection enables you to detect whether a stack’s actual configuration differs, or has drifted, from its expected configuration.
- Drift detection help identify stack resources to which configuration changes have been made outside of CloudFormation management
- Drift detection can detect drift on an entire stack or individual resources
- Corrective action can be taken to make sure the stack resources are again in sync with the definitions in the stack template, such as updating the drifted resources directly so that they agree with their template definition
- Resolving drift helps to ensure configuration consistency and successful stack operations.
- CloudFormation detects drift on those AWS resources that support drift detection. Resources that don’t support drift detection are assigned a drift status of NOT_CHECKED.
- Drift detection can be performed on stacks with the following statuses:
CREATE_COMPLETE,UPDATE_COMPLETE,UPDATE_ROLLBACK_COMPLETE, andUPDATE_ROLLBACK_FAILED. - CloudFormation does not detect drift on any nested stacks that belong to that stack. Instead, you can initiate a drift detection operation directly on the nested stack.
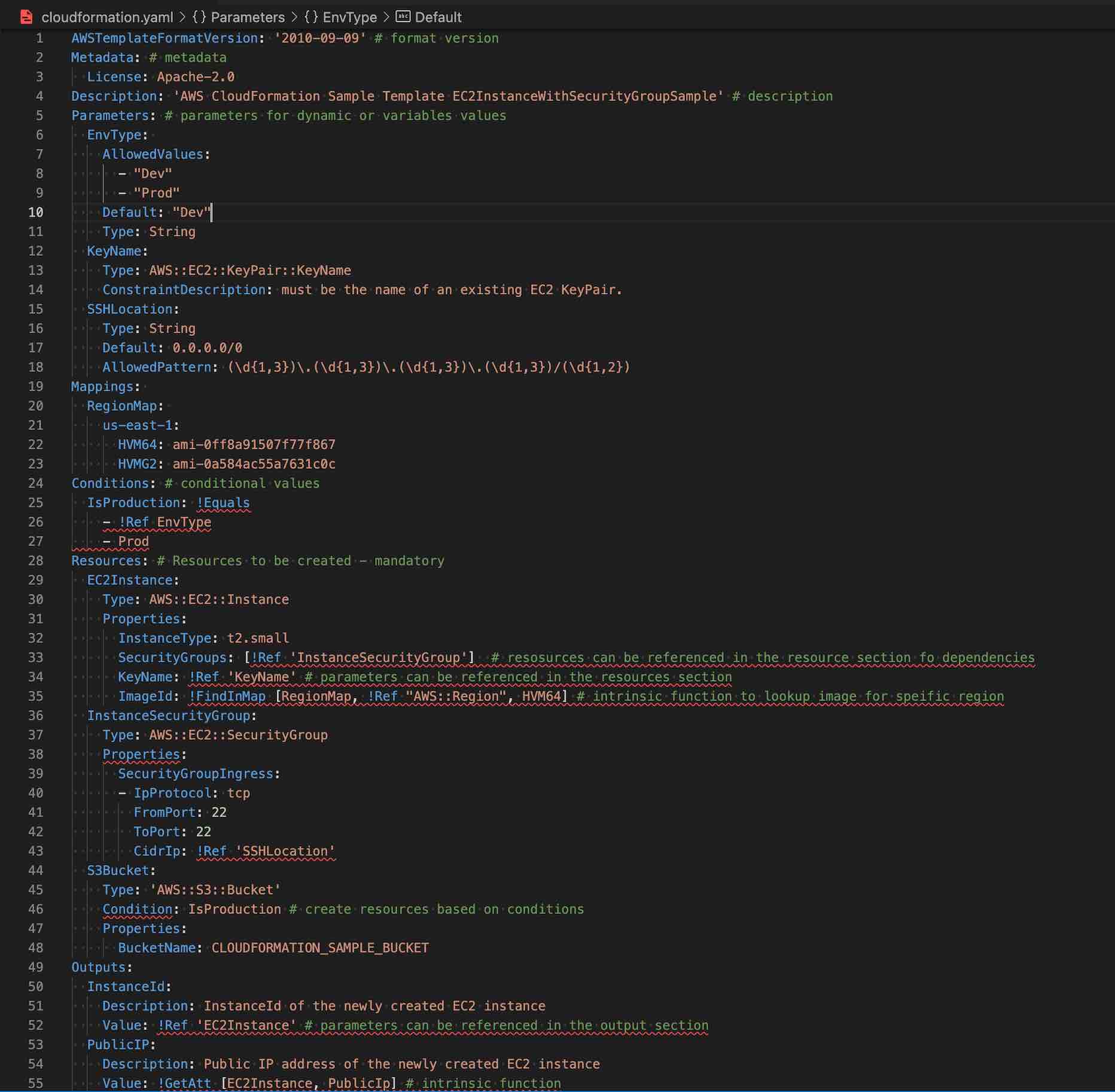
CloudFormation Template Anatomy
- Resources (required)
- Specifies the stack resources and their properties, such as an EC2 instance or an S3 bucket that would be created.
- Resources can be referred to in the Resources and Outputs sections
- Parameters (optional)
- Pass values to the template at runtime (during stack creation or update)
- Parameters can be referred from the Resources and Outputs sections
- Can be referred using
Fn::Refor!Ref
- Mappings (optional)
- A mapping of keys and associated values that used to specify conditional parameter values, similar to a lookup table.
- Can be referred using
Fn::FindInMapor!FindInMap
- Outputs (optional)
- Describes the values that are returned whenever you view your stack’s properties.
- Format Version (optional)
- AWS CloudFormation template version that the template conforms to.
- Description (optional)
- A text string that describes the template. This section must always follow the template format version section.
- Metadata (optional)
- Objects that provide additional information about the template.
- Rules (optional)
- Validates a parameter or a combination of parameters passed to a template during stack creation or stack update.
- Conditions (optional)
- Conditions control whether certain resources are created or whether certain resource properties are assigned a value during stack creation or update.
- Transform (optional)
- For serverless applications (also referred to as Lambda-based applications), specifies the version of the AWS Serverless Application Model (AWS SAM) to use.
- When you specify a transform, you can use AWS SAM syntax to declare resources in the template. The model defines the syntax that you can use and how it’s processed.
CloudFormation Access Control
- IAM
- IAM can be applied with CloudFormation to access control for users whether they can view stack templates, create stacks, or delete stacks
- IAM permissions need to be provided for the user to the AWS services and resources provisioned when the stack is created
- Before a stack is created, AWS CloudFormation validates the template to check for IAM resources that it might create
- Service Role
- A service role is an AWS IAM role that allows AWS CloudFormation to make calls to resources in a stack on the user’s behalf
- By default, AWS CloudFormation uses a temporary session that it generates from the user credentials for stack operations.
- For a service role, AWS CloudFormation uses the role’s credentials.
- When a service role is specified, AWS CloudFormation always uses that role for all operations that are performed on that stack.
Template Resource Attributes
- CreationPolicy Attribute
- is invoked during the associated resource creation.
- can be associated with a resource to prevent its status from reaching create complete until CloudFormation receives a specified number of success signals or the timeout period is exceeded.
- helps to wait on resource configuration actions before stack creation proceeds for e.g. software installation on an EC2 instance
- DeletionPolicy Attribute
- preserve or (in some cases) backup a resource when its stack is deleted
- CloudFormation deletes the resource if a resource has no DeletionPolicy attribute, by default.
- To keep a resource when its stack is deleted,
- default, Delete where the resources would be deleted.
- specify Retain for that resource, to prevent deletion.
- specify Snapshot to create a snapshot before deleting the resource, if the snapshot capability is supported e.g. RDS, EC2 volume, etc.
- DependsOn Attribute
- helps determine dependency order and specify that the creation of a specific resource follows another.
- the resource is created only after the creation of the resource specified in the DependsOn attribute.
- Metadata Attribute
- enables association of structured data with a resource
- UpdatePolicy Attribute
- Defines how AWS CloudFormation handles updates to the resources
- For
AWS::AutoScaling::AutoScalingGroupresources, CloudFormation invokes one of three update policies depending on the type of change or whether a scheduled action is associated with the Auto Scaling group.- The
AutoScalingReplacingUpdateandAutoScalingRollingUpdatepolicies apply only when you do one or more of the following:- Change the Auto Scaling group’s
AWS::AutoScaling::LaunchConfiguration - Change the Auto Scaling group’s VPCZoneIdentifier property
- Change the Auto Scaling group’s LaunchTemplate property
- Update an Auto Scaling group that contains instances that don’t match the current LaunchConfiguration.
- Change the Auto Scaling group’s
- The
AutoScalingScheduledActionpolicy applies when you update a stack that includes an Auto Scaling group with an associated scheduled action.
- The
- For
AWS::Lambda::Aliasresources, CloudFormation performs a CodeDeploy deployment when the version changes on the alias.
CloudFormation Termination Protection
- Termination protection helps prevent a stack from being accidentally deleted.
- Termination protection on stacks is disabled by default.
- Termination protection can be enabled on a stack creation
- Termination protection can be set on a stack with any status except
DELETE_IN_PROGRESSorDELETE_COMPLETE - Enabling or disabling termination protection on a stack sets it for any nested stacks belonging to that stack as well. You can’t enable or disable termination protection directly on a nested stack.
- If a user attempts to directly delete a nested stack belonging to a stack that has termination protection enabled, the operation fails and the nested stack remains unchanged.
- If a user performs a stack update that would delete the nested stack, AWS CloudFormation deletes the nested stack accordingly.
CloudFormation Stack Policy
- Stack policy can prevent stack resources from being unintentionally updated or deleted during a stack update.
- By default, all update actions are allowed on all resources and anyone with stack update permissions can update all of the resources in the stack.
- During an update, some resources might require an interruption or be completely replaced, resulting in new physical IDs or completely new storage and hence need to be prevented.
- A stack policy is a JSON document that defines the update actions that can be performed on designated resources.
- After you set a stack policy, all of the resources in the stack are protected by default.
- Updates on specific resources can be added using an explicit Allow statement for those resources in the stack policy.
- Only one stack policy can be defined per stack, but multiple resources can be protected within a single policy.
- A stack policy applies to all CloudFormation users who attempt to update the stack. You can’t associate different stack policies with different users
- A stack policy applies only during stack updates. It doesn’t provide access controls like an IAM policy.
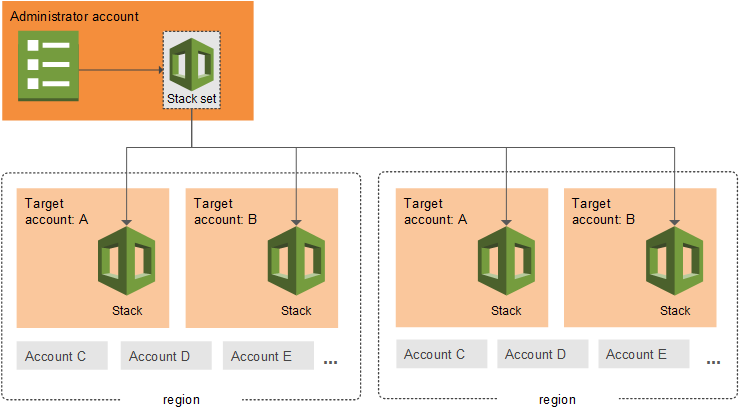
CloudFormation StackSets
- CloudFormation StackSets extends the functionality of stacks by enabling you to create, update, or delete stacks across multiple accounts and Regions with a single operation.
- Using an administrator account, an AWS CloudFormation template can be defined, managed, and used as the basis for provisioning stacks into selected target accounts across specified AWS Regions.
CloudFormation Registry
- CloudFormation registry helps manage extensions, both public and private, such as resources, modules, and hooks that are available for use in your AWS account.
- CloudFormation registry offers several advantages over custom resources
- Supports the modeling, provisioning, and managing of third-party application resources
- Supports the
Create,Read,Update,Delete, andList(CRUDL) operations - Supports drift detection on private and third-party resource types
CloudFormation Helper Scripts
Refer blog Post @ CloudFormation Helper Scripts
CloudFormation Best Practices
Refer blog Post @ CloudFormation Best Practices
AWS Certification Exam Practice Questions
- Questions are collected from Internet and the answers are marked as per my knowledge and understanding (which might differ with yours).
- AWS services are updated everyday and both the answers and questions might be outdated soon, so research accordingly.
- AWS exam questions are not updated to keep up the pace with AWS updates, so even if the underlying feature has changed the question might not be updated
- Open to further feedback, discussion and correction.
- What does Amazon CloudFormation provide?
- The ability to setup Autoscaling for Amazon EC2 instances.
- A templated resource creation for Amazon Web Services.
- A template to map network resources for Amazon Web Services
- None of these
- A user is planning to use AWS CloudFormation for his automatic deployment requirements. Which of the below mentioned components are required as a part of the template?
- Parameters
- Outputs
- Template version
- Resources
- In regard to AWS CloudFormation, what is a stack?
- Set of AWS templates that are created and managed as a template
- Set of AWS resources that are created and managed as a template
- Set of AWS resources that are created and managed as a single unit
- Set of AWS templates that are created and managed as a single unit
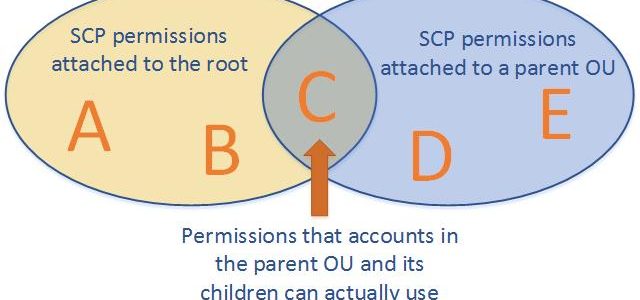
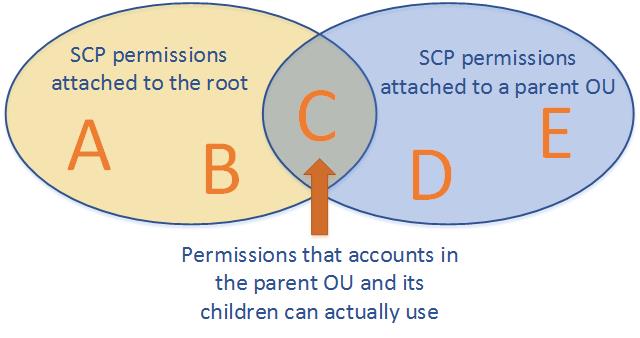
- A large enterprise wants to adopt CloudFormation to automate administrative tasks and implement the security principles of least privilege and separation of duties. They have identified the following roles with the corresponding tasks in the company: (i) network administrators: create, modify and delete VPCs, subnets, NACLs, routing tables, and security groups (ii) application operators: deploy complete application stacks (ELB, Auto -Scaling groups, RDS) whereas all resources must be deployed in the VPCs managed by the network administrators (iii) Both groups must maintain their own CloudFormation templates and should be able to create, update and delete only their own CloudFormation stacks. The company has followed your advice to create two IAM groups, one for applications and one for networks. Both IAM groups are attached to IAM policies that grant rights to perform the necessary task of each group as well as the creation, update and deletion of CloudFormation stacks. Given setup and requirements, which statements represent valid design considerations? Choose 2 answers [PROFESSIONAL]
- Network stack updates will fail upon attempts to delete a subnet with EC2 instances (Subnets cannot be deleted with instances in them)
- Unless resource level permissions are used on the CloudFormation: DeleteStack action, network administrators could tear down application stacks (Network administrators themselves need permission to delete resources within the application stack & CloudFormation makes calls to create, modify, and delete those resources on their behalf)
- The application stack cannot be deleted before all network stacks are deleted (Application stack can be deleted before network stack)
- Restricting the launch of EC2 instances into VPCs requires resource level permissions in the IAM policy of the application group (IAM permissions need to be given explicitly to launch instances )
- Nesting network stacks within application stacks simplifies management and debugging, but requires resource level permissions in the IAM policy of the network group (Although stacks can be nested, Network group will need to have all the application group permissions)
- Your team is excited about the use of AWS because now they have access to programmable infrastructure. You have been asked to manage your AWS infrastructure in a manner similar to the way you might manage application code. You want to be able to deploy exact copies of different versions of your infrastructure, stage changes into different environments, revert back to previous versions, and identify what versions are running at any particular time (development, test, QA, production). Which approach addresses this requirement?
- Use cost allocation reports and AWS Opsworks to deploy and manage your infrastructure.
- Use AWS CloudWatch metrics and alerts along with resource tagging to deploy and manage your infrastructure.
- Use AWS Beanstalk and a version control system like GIT to deploy and manage your infrastructure.
- Use AWS CloudFormation and a version control system like GIT to deploy and manage your infrastructure.
- A user is usingCloudFormation to launch an EC2 instance and then configure an application after the instance is launched. The user wants the stack creation of ELB and AutoScaling to wait until the EC2 instance is launched and configured properly. How can the user configure this?
- It is not possible that the stack creation will wait until one service is created and launched
- The user can use the HoldCondition resource to wait for the creation of the other dependent resources
- The user can use the DependentCondition resource to hold the creation of the other dependent resources
- The user can use the WaitCondition resource to hold the creation of the other dependent resources
- A user has created a CloudFormation stack. The stack creates AWS services, such as EC2 instances, ELB, AutoScaling, and RDS. While creating the stack it created EC2, ELB and AutoScaling but failed to create RDS. What will CloudFormation do in this scenario?
- CloudFormation can never throw an error after launching a few services since it verifies all the steps before launching
- It will warn the user about the error and ask the user to manually create RDS
- Rollback all the changes and terminate all the created services
- It will wait for the user’s input about the error and correct the mistake after the input
- A user is planning to use AWS CloudFormation. Which of the below mentioned functionalities does not help him to correctly understand CloudFormation?
- CloudFormation follows the DevOps model for the creation of Dev & Test
- AWS CloudFormation does not charge the user for its service but only charges for the AWS resources created with it
- CloudFormation works with a wide variety of AWS services, such as EC2, EBS, VPC, IAM, S3, RDS, ELB, etc
- CloudFormation provides a set of application bootstrapping scripts which enables the user to install Software
- A customer is using AWS for Dev and Test. The customer wants to setup the Dev environment with CloudFormation. Which of the below mentioned steps are not required while using CloudFormation?
- Create a stack
- Configure a service
- Create and upload the template
- Provide the parameters configured as part of the template
- A marketing research company has developed a tracking system that collects user behavior during web marketing campaigns on behalf of their customers all over the world. The tracking system consists of an auto-scaled group of Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances behind an elastic load balancer (ELB), and the collected data is stored in Amazon DynamoDB. After the campaign is terminated, the tracking system is torn down and the data is moved to Amazon Redshift, where it is aggregated, analyzed and used to generate detailed reports. The company wants to be able to instantiate new tracking systems in any region without any manual intervention and therefore adopted AWS CloudFormation. What needs to be done to make sure that the AWS CloudFormation template works in every AWS region? Choose 2 answers [PROFESSIONAL]
- IAM users with the right to start AWS CloudFormation stacks must be defined for every target region. (IAM users are global)
- The names of the Amazon DynamoDB tables must be different in every target region. (DynamoDB names should be unique only within a region)
- Use the built-in function of AWS CloudFormation to set the AvailabilityZone attribute of the ELB resource.
- Avoid using DeletionPolicies for EBS snapshots. (Don’t want the data to be retained)
- Use the built-in Mappings and FindInMap functions of AWS CloudFormation to refer to the AMI ID set in the ImageId attribute of the Auto Scaling::LaunchConfiguration resource.
- A gaming company adopted AWS CloudFormation to automate load -testing of their games. They have created an AWS CloudFormation template for each gaming environment and one for the load -testing stack. The load – testing stack creates an Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) Postgres database and two web servers running on Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) that send HTTP requests, measure response times, and write the results into the database. A test run usually takes between 15 and 30 minutes. Once the tests are done, the AWS CloudFormation stacks are torn down immediately. The test results written to the Amazon RDS database must remain accessible for visualization and analysis. Select possible solutions that allow access to the test results after the AWS CloudFormation load -testing stack is deleted. Choose 2 answers. [PROFESSIONAL]
- Define a deletion policy of type Retain for the Amazon QDS resource to assure that the RDS database is not deleted with the AWS CloudFormation stack.
- Define a deletion policy of type Snapshot for the Amazon RDS resource to assure that the RDS database can be restored after the AWS CloudFormation stack is deleted.
- Define automated backups with a backup retention period of 30 days for the Amazon RDS database and perform point -in -time recovery of the database after the AWS CloudFormation stack is deleted. (as the environment is required for limited time the automated backup will not serve the purpose)
- Define an Amazon RDS Read-Replica in the load-testing AWS CloudFormation stack and define a dependency relation between master and replica via the DependsOn attribute. (read replica not needed and will be deleted when the stack is deleted)
- Define an update policy to prevent deletion of the Amazon RDS database after the AWS CloudFormation stack is deleted. (UpdatePolicy does not apply to RDS)
- When working with AWS CloudFormation Templates what is the maximum number of stacks that you can create?
- 5000
- 500
- 2000 (Refer link – The limit keeps on changing to check for the latest)
- 100
- What happens, by default, when one of the resources in a CloudFormation stack cannot be created?
- Previously created resources are kept but the stack creation terminates
- Previously created resources are deleted and the stack creation terminates
- Stack creation continues, and the final results indicate which steps failed
- CloudFormation templates are parsed in advance so stack creation is guaranteed to succeed.
- You need to deploy an AWS stack in a repeatable manner across multiple environments. You have selected CloudFormation as the right tool to accomplish this, but have found that there is a resource type you need to create and model, but is unsupported by CloudFormation. How should you overcome this challenge? [PROFESSIONAL]
- Use a CloudFormation Custom Resource Template by selecting an API call to proxy for create, update, and delete actions. CloudFormation will use the AWS SDK, CLI, or API method of your choosing as the state transition function for the resource type you are modeling.
- Submit a ticket to the AWS Forums. AWS extends CloudFormation Resource Types by releasing tooling to the AWS Labs organization on GitHub. Their response time is usually 1 day, and they complete requests within a week or two.
- Instead of depending on CloudFormation, use Chef, Puppet, or Ansible to author Heat templates, which are declarative stack resource definitions that operate over the OpenStack hypervisor and cloud environment.
- Create a CloudFormation Custom Resource Type by implementing create, update, and delete functionality, either by subscribing a Custom Resource Provider to an SNS topic, or by implementing the logic in AWS Lambda. (Refer link)
- What is a circular dependency in AWS CloudFormation?
- When a Template references an earlier version of itself.
- When Nested Stacks depend on each other.
- When Resources form a DependOn loop. (Refer link, to resolve a dependency error, add a DependsOn attribute to resources that depend on other resources in the template. Some cases for e.g. EIP and VPC with IGW where EIP depends on IGW need explicitly declaration for the resources to be created in correct order)
- When a Template references a region, which references the original Template.
- You need to run a very large batch data processing job one time per day. The source data exists entirely in S3, and the output of the processing job should also be written to S3 when finished. If you need to version control this processing job and all setup and teardown logic for the system, what approach should you use?
- Model an AWS EMR job in AWS Elastic Beanstalk. (cannot directly model EMR Clusters)
- Model an AWS EMR job in AWS CloudFormation. (EMR cluster can be modeled using CloudFormation. Refer link)
- Model an AWS EMR job in AWS OpsWorks. (cannot directly model EMR Clusters)
- Model an AWS EMR job in AWS CLI Composer. (does not exist)
- Your company needs to automate 3 layers of a large cloud deployment. You want to be able to track this deployment’s evolution as it changes over time, and carefully control any alterations. What is a good way to automate a stack to meet these requirements? [PROFESSIONAL]
- Use OpsWorks Stacks with three layers to model the layering in your stack.
- Use CloudFormation Nested Stack Templates, with three child stacks to represent the three logical layers of your cloud. (CloudFormation allows source controlled, declarative templates as the basis for stack automation and Nested Stacks help achieve clean separation of layers while simultaneously providing a method to control all layers at once when needed)
- Use AWS Config to declare a configuration set that AWS should roll out to your cloud.
- Use Elastic Beanstalk Linked Applications, passing the important DNS entries between layers using the metadata interface.
- You have been asked to de-risk deployments at your company. Specifically, the CEO is concerned about outages that occur because of accidental inconsistencies between Staging and Production, which sometimes cause unexpected behaviors in Production even when Staging tests pass. You already use Docker to get high consistency between Staging and Production for the application environment on your EC2 instances. How do you further de-risk the rest of the execution environment, since in AWS, there are many service components you may use beyond EC2 virtual machines? [PROFESSIONAL]
- Develop models of your entire cloud system in CloudFormation. Use this model in Staging and Production to achieve greater parity. (Only CloudFormation’s JSON Templates allow declarative version control of repeatedly deployable models of entire AWS clouds. Refer link)
- Use AWS Config to force the Staging and Production stacks to have configuration parity. Any differences will be detected for you so you are aware of risks.
- Use AMIs to ensure the whole machine, including the kernel of the virual machines, is consistent, since Docker uses Linux Container (LXC) technology, and we need to make sure the container environment is consistent.
- Use AWS ECS and Docker clustering. This will make sure that the AMIs and machine sizes are the same across both environments.
- Which code snippet below returns the URL of a load balanced web site created in CloudFormation with an AWS::ElasticLoadBalancing::LoadBalancer resource name “ElasticLoad Balancer”? [Developer]
- “Fn::Join” : [“”, [ “http://”, {“Fn::GetAtt” : [ “ElasticLoadBalancer”,”DNSName”]}]] (Refer link)
- “Fn::Join” : [“”,[ “http://”, {“Fn::GetAtt” : [ “ElasticLoadBalancer”,”Url”]}]]
- “Fn::Join” : [“”, [ “http://”, {“Ref” : “ElasticLoadBalancerUrl”}]]
- “Fn::Join” : [“”, [ “http://”, {“Ref” : “ElasticLoadBalancerDNSName”}]]
- For AWS CloudFormation, which stack state refuses UpdateStack calls? [Developer]
- <code>UPDATE_ROLLBACK_FAILED</code> (Refer link)
- <code>UPDATE_ROLLBACK_COMPLETE</code>
- <code>UPDATE_COMPLETE</code>
- <code>CREATE_COMPLETE</code>
- Which of these is not a Pseudo Parameter in AWS CloudFormation? [Developer]
- AWS::StackName
- AWS::AccountId
- AWS::StackArn (Refer link)
- AWS::NotificationARNs
- Which of these is not an intrinsic function in AWS CloudFormation? [Developer]
- Fn::SplitValue (Refer link)
- Fn::FindInMap
- Fn::Select
- Fn::GetAZs
- Which of these is not a CloudFormation Helper Script? [Developer]
- cfn-signal
- cfn-hup
- cfn-request (Refer link)
- cfn-get-metadata
- What method should I use to author automation if I want to wait for a CloudFormation stack to finish completing in a script? [Developer]
- Event subscription using SQS.
- Event subscription using SNS.
- Poll using <code>ListStacks</code> / <code>list-stacks</code>. (Only polling will make a script wait to complete. ListStacks / list-stacks is a real method. Refer link)
- Poll using <code>GetStackStatus</code> / <code>get-stack-status</code>. (GetStackStatus / get-stack-status does not exist)
- Which status represents a failure state in AWS CloudFormation? [Developer]
- <code>UPDATE_COMPLETE_CLEANUP_IN_PROGRESS</code> (UPDATE_COMPLETE_CLEANUP_IN_PROGRESS means an update was successful, and CloudFormation is deleting any replaced, no longer used resources)
- <code>DELETE_COMPLETE_WITH_ARTIFACTS</code> (DELETE_COMPLETE_WITH_ARTIFACTS does not exist)
- <code>ROLLBACK_IN_PROGRESS</code> (ROLLBACK_IN_PROGRESS means an UpdateStack operation failed and the stack is in the process of trying to return to the valid, pre-update state Refer link)
- <code>ROLLBACK_FAILED</code> (ROLLBACK_FAILED is not a CloudFormation state but UPDATE_ROLLBACK_FAILED is)
- Which of these is not an intrinsic function in AWS CloudFormation? [Developer]
- Fn::Equals
- Fn::If
- Fn::Not
- Fn::Parse (Complete list of Intrinsic Functions: Fn::Base64, Fn::And, Fn::Equals, Fn::If, Fn::Not, Fn::Or, Fn::FindInMap, Fn::GetAtt, Fn::GetAZs, Fn::Join, Fn::Select, Refer link)
- You need to create a Route53 record automatically in CloudFormation when not running in production during all launches of a Template. How should you implement this? [Developer]
- Use a <code>Parameter</code> for <code>environment</code>, and add a <code>Condition</code> on the Route53 <code>Resource</code> in the template to create the record only when <code>environment</code> is not <code>production</code>. (Best way to do this is with one template, and a Condition on the resource. Route53 does not allow null strings for Refer link)
- Create two templates, one with the Route53 record value and one with a null value for the record. Use the one without it when deploying to production.
- Use a <code>Parameter</code> for <code>environment</code>, and add a <code>Condition</code> on the Route53 <code>Resource</code> in the template to create the record with a null string when <code>environment</code> is <code>production</code>.
- Create two templates, one with the Route53 record and one without it. Use the one without it when deploying to production.