Storage Options Whitepaper
AWS Storage Options is one of the most important Whitepaper for AWS Solution Architect Professional Certification exam and covers a brief summary of each AWS storage options, their ideal usage patterns, anti-patterns, performance, durability and availability, scalability etc.
Overview
- AWS offers multiple cloud-based storage options. Each has a unique combination of performance, durability, availability, cost, and interface, as well as other characteristics such as scalability and elasticity
- All storage options are ideally suited for some uses cases and there are certain Anti-Patterns which should be taken in account while making a storage choice

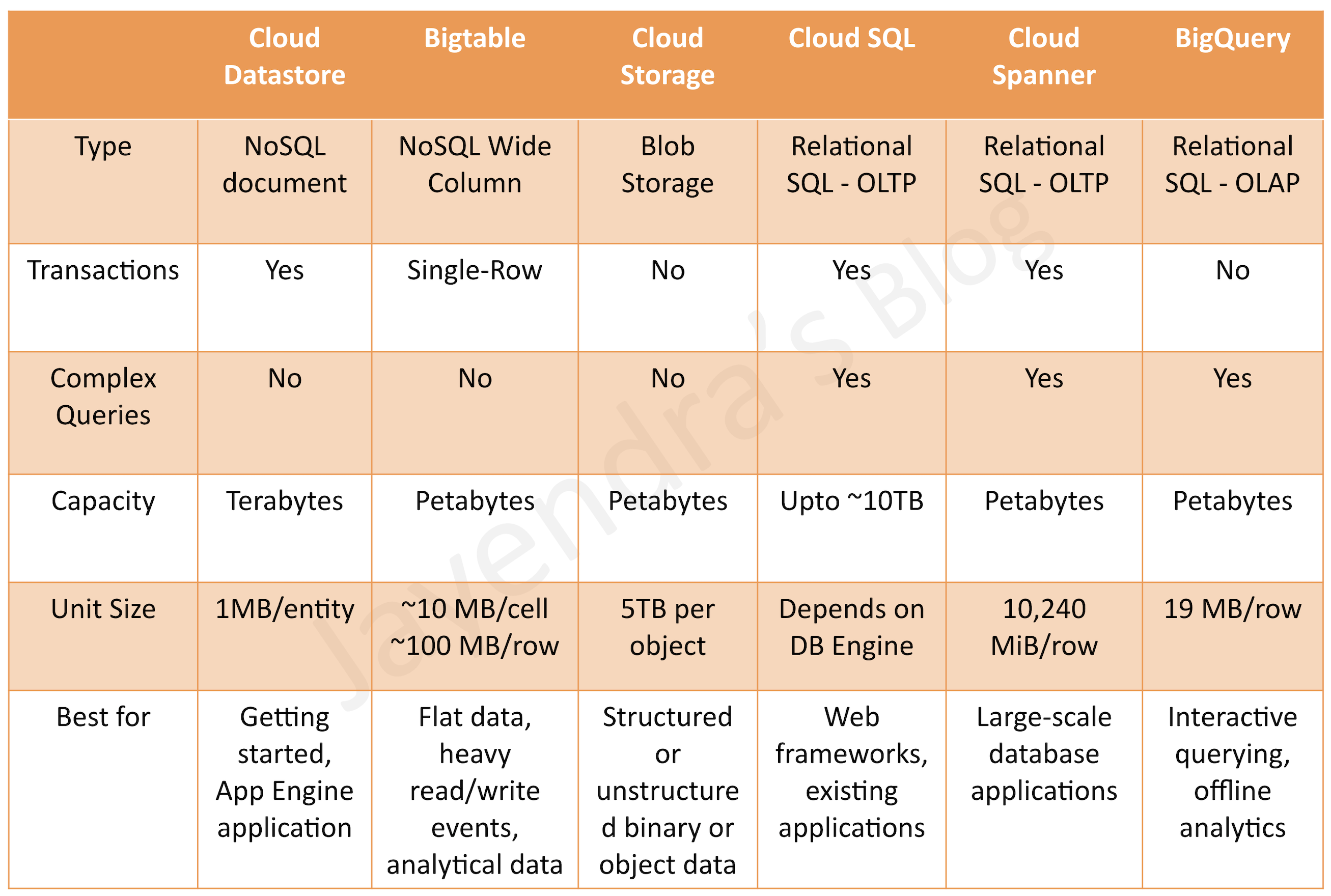
Amazon S3 & Amazon Glacier
More Details @ AWS Storage Options – S3 & Glacier
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) & Instance Store Volumes
More details @ AWS Storage Options – EBS & Instance Store
Amazon RDS, DynamoDB & Database on EC2
More details @ AWS Storage Options – RDS, DynamoDB & Database on EC2
Amazon SQS & Redshift
More details @ AWS Storage Options – SQS & Redshift
Amazon CloudFront & Elasticache
More details @ AWS Storage Options – CloudFront & ElastiCache
Amazon Storage Gateway & Import/Export
More details @ AWS Storage Options – Storage Gateway & Import/Export

AWS Certification Exam Practice Questions
- Questions are collected from Internet and the answers are marked as per my knowledge and understanding (which might differ with yours).
- AWS services are updated everyday and both the answers and questions might be outdated soon, so research accordingly.
- AWS exam questions are not updated to keep up the pace with AWS updates, so even if the underlying feature has changed the question might not be updated
- Open to further feedback, discussion and correction.
- You are developing a highly available web application using stateless web servers. Which services are suitable for storing session state data? Choose 3 answers.
- Elastic Load Balancing
- Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS)
- Amazon CloudWatch
- Amazon ElastiCache
- Amazon DynamoDB
- AWS Storage Gateway
- Your firm has uploaded a large amount of aerial image data to S3. In the past, in your on-premises environment, you used a dedicated group of servers to oaten process this data and used Rabbit MQ, an open source messaging system, to get job information to the servers. Once processed the data would go to tape and be shipped offsite. Your manager told you to stay with the current design, and leverage AWS archival storage and messaging services to minimize cost. Which is correct? [PROFESSIONAL]
- Use SQS for passing job messages, use Cloud Watch alarms to terminate EC2 worker instances when they become idle. Once data is processed, change the storage class of the S3 objects to Reduced Redundancy Storage.
- Setup Auto-Scaled workers triggered by queue depth that use spot instances to process messages in SQS. Once data is processed, change the storage class of the S3 objects to Reduced Redundancy Storage.
- Setup Auto-Scaled workers triggered by queue depth that use spot instances to process messages in SQS. Once data is processed, change the storage class of the S3 objects to Glacier.
- Use SNS to pass job messages use Cloud Watch alarms to terminate spot worker instances when they become idle. Once data is processed, change the storage class of the S3 object to Glacier.
- You are developing a new mobile application and are considering storing user preferences in AWS, which would provide a more uniform cross-device experience to users using multiple mobile devices to access the application. The preference data for each user is estimated to be 50KB in size. Additionally 5 million customers are expected to use the application on a regular basis. The solution needs to be cost-effective, highly available, scalable and secure, how would you design a solution to meet the above requirements? [PROFESSIONAL]
- Setup an RDS MySQL instance in 2 availability zones to store the user preference data. Deploy a public facing application on a server in front of the database to manage security and access credentials
- Setup a DynamoDB table with an item for each user having the necessary attributes to hold the user preferences. The mobile application will query the user preferences directly from the DynamoDB table. Utilize STS. Web Identity Federation, and DynamoDB Fine Grained Access Control to authenticate and authorize access
- Setup an RDS MySQL instance with multiple read replicas in 2 availability zones to store the user preference data .The mobile application will query the user preferences from the read replicas. Leverage the MySQL user management and access privilege system to manage security and access credentials.
- Store the user preference data in S3 Setup a DynamoDB table with an item for each user and an item attribute pointing to the user’ S3 object. The mobile application will retrieve the S3 URL from DynamoDB and then access the S3 object directly utilize STS, Web identity Federation, and S3 ACLs to authenticate and authorize access.
- A company is building a voting system for a popular TV show, viewers would watch the performances then visit the show’s website to vote for their favorite performer. It is expected that in a short period of time after the show has finished the site will receive millions of visitors. The visitors will first login to the site using their Amazon.com credentials and then submit their vote. After the voting is completed the page will display the vote totals. The company needs to build the site such that can handle the rapid influx of traffic while maintaining good performance but also wants to keep costs to a minimum. Which of the design patterns below should they use? [PROFESSIONAL]
- Use CloudFront and an Elastic Load balancer in front of an auto-scaled set of web servers, the web servers will first can the Login With Amazon service to authenticate the user then process the users vote and store the result into a multi-AZ Relational Database Service instance.
- Use CloudFront and the static website hosting feature of S3 with the Javascript SDK to call the Login With Amazon service to authenticate the user, use IAM Roles to gain permissions to a DynamoDB table to store the users vote.
- Use CloudFront and an Elastic Load Balancer in front of an auto-scaled set of web servers, the web servers will first call the Login with Amazon service to authenticate the user, the web servers will process the users vote and store the result into a DynamoDB table using IAM Roles for EC2 instances to gain permissions to the DynamoDB table.
- Use CloudFront and an Elastic Load Balancer in front of an auto-scaled set of web servers, the web servers will first call the Login. With Amazon service to authenticate the user, the web servers would process the users vote and store the result into an SQS queue using IAM Roles for EC2 Instances to gain permissions to the SQS queue. A set of application servers will then retrieve the items from the queue and store the result into a DynamoDB table
- A large real-estate brokerage is exploring the option to adding a cost-effective location-based alert to their existing mobile application. The application backend infrastructure currently runs on AWS. Users who opt in to this service will receive alerts on their mobile device regarding real-estate offers in proximity to their location. For the alerts to be relevant delivery time needs to be in the low minute count. The existing mobile app has 5 million users across the US. Which one of the following architectural suggestions would you make to the customer? [PROFESSIONAL]
- Mobile application will submit its location to a web service endpoint utilizing Elastic Load Balancing and EC2 instances. DynamoDB will be used to store and retrieve relevant offers. EC2 instances will communicate with mobile earners/device providers to push alerts back to mobile application. —
- Use AWS Direct Connect or VPN to establish connectivity with mobile carriers EC2 instances will receive the mobile applications location through carrier connection: RDS will be used to store and relevant offers. EC2 instances will communicate with mobile carriers to push alerts back to the mobile application
- Mobile application will send device location using SQS. EC2 instances will retrieve the relevant offers from DynamoDB. AWS Mobile Push will be used to send offers to the mobile application
- Mobile application will send device location using AWS Mobile Push. EC2 instances will retrieve the relevant offers from DynamoDB. EC2 instances will communicate with mobile carriers/device providers to push alerts back to the mobile application.
- You are running a news website in the eu-west-1 region that updates every 15 minutes. The website has a worldwide audience and it uses an Auto Scaling group behind an Elastic Load Balancer and an Amazon RDS database. Static content resides on Amazon S3, and is distributed through Amazon CloudFront. Your Auto Scaling group is set to trigger a scale up event at 60% CPU utilization; you use an Amazon RDS extra-large DB instance with 10.000 Provisioned IOPS its CPU utilization is around 80%. While freeable memory is in the 2 GB range. Web analytics reports show that the average load time of your web pages is around 1.5 to 2 seconds, but your SEO consultant wants to bring down the average load time to under 0.5 seconds. How would you improve page load times for your users? (Choose 3 answers) [PROFESSIONAL]
- Lower the scale up trigger of your Auto Scaling group to 30% so it scales more aggressively.
- Add an Amazon ElastiCache caching layer to your application for storing sessions and frequent DB queries
- Configure Amazon CloudFront dynamic content support to enable caching of re-usable content from your site
- Switch Amazon RDS database to the high memory extra-large Instance type
- Set up a second installation in another region, and use the Amazon Route 53 latency-based routing feature to select the right region.
- A read only news reporting site with a combined web and application tier and a database tier that receives large and unpredictable traffic demands must be able to respond to these traffic fluctuations automatically. What AWS services should be used meet these requirements? [PROFESSIONAL]
- Stateless instances for the web and application tier synchronized using ElastiCache Memcached in an autoscaling group monitored with CloudWatch. And RDS with read replicas.
- Stateful instances for the web and application tier in an autoscaling group monitored with CloudWatch and RDS with read replicas
- Stateful instances for the web and application tier in an autoscaling group monitored with CloudWatch. And multi-AZ RDS
- Stateless instances for the web and application tier synchronized using ElastiCache Memcached in an autoscaling group monitored with CloudWatch and multi-AZ RDS
- You have a periodic Image analysis application that gets some files as input, analyzes them and for each file writes some data in output to a ten file. The number of files in input per day is high and concentrated in a few hours of the day. Currently you have a server on EC2 with a large EBS volume that hosts the input data and the results it takes almost 20 hours per day to complete the process. What services could be used to reduce the elaboration time and improve the availability of the solution? [PROFESSIONAL]
- S3 to store I/O files. SQS to distribute elaboration commands to a group of hosts working in parallel. Auto scaling to dynamically size the group of hosts depending on the length of the SQS queue
- EBS with Provisioned IOPS (PIOPS) to store I/O files. SNS to distribute elaboration commands to a group of hosts working in parallel Auto Scaling to dynamically size the group of hosts depending on the number of SNS notifications
- S3 to store I/O files, SNS to distribute evaporation commands to a group of hosts working in parallel. Auto scaling to dynamically size the group of hosts depending on the number of SNS notifications
- EBS with Provisioned IOPS (PIOPS) to store I/O files SOS to distribute elaboration commands to a group of hosts working in parallel Auto Scaling to dynamically size the group to hosts depending on the length of the SQS queue.
- A 3-tier e-commerce web application is current deployed on-premises and will be migrated to AWS for greater scalability and elasticity. The web server currently shares read-only data using a network distributed file system The app server tier uses a clustering mechanism for discovery and shared session state that depends on IP multicast The database tier uses shared-storage clustering to provide database fail over capability, and uses several read slaves for scaling. Data on all servers and the distributed file system directory is backed up weekly to off-site tapes. Which AWS storage and database architecture meets the requirements of the application? [PROFESSIONAL]
- Web servers store read-only data in S3, and copy from S3 to root volume at boot time. App servers share state using a combination of DynamoDB and IP unicast. Database use RDS with multi-AZ deployment and one or more Read Replicas. Backup web and app servers backed up weekly via AMIs, database backed up via DB snapshots.
- Web servers store read-only data in S3, and copy from S3 to root volume at boot time. App servers share state using a combination of DynamoDB and IP unicast. Database use RDS with multi-AZ deployment and one or more Read replicas. Backup web servers app servers, and database backed up weekly to Glacier using snapshots (Snapshots to Glacier don’t work directly with EBS snapshots)
- Web servers store read-only data in S3 and copy from S3 to root volume at boot time. App servers share state using a combination of DynamoDB and IP unicast. Database use RDS with multi-AZ deployment. Backup web and app servers backed up weekly via AMIs. Database backed up via DB snapshots (Need Read replicas for scalability and elasticity)
- Web servers, store read-only data in an EC2 NFS server, mount to each web server at boot time App servers share state using a combination of DynamoDB and IP multicast Database use RDS with multi-AZ deployment and one or more Read Replicas Backup web and app servers backed up weekly via AMIs database backed up via DB snapshots (IP multicast not available in AWS)
- Our company is getting ready to do a major public announcement of a social media site on AWS. The website is running on EC2 instances deployed across multiple Availability Zones with a Multi-AZ RDS MySQL Extra Large DB Instance. The site performs a high number of small reads and writes per second and relies on an eventual consistency model. After comprehensive tests you discover that there is read contention on RDS MySQL. Which are the best approaches to meet these requirements? (Choose 2 answers) [PROFESSIONAL]
- Deploy ElasticCache in-memory cache running in each availability zone
- Implement sharding to distribute load to multiple RDS MySQL instances (Would distributed read write both, focus is on read contention)
- Increase the RDS MySQL Instance size and Implement provisioned IOPS (Would distributed read write both, focus is on read contention)
- Add an RDS MySQL read replica in each availability zone
- Run 2-tier app with the following: an ELB, three web app server on EC2, and 1 MySQL RDS db. With grown load, db queries take longer and longer and slow down the overall response time for user request. What Options could speed up performance? (Choose 3) [PROFESSIONAL]
- Create an RDS read-replica and redirect half of the database read request to it
- Cache database queries in amazon ElastiCache
- Setup RDS in multi-availability zone mode.
- Shard the database and distribute loads between shards.
- Use amazon CloudFront to cache database queries.
- You have a web application leveraging an Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) In front of the web servers deployed using an Auto Scaling Group Your database is running on Relational Database Service (RDS) The application serves out technical articles and responses to them in general there are more views of an article than there are responses to the article. On occasion, an article on the site becomes extremely popular resulting in significant traffic Increases that causes the site to go down. What could you do to help alleviate the pressure on the infrastructure while maintaining availability during these events? Choose 3 answers [PROFESSIONAL]
- Leverage CloudFront for the delivery of the articles.
- Add RDS read-replicas for the read traffic going to your relational database
- Leverage Elastic Cache for caching the most frequently used data.
- Use SQS to queue up the requests for the technical posts and deliver them out of the queue (does not process and would not be real time)
- Use Route53 health checks to fail over to an S3 bucket for an error page (more of an error handling then availability)
- Your website is serving on-demand training videos to your workforce. Videos are uploaded monthly in high resolution MP4 format. Your workforce is distributed globally often on the move and using company-provided tablets that require the HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) protocol to watch a video. Your company has no video transcoding expertise and it required you might need to pay for a consultant. How do you implement the most cost-efficient architecture without compromising high availability and quality of video delivery? [PROFESSIONAL]
- Elastic Transcoder to transcode original high-resolution MP4 videos to HLS. S3 to host videos with lifecycle Management to archive original flies to Glacier after a few days. CloudFront to serve HLS transcoded videos from S3 (Elastic Transcoder for High quality, S3 to host videos cheaply, Glacier for archives and CloudFront for high availability)
- A video transcoding pipeline running on EC2 using SQS to distribute tasks and Auto Scaling to adjust the number or nodes depending on the length of the queue S3 to host videos with Lifecycle Management to archive all files to Glacier after a few days CloudFront to serve HLS transcoding videos from Glacier
- Elastic Transcoder to transcode original high-resolution MP4 videos to HLS EBS volumes to host videos and EBS snapshots to incrementally backup original rues after a few days. CloudFront to serve HLS transcoded videos from EC2.
- A video transcoding pipeline running on EC2 using SQS to distribute tasks and Auto Scaling to adjust the number of nodes depending on the length of the queue. EBS volumes to host videos and EBS snapshots to incrementally backup original files after a few days. CloudFront to serve HLS transcoded videos from EC2
- To meet regulatory requirements, a pharmaceuticals company needs to archive data after a drug trial test is concluded. Each drug trial test may generate up to several thousands of files, with compressed file sizes ranging from 1 byte to 100MB. Once archived, data rarely needs to be restored, and on the rare occasion when restoration is needed, the company has 24 hours to restore specific files that match certain metadata. Searches must be possible by numeric file ID, drug name, participant names, date ranges, and other metadata. Which is the most cost-effective architectural approach that can meet the requirements? [PROFESSIONAL]
- Store individual files in Amazon Glacier, using the file ID as the archive name. When restoring data, query the Amazon Glacier vault for files matching the search criteria. (Individual files are expensive and does not allow searching by participant names etc)
- Store individual files in Amazon S3, and store search metadata in an Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) multi-AZ database. Create a lifecycle rule to move the data to Amazon Glacier after a certain number of days. When restoring data, query the Amazon RDS database for files matching the search criteria, and move the files matching the search criteria back to S3 Standard class. (As the data is not needed can be stored to Glacier directly and the data need not be moved back to S3 standard)
- Store individual files in Amazon Glacier, and store the search metadata in an Amazon RDS multi-AZ database. When restoring data, query the Amazon RDS database for files matching the search criteria, and retrieve the archive name that matches the file ID returned from the database query. (Individual files and Multi-AZ is expensive)
- First, compress and then concatenate all files for a completed drug trial test into a single Amazon Glacier archive. Store the associated byte ranges for the compressed files along with other search metadata in an Amazon RDS database with regular snapshotting. When restoring data, query the database for files that match the search criteria, and create restored files from the retrieved byte ranges.
- Store individual compressed files and search metadata in Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3). Create a lifecycle rule to move the data to Amazon Glacier, after a certain number of days. When restoring data, query the Amazon S3 bucket for files matching the search criteria, and retrieve the file to S3 reduced redundancy in order to move it back to S3 Standard class. (Once the data is moved from S3 to Glacier the metadata is lost, as Glacier does not have metadata and must be maintained externally)
- A document storage company is deploying their application to AWS and changing their business model to support both free tier and premium tier users. The premium tier users will be allowed to store up to 200GB of data and free tier customers will be allowed to store only 5GB. The customer expects that billions of files will be stored. All users need to be alerted when approaching 75 percent quota utilization and again at 90 percent quota use. To support the free tier and premium tier users, how should they architect their application? [PROFESSIONAL]
- The company should utilize an amazon simple work flow service activity worker that updates the users data counter in amazon dynamo DB. The activity worker will use simple email service to send an email if the counter increases above the appropriate thresholds.
- The company should deploy an amazon relational data base service relational database with a store objects table that has a row for each stored object along with size of each object. The upload server will query the aggregate consumption of the user in questions by first determining the files store by the user, and then querying the stored objects table for respective file sizes) and send an email via amazon simple email service if the thresholds are breached.
- The company should write both the content length and the username of the files owner as S3 metadata for the object. They should then create a file watcher to iterate over each object and aggregate the size for each user and send a notification via amazon simple queue service to an emailing service if the storage threshold is exceeded.
- The company should create two separated amazon simple storage service buckets one for data storage for free tier users and another for data storage for premium tier users. An amazon simple workflow service activity worker will query all objects for a given user based on the bucket the data is stored
- Your company has been contracted to develop and operate a website that tracks NBA basketball statistics. Statistical data to derive reports like “best game-winning shots from the regular season” and more frequently built reports like “top shots of the game” need to be stored durably for repeated lookup. Leveraging social media techniques, NBA fans submit and vote on new report types from the existing data set so the system needs to accommodate variability in data queries and new static reports must be generated and posted daily. Initial research in the design phase indicates that there will be over 3 million report queries on game day by end users and other applications that use this application as a data source. It is expected that this system will gain in popularity over time and reach peaks of 10-15 million report queries of the system on game days. Select the answer that will allow your application to best meet these requirements while minimizing costs. [PROFESSIONAL]
- Launch a multi-AZ MySQL Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) Read Replica connected to your multi AZ master database and generate reports by querying the Read Replica. Perform a daily table cleanup.
- Implement a multi-AZ MySQL RDS deployment and have the application generate reports from Amazon ElastiCache for in-memory performance results. Utilize the default expire parameter for items in the cache.
- Generate reports from a multi-AZ MySQL Amazon RDS deployment and have an offline task put reports in Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) and use CloudFront to cache the content. Use a TTL to expire objects daily. (Offline task with S3 storage and CloudFront cache)
- Query a multi-AZ MySQL RDS instance and store the results in a DynamoDB table. Generate reports from the DynamoDB table. Remove stale tables daily.
References