AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C01 Exam Learning Path (Obsolete)
SAA-C01 is Obsolete now, Please refer SAA-C03 Learning Path
AWS Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C01 exam is the latest AWS exam and would replace the old CSA-Associate exam. It basically validates the ability to effectively demonstrate knowledge of how to architect and deploy secure and robust applications on AWS technologies
- Define a solution using architectural design principles based on customer requirements.
- Provide implementation guidance based on best practices to the organization throughout the life cycle of the project.
Refer AWS_Solution_Architect_-_Associate_SAA-C01_Exam_Blue_Print
AWS Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C01 Exam Summary
- AWS has updated the exam concepts from the focus being on individual services to more building of scalable, highly available, cost-effective, performant, resilient and operational effective architecture
- Although, most of the services covered by the the old exam are the same. There are few new additions like API Gateway, Lambda, ECS, Aurora
- Exam surely covers the architecture aspects in deep, so you must be able to visualize the architecture, even draw them out in the exam just to understand how it would work and how different services relate.
- Be sure to cover the following topics
- Networking
- Be sure to create VPC from scratch. This is mandatory.
- Create VPC and understand whats an CIDR.
- Create public and private subnets, configure proper routes, security groups, NACLs.
- Create Bastion for communication with instances
- Create NAT Gateway or Instances for instances in private subnets to interact with internet
- Create two tier architecture with application in public and database in private subnets
- Create three tier architecture with web servers in public, application and database servers in private.
- Make sure to understand how the communication happens between Internet, Public subnets, Private subnets, NAT, Bastion etc.
- Understand VPC endpoints and what services it can help interact
- Understand difference between NAT Gateway and NAT Instance
- Understand how NAT high availability can be achieved
- Understand CloudFront as CDN and the static and dynamic caching it provides, what can be its origin (it can point to on-premises sources)
- Understand Route 53 for routing, health checks and various routing policies it provides and their use cases mainly for high availability
- Be sure to cover ELB in deep. AWS has introduced ALB and NLB and there are lot of questions on ALB
- Understand ALB features with its ability for content based and URL based routing with support for dynamic port mapping with ECS
- Be sure to create VPC from scratch. This is mandatory.
- Storage
- Understand various storage options S3, EBS, Instance store, EFS, Glacier and what are the use cases and anti patterns for each
- Would recommend referring Storage Options whitepaper, although a bit dated 90% still holds right
- Understand various EBS volume types and their use cases in terms of IOPS and throughput. SSD for IOPS and HDD for throughput
- Understand Burst performance and I/O credits to handle occasional peaks
- Understand S3 features like different storage classes with lifecycle policies, static website hosting, versioning, Pre-Signed URLs for both upload and download, CORS
- Understand Glacier as an archival storage with various retrieval patterns
- Glacier Expedited retrieval now allows object retrieval within mins
- Understand Storage gateway and its different types
- Compute
- Understand EC2 as a whole
- Understand Auto Scaling and ELB, how they work together to provide High Available and Scalable solution
- Understand EC2 various purchase types – Reserved, On-demand and Spot and their use cases
- Understand Reserved purchase types with the introduction of Scheduled and Convertible types
- Understand Lambda and serverless architecture, its features and use cases. How do you benefit from Lambda?
- Understand ECS with its ability to deploy containers and micro services architecture
- Know Elastic Beanstalk at a high level, what it provides and its ability to get an application running quickly
- Databases
- Understand relational and NoSQLs data storage options which include RDS, DynamoDB, Aurora and their use cases
- Aurora has been added to the exam and most of time the questions refer to Aurora given its abilities for multiple read replicas and replication of data across AZs
- Understand S3 is not a storage option for database
- Understand RDS features – Read Replicas for scalability, Multi-AZ for High Availability, Automated Backups, underlying volume types
- Understand DynamoDB with its low latency performance, DAX
- Understand DynamoDB provisioned throughput for Read/Writes
- Know ElastiCache use cases, mainly for caching performance
- Analytics
- Security
- Understand IAM as a whole
- Focus on IAM role and its use case especially with EC2 instance
- Understand IAM identity providers and federation and use cases
- Understand MFA and How would implement two factor authentication for your application
- Understand encryption services
- KMS for key management and envelope encryption
- Focus on S3 with SSE, SSE-C, SSE-KMS
- Know SQS now provides SSE support
- Refer Disaster Recovery whitepaper, be sure you know the different recovery types with impact on RTO/RPO.
- Management Tools
- Understand CloudWatch monitoring to provide operational transparency
- Know which EC2 metrics it can track. Remember, it cannot track memory and disk space/swap utilization
- Understand CloudWatch is extendable with custom metrics
- Understand CloudTrail for Audit
- Have a basic understanding of CloudFormation, OpsWorks
- Integration Tools
- Understand SQS as message queuing service and SNS as pub/sub notification service
- Understand SQS features like visibility, long poll vs short poll
- Focus on SQS as a decoupling service
- AWS has released SQS FIFO, make sure you know the differences between standard and FIFO
- Networking
NOTE: I have just marked the topics inline with the AWS Exam Blue Print. So be sure to check the same, as it is updated regularly and go through Whitepapers, FAQs and Re-Invent videos.
AWS Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C01 Exam Resources
- Online Courses
- DolfinEd Udemy AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate Exam Mastery – [Highest rated] AWS course which covers the exam topics in detail, is extensive, scenario based practice questions and visual aids.
- Stephane Maarek – Ultimate AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate 2019 [Highest Rated]
- A Cloud Guru – AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate 2018
- Linux Academy – AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate 2018
- Zeal Vora – AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate 2020 course
- Practice tests
- Braincert AWS Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C01 Practice Exams, which provide extensive scenario based questions
- Udemy AWS Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C01 Practice Exams
- Signed up with AWS for the Free Tier account which provides a lot of the Services to be tried for free with certain limits which are more than enough to get things going. Be sure to decommission services beyond the free limits, preventing any surprises 🙂
- Also, use QwikLabs for introductory courses which are free
- Read the FAQs atleast for the important topics, as they cover important points and are good for quick review
AWS Cloud Computing Whitepapers
- Architecting for the AWS Cloud: Best Practices
- AWS Well-Architected Framework whitepaper (This is theoretical paper, with loads of theory and is tiresome. If you cover the above topics, you can skip this one)
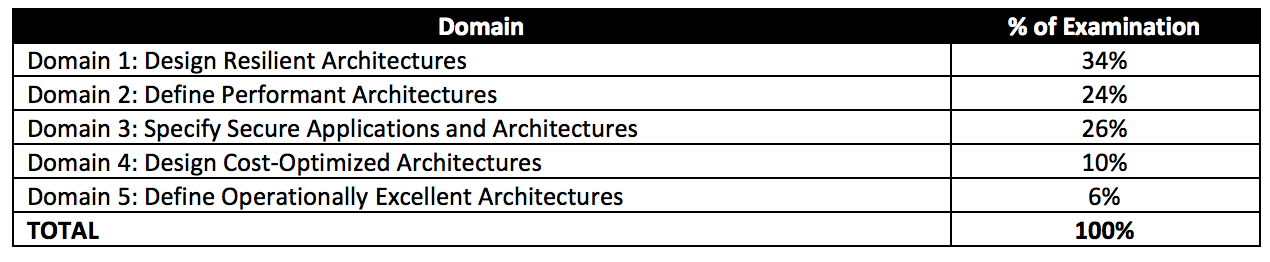
AWS Solutions Architect – Associate Exam Contents
Domain 1: Design Resilient Architectures
- Choose reliable/resilient storage.
- Determine how to design decoupling mechanisms using AWS services.
- Determine how to design a multi-tier architecture solution.
- Determine how to design high availability and/or fault tolerant architectures.
Domain 2: Define Performant Architectures
- Choose performant storage and databases.
- Apply caching to improve performance.
- Design solutions for elasticity and scalability.
Domain 3: Specify Secure Applications and Architectures
- Determine how to secure application tiers.
- Determine how to secure data.
- Define the networking infrastructure for a single VPC application.
Domain 4: Design Cost-Optimized Architectures
- Determine how to design cost-optimized storage.
- Determine how to design cost-optimized compute.
Domain 5: Define Operationally-Excellent Architectures
- Choose design features in solutions that enable operational excellence.