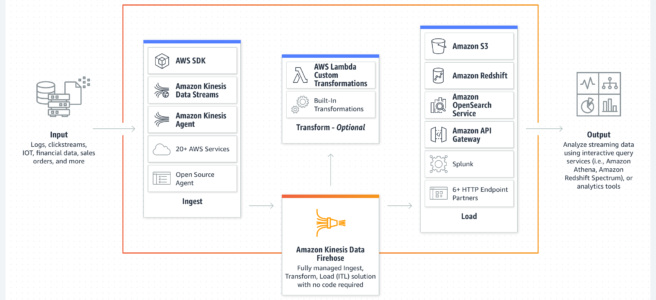
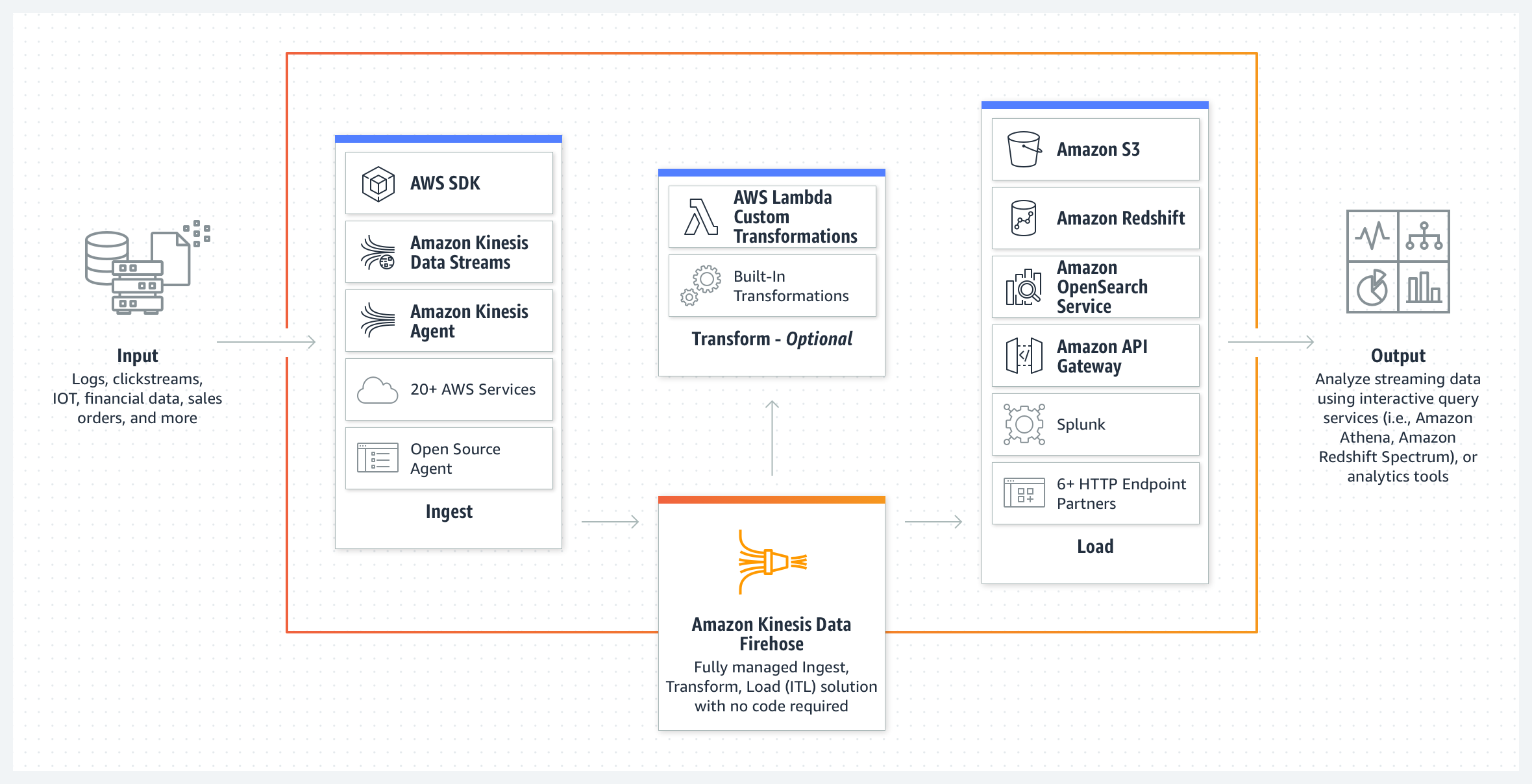
AWS Kinesis Data Firehose – KDF
- Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose is a fully managed service for delivering real-time streaming data
- Kinesis Data Firehose automatically scales to match the throughput of the data and requires no ongoing administration or need to write applications or manage resources
- is a data transfer solution for delivering real-time streaming data to destinations such as S3, Redshift, Elasticsearch service, and Splunk.
- is NOT Real Time, but Near Real Time as it supports batching and buffers streaming data to a certain size (Buffer Size in MBs) or for a certain period of time (Buffer Interval in seconds) before delivering it to destinations.
- supports data compression, minimizing the amount of storage used at the destination. It currently supports GZIP, ZIP, and SNAPPY compression formats. Only GZIP is supported if the data is further loaded to Redshift.
- supports data at rest encryption using KMS after the data is delivered to the S3 bucket.
- supports multiple producers as datasource, which include Kinesis data stream, Kinesis Agent, or the Kinesis Data Firehose API using the AWS SDK, CloudWatch Logs, CloudWatch Events, or AWS IoT
- supports out of box data transformation as well as custom transformation using the Lambda function to transform incoming source data and deliver the transformed data to destinations
- supports source record backup with custom data transformation with Lambda, where Kinesis Data Firehose will deliver the un-transformed incoming data to a separate S3 bucket.
- uses at least once semantics for data delivery. In rare circumstances such as request timeout upon data delivery attempt, delivery retry by Firehose could introduce duplicates if the previous request eventually goes through.
- supports Interface VPC Interface Endpoint (AWS Private Link) to keep traffic between the VPC and Kinesis Data Firehose from leaving the Amazon network.
Kinesis Key Concepts
- Kinesis Data Firehose delivery stream
- Underlying entity of Kinesis Data Firehose, where the data is sent
- Record
- Data sent by data producer to a Kinesis Data Firehose delivery stream
- Maximum size of a record (before Base64-encoding) is 1024 KB.
- Data producer
- Producers send records to Kinesis Data Firehose delivery streams.
- Buffer size and buffer interval
- Kinesis Data Firehose buffers incoming streaming data to a certain size or for a certain time period before delivering it to destinations
- Buffer size and buffer interval can be configured while creating the delivery stream
- Buffer size is in MBs and ranges from 1MB to 128MB for the S3 destination and 1MB to 100MB for the OpenSearch Service destination.
- Buffer interval is in seconds and ranges from 60 secs to 900 secs
- Firehose raises buffer size dynamically to catch up and make sure that all data is delivered to the destination, if data delivery to the destination is falling behind data writing to the delivery stream
- Buffer size is applied before compression.
- Destination
- A destination is the data store where the data will be delivered.
- supports S3, Redshift, Elasticsearch, and Splunk as destinations.
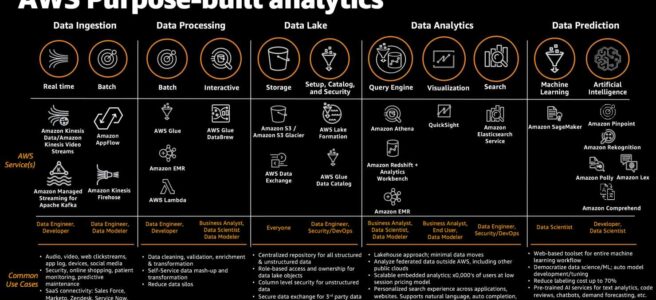
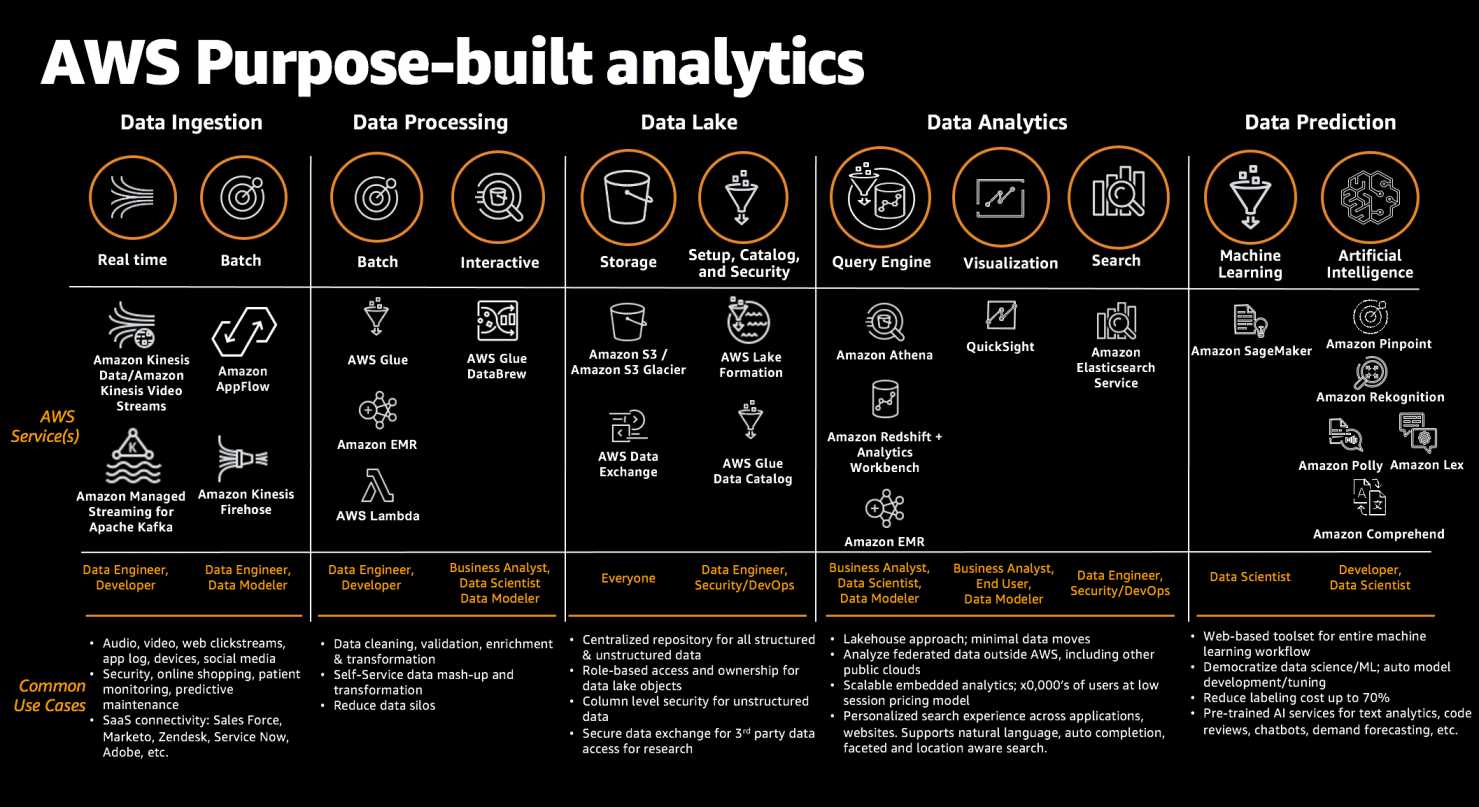
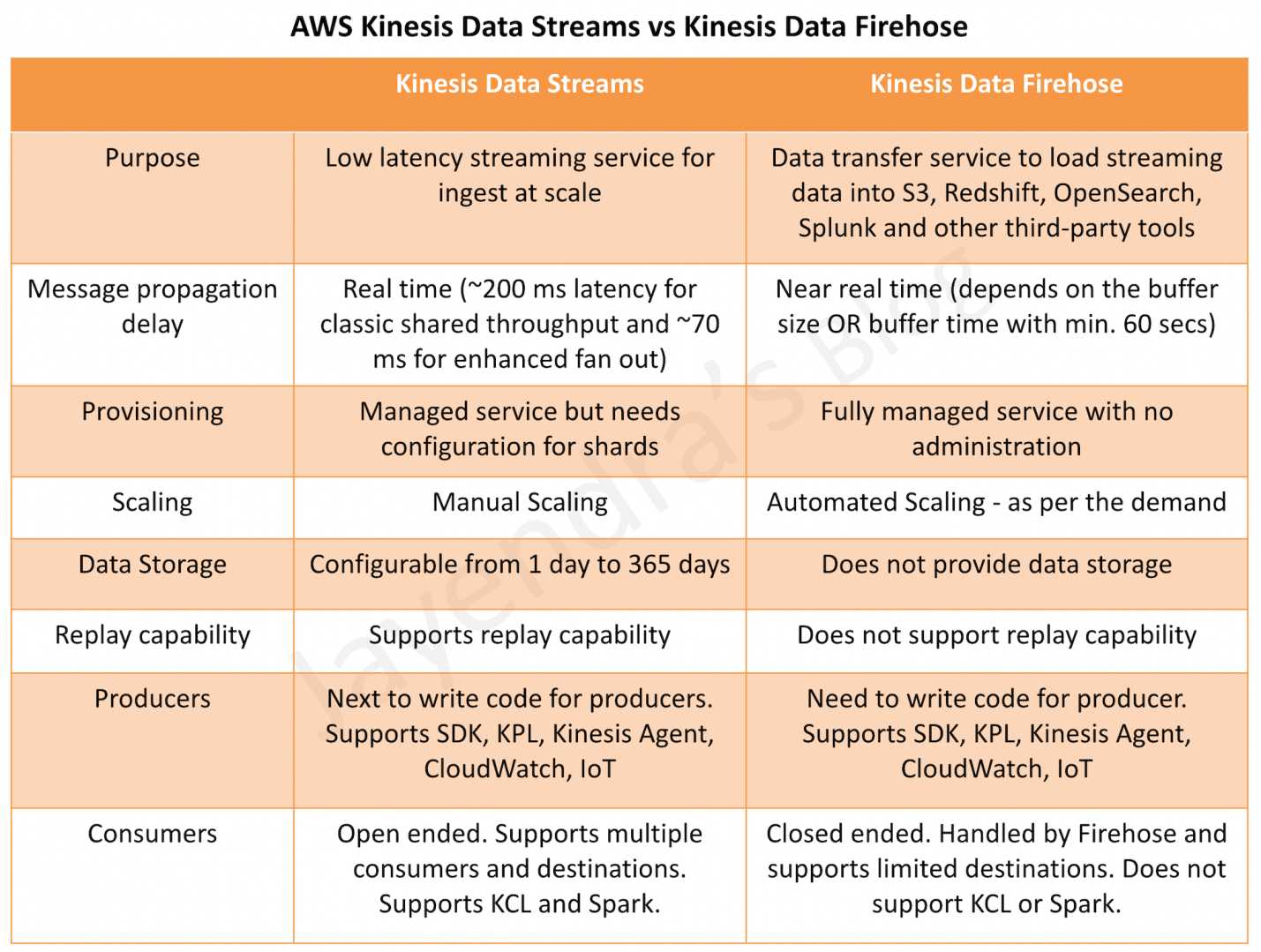
Kinesis Data Firehose vs Kinesis Data Streams
AWS Certification Exam Practice Questions
- A user is designing a new service that receives location updates from 3600 rental cars every hour. The cars location needs to be uploaded to an Amazon S3 bucket. Each location must also be checked for distance from the original rental location. Which services will process the updates and automatically scale?
- Amazon EC2 and Amazon EBS
- Amazon Kinesis Firehose and Amazon S3
- Amazon ECS and Amazon RDS
- Amazon S3 events and AWS Lambda
- You need to perform ad-hoc SQL queries on massive amounts of well-structured data. Additional data comes in constantly at a high velocity, and you don’t want to have to manage the infrastructure processing it if possible. Which solution should you use?
- Kinesis Firehose and RDS
- EMR running Apache Spark
- Kinesis Firehose and Redshift
- EMR using Hive
- Your organization needs to ingest a big data stream into their data lake on Amazon S3. The data may stream in at a rate of hundreds of megabytes per second. What AWS service will accomplish the goal with the least amount of management?
- Amazon Kinesis Firehose
- Amazon Kinesis Streams
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon SQS
- A startup company is building an application to track the high scores for a popular video game. Their Solution Architect is tasked with designing a solution to allow real-time processing of scores from millions of players worldwide. Which AWS service should the Architect use to provide reliable data ingestion from the video game into the datastore?
- AWS Data Pipeline
- Amazon Kinesis Firehose
- Amazon DynamoDB Streams
- Amazon Elasticsearch Service
- A company has an infrastructure that consists of machines which keep sending log information every 5 minutes. The number of these machines can run into thousands and it is required to ensure that the data can be analyzed at a later stage. Which of the following would help in fulfilling this requirement?
- Use Kinesis Firehose with S3 to take the logs and store them in S3 for further processing.
- Launch an Elastic Beanstalk application to take the processing job of the logs.
- Launch an EC2 instance with enough EBS volumes to consume the logs which can be used for further processing.
- Use CloudTrail to store all the logs which can be analyzed at a later stage.