RDS Multi-AZ vs Read Replica
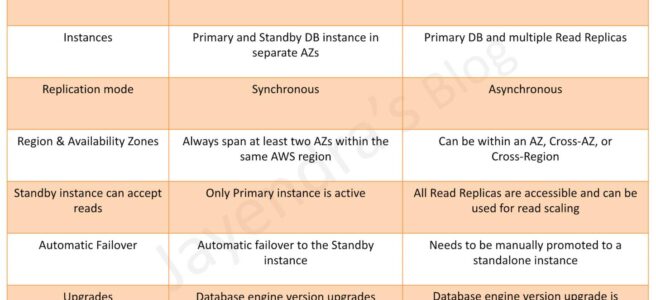
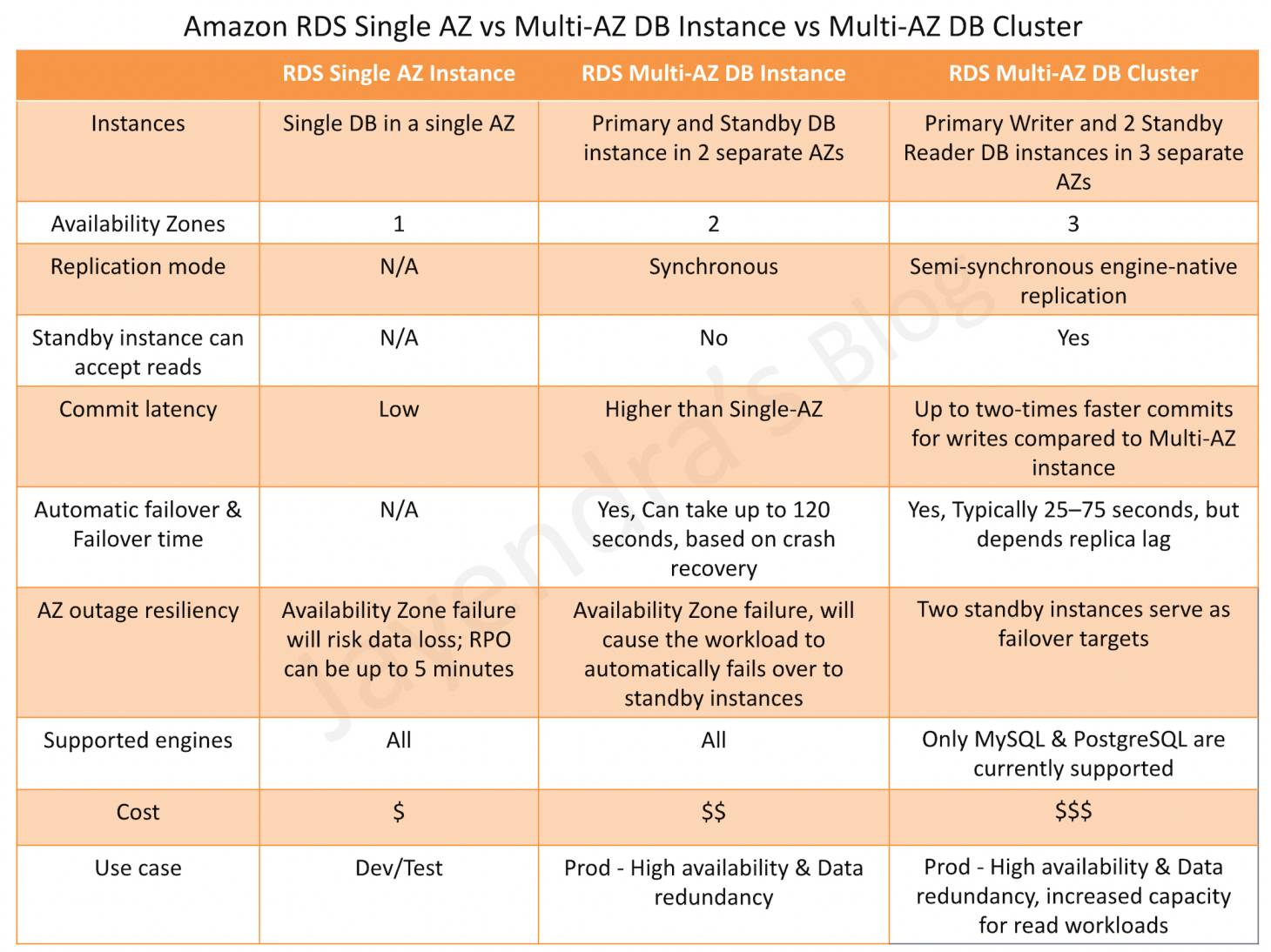
RDS DB instances replicas can be created in two ways Multi-AZ & Read Replica, which provide high availability, durability, and scalability to RDS.
Purpose
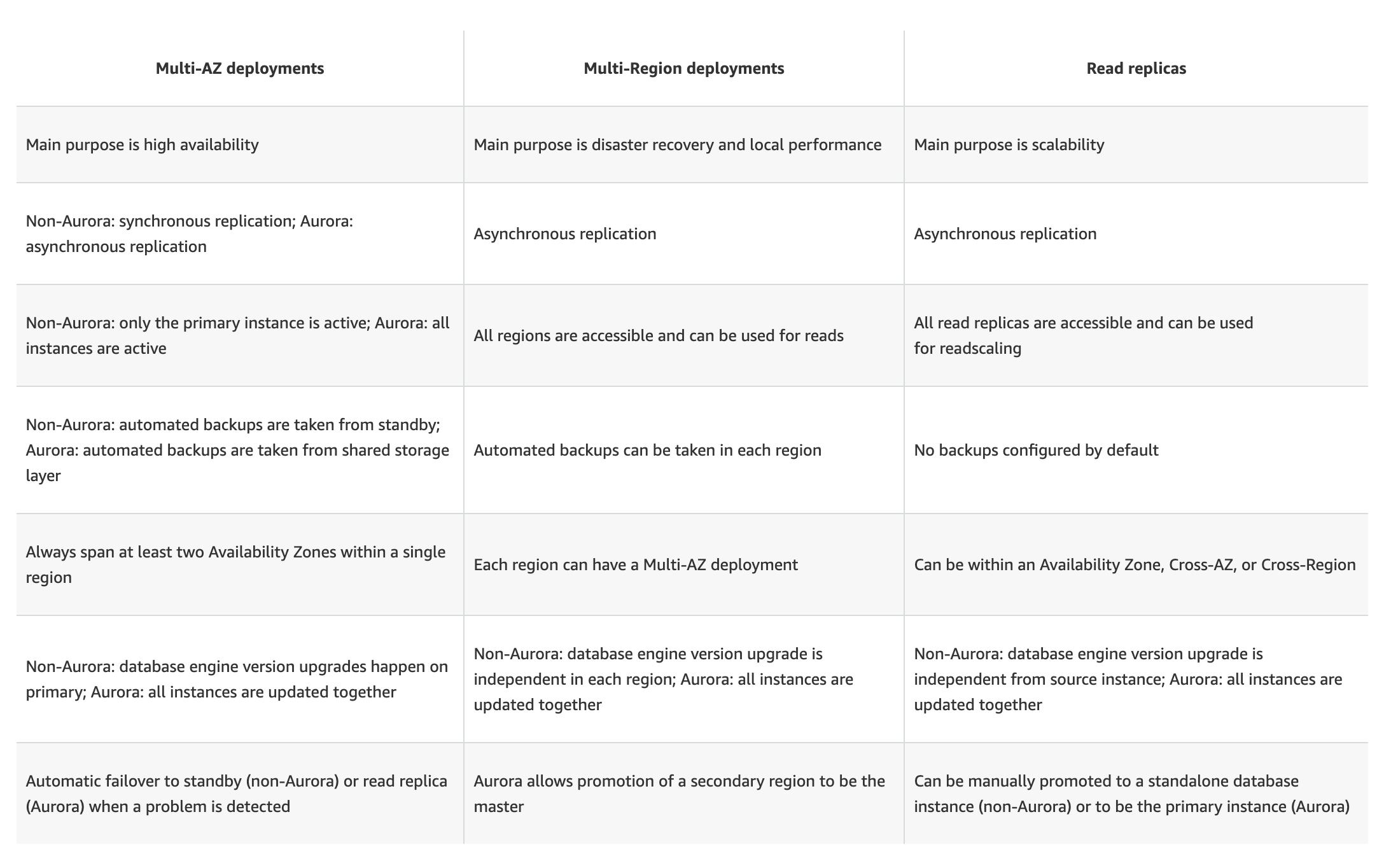
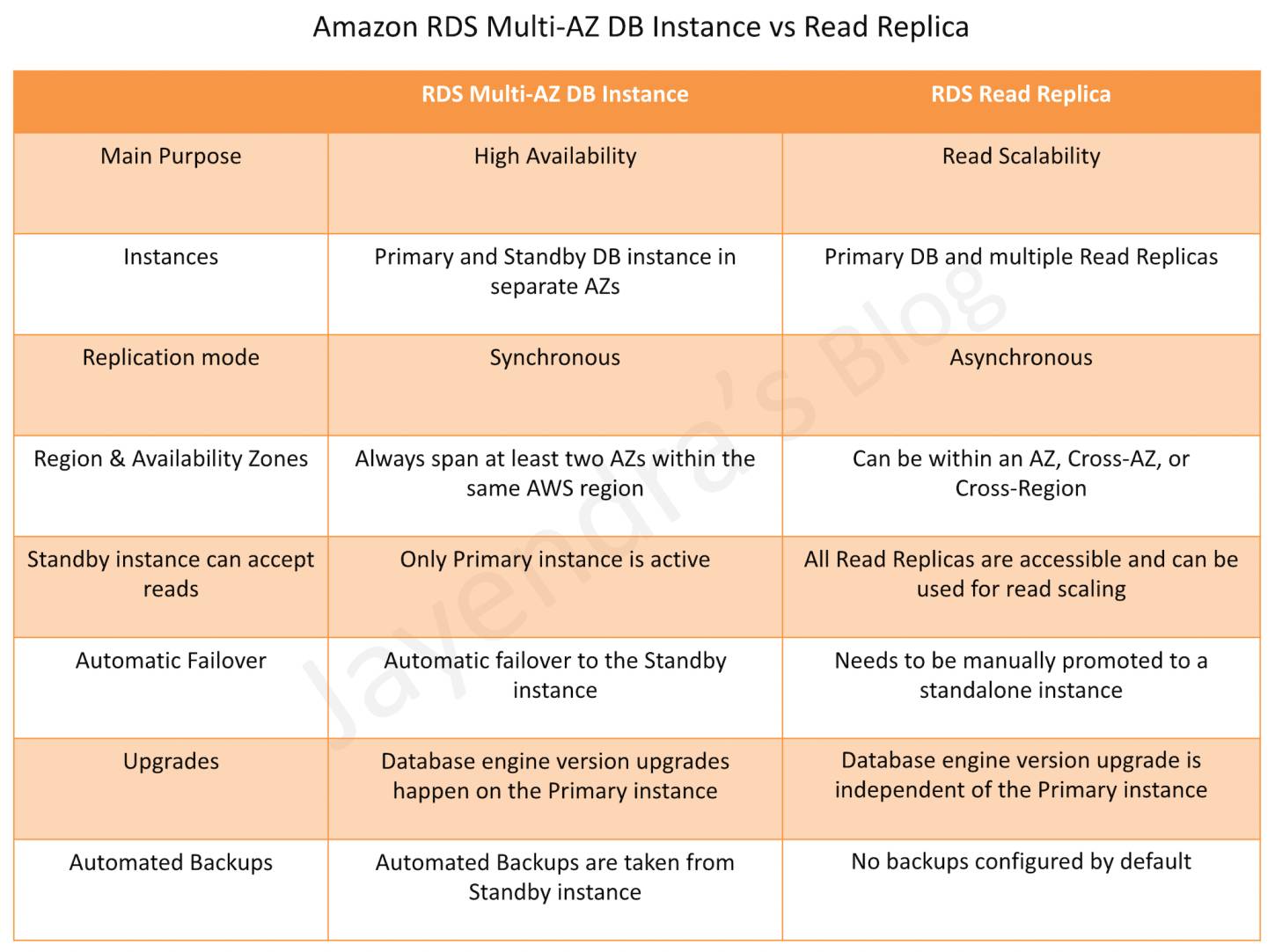
- Multi-AZ DB Instance deployments provide high availability, durability, and automatic failover support.
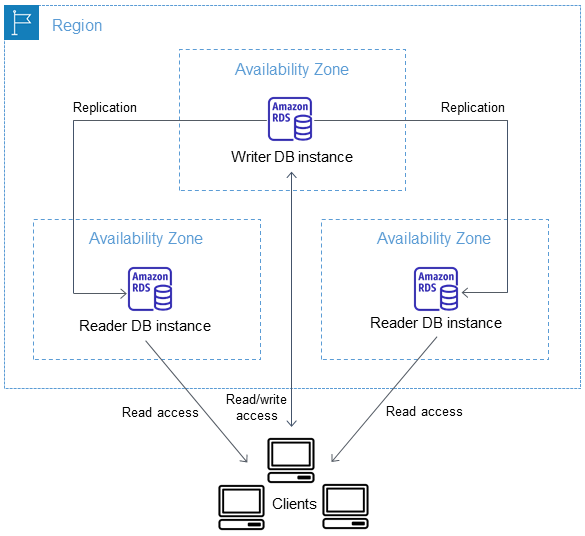
- Read replicas enable increased scalability and database availability in the case of an AZ failure. Read Replicas allow elastic scaling beyond the capacity constraints of a single DB instance for read-heavy database workloads
Region & Availability Zones
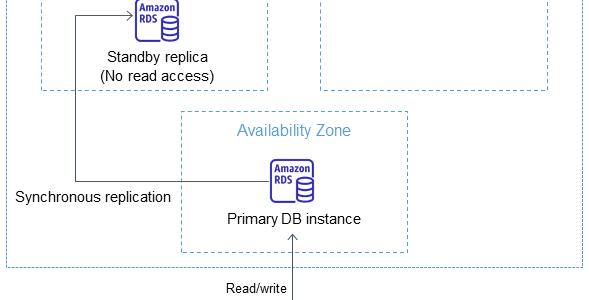
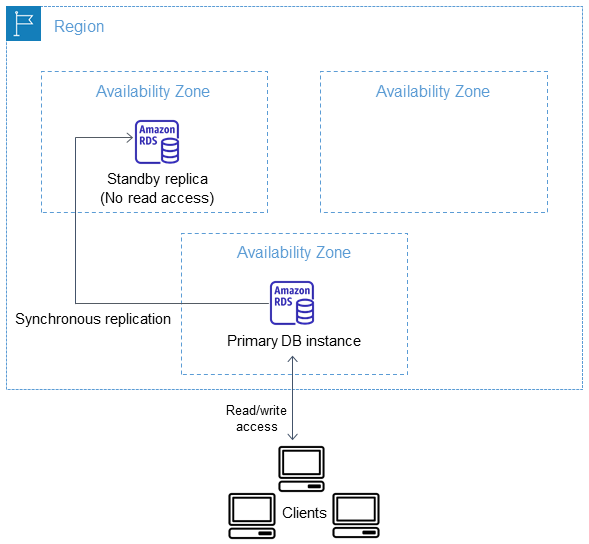
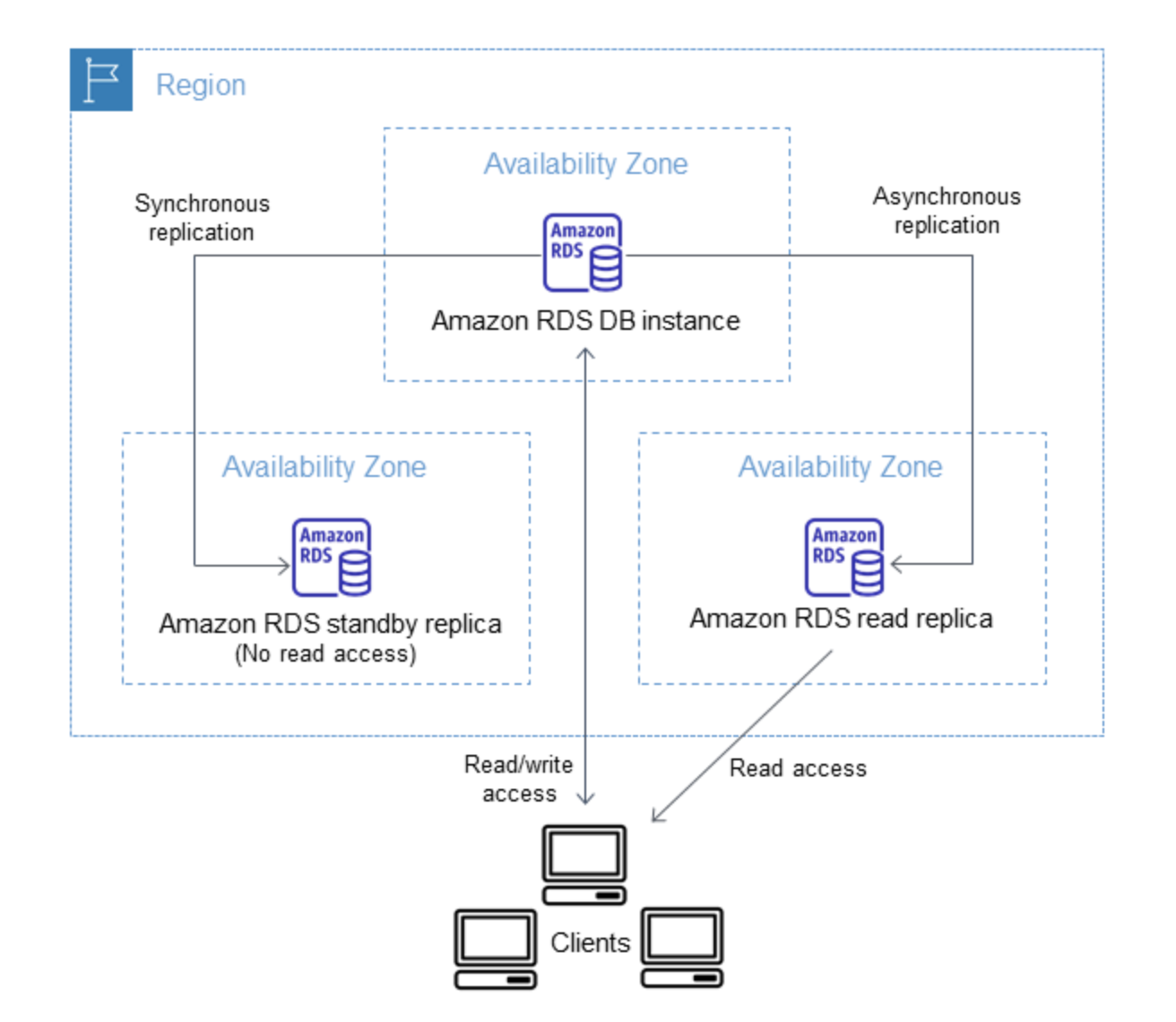
- RDS Multi-AZ deployment automatically provisions and manages a standby instance in a different AZ (independent infrastructure in a physically separate location) within the same AWS region.
- RDS Read Replicas can be provisioned within the same AZ, Cross-AZ or even as a Cross-Region replica.
Replication Mode
- RDS Multi-AZ deployment manages a synchronous standby instance in a different AZ
- RDS Read Replicas has the data replicated asynchronously from the Primary instance to the read replicas
Standby Instance can Accept Reads
- Multi-AZ DB instance deployment is a high-availability solution and the standby instance does not support requests.
- Read Replica deployment provides readable instances to increase application read-throughput.
Automatic Failover & Failover Time
- Multi-AZ DB instance deployment performs an automatic failover to the standby instance without administrative intervention, and the failover time can be up to 120 seconds based on the crash recovery.
- Planned database maintenance
- Software patching
- Rebooting the Primary instance with failover
- Primary DB instance connectivity or host failure, or an
- Availability Zone failure
- RDS maintains the same endpoint for the DB Instance after a failover, so the application can resume database operation without the need for manual administrative intervention.
- Read Replica deployment does not provide automatic failover. Read Replica instance needs to be manually promoted to a Standalone instance.
Upgrades
- For a Multi-AZ deployment, Database engine version upgrades happen on the Primary instance.
- For Read Replicas, the Database engine version upgrade is independent of the Primary instance.
Automated Backups
- Multi-AZ deployment has the Automated Backups taken from the Standby instance
- Read Replicas do not have any backups configured, by default.
AWS Certification Exam Practice Questions
- Questions are collected from Internet and the answers are marked as per my knowledge and understanding (which might differ with yours).
- AWS services are updated everyday and both the answers and questions might be outdated soon, so research accordingly.
- AWS exam questions are not updated to keep up the pace with AWS updates, so even if the underlying feature has changed the question might not be updated
- Open to further feedback, discussion and correction.
- You are running a successful multi-tier web application on AWS and your marketing department has asked you to add a reporting tier to the application. The reporting tier will aggregate and publish status reports every 30 minutes from user-generated information that is being stored in your web applications database. You are currently running a Multi-AZ RDS MySQL instance for the database tier. You also have implemented ElastiCache as a database caching layer between the application tier and database tier. Please select the answer that will allow you to successfully implement the reporting tier with as little impact as possible to your database.
- Continually send transaction logs from your master database to an S3 bucket and generate the reports of the S3 bucket using S3 byte range requests.
- Generate the reports by querying the synchronously replicated standby RDS MySQL instance maintained through Multi-AZ (Standby instance cannot be used as a scaling solution)
- Launch an RDS Read Replica connected to your Multi-AZ master database and generate reports by querying the Read Replica.
- Generate the reports by querying the ElastiCache database caching tier. (ElasticCache does not maintain full data and is simply a caching solution)
- A company is deploying a new two-tier web application in AWS. The company has limited staff and requires high availability, and the application requires complex queries and table joins. Which configuration provides the solution for the company’s requirements?
- MySQL Installed on two Amazon EC2 Instances in a single Availability Zone (does not provide High Availability out of the box)
- Amazon RDS for MySQL with Multi-AZ
- Amazon ElastiCache (Just a caching solution)
- Amazon DynamoDB (Not suitable for complex queries and joins)
- Your company is getting ready to do a major public announcement of a social media site on AWS. The website is running on EC2 instances deployed across multiple Availability Zones with a Multi-AZ RDS MySQL Extra Large DB Instance. The site performs a high number of small reads and writes per second and relies on an eventual consistency model. After comprehensive tests you discover that there is read contention on RDS MySQL. Which are the best approaches to meet these requirements? (Choose 2 answers)
- Deploy ElastiCache in-memory cache running in each availability zone
- Implement sharding to distribute load to multiple RDS MySQL instances (this is only a read contention, the writes work fine)
- Increase the RDS MySQL Instance size and Implement provisioned IOPS (not scalable, this is only a read contention, the writes work fine)
- Add an RDS MySQL read replica in each availability zone
- Your company has HQ in Tokyo and branch offices all over the world and is using logistics software with a multi-regional deployment on AWS in Japan, Europe and US. The logistic software has a 3-tier architecture and currently uses MySQL 5.6 for data persistence. Each region has deployed its own database. In the HQ region you run an hourly batch process reading data from every region to compute cross-regional reports that are sent by email to all offices this batch process must be completed as fast as possible to quickly optimize logistics. How do you build the database architecture in order to meet the requirements?
- For each regional deployment, use RDS MySQL with a master in the region and a read replica in the HQ region
- For each regional deployment, use MySQL on EC2 with a master in the region and send hourly EBS snapshots to the HQ region
- For each regional deployment, use RDS MySQL with a master in the region and send hourly RDS snapshots to the HQ region
- For each regional deployment, use MySQL on EC2 with a master in the region and use S3 to copy data files hourly to the HQ region
- Use Direct Connect to connect all regional MySQL deployments to the HQ region and reduce network latency for the batch process
- What would happen to an RDS (Relational Database Service) Multi-Availability Zone deployment if the primary DB instance fails?
- IP of the primary DB Instance is switched to the standby DB Instance.
- A new DB instance is created in the standby availability zone.
- The canonical name record (CNAME) is changed from primary to standby.
- The RDS (Relational Database Service) DB instance reboots.
- Your business is building a new application that will store its entire customer database on a RDS MySQL database, and will have various applications and users that will query that data for different purposes. Large analytics jobs on the database are likely to cause other applications to not be able to get the query results they need to, before time out. Also, as your data grows, these analytics jobs will start to take more time, increasing the negative effect on the other applications. How do you solve the contention issues between these different workloads on the same data?
- Enable Multi-AZ mode on the RDS instance
- Use ElastiCache to offload the analytics job data
- Create RDS Read-Replicas for the analytics work
- Run the RDS instance on the largest size possible
- Will my standby RDS instance be in the same Availability Zone as my primary?
- Only for Oracle RDS types
- Yes
- Only if configured at launch
- No
Is creating a Read Replica of another Read Replica supported?Only in certain regionsOnly with MySQL based RDSOnly for Oracle RDS typesNo
- A user is planning to set up the Multi-AZ feature of RDS. Which of the below mentioned conditions won’t take advantage of the Multi-AZ feature?
- Availability zone outage
- A manual failover of the DB instance using Reboot with failover option
- Region outage
- When the user changes the DB instance’s server type
- When you run a DB Instance as a Multi-AZ deployment, the “_____” serves database writes and reads
- secondary
- backup
- stand by
- primary
- When running my DB Instance as a Multi-AZ deployment, can I use the standby for read or write operations?
- Yes
- Only with MSSQL based RDS
- Only for Oracle RDS instances
- No
- Read Replicas require a transactional storage engine and are only supported for the _________ storage engine
- OracleISAM
- MSSQLDB
- InnoDB
- MyISAM
- A user is configuring the Multi-AZ feature of an RDS DB. The user came to know that this RDS DB does not use the AWS technology, but uses server mirroring to achieve replication. Which DB is the user using right now?
- MySQL
- Oracle
- MS SQL
- PostgreSQL
- If I have multiple Read Replicas for my master DB Instance and I promote one of them, what happens to the rest of the Read Replicas?
- The remaining Read Replicas will still replicate from the older master DB Instance
- The remaining Read Replicas will be deleted
- The remaining Read Replicas will be combined to one read replica
- If you have chosen Multi-AZ deployment, in the event of a planned or unplanned outage of your primary DB Instance, Amazon RDS automatically switches to the standby replica. The automatic failover mechanism simply changes the ______ record of the main DB Instance to point to the standby DB Instance.
- DNAME
- CNAME
- TXT
- MX
- When automatic failover occurs, Amazon RDS will emit a DB Instance event to inform you that automatic failover occurred. You can use the _____ to return information about events related to your DB Instance
- FetchFailure
- DescriveFailure
- DescribeEvents
- FetchEvents
- The new DB Instance that is created when you promote a Read Replica retains the backup window period.
- TRUE
- FALSE
- Will I be alerted when automatic failover occurs?
- Only if SNS configured
- No
- Yes
- Only if Cloudwatch configured
- Can I initiate a “forced failover” for my MySQL Multi-AZ DB Instance deployment?
- Only in certain regions
- Only in VPC
- Yes
- No
- A user is accessing RDS from an application. The user has enabled the Multi-AZ feature with the MS SQL RDS DB. During a planned outage how will AWS ensure that a switch from DB to a standby replica will not affect access to the application?
- RDS will have an internal IP which will redirect all requests to the new DB
- RDS uses DNS to switch over to standby replica for seamless transition
- The switch over changes Hardware so RDS does not need to worry about access
- RDS will have both the DBs running independently and the user has to manually switch over
- Which of the following is part of the failover process for a Multi-AZ Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) instance?
- The failed RDS DB instance reboots.
- The IP of the primary DB instance is switched to the standby DB instance.
- The DNS record for the RDS endpoint is changed from primary to standby.
- A new DB instance is created in the standby availability zone.
- Which of these is not a reason a Multi-AZ RDS instance will failover?
- An Availability Zone outage
- A manual failover of the DB instance was initiated using Reboot with failover
- To autoscale to a higher instance class (Refer link)
- Master database corruption occurs
- The primary DB instance fails
- You need to scale an RDS deployment. You are operating at 10% writes and 90% reads, based on your logging. How best can you scale this in a simple way?
- Create a second master RDS instance and peer the RDS groups.
- Cache all the database responses on the read side with CloudFront.
- Create read replicas for RDS since the load is mostly reads.
- Create a Multi-AZ RDS installs and route read traffic to standby.
- How does Amazon RDS multi Availability Zone model work?
- A second, standby database is deployed and maintained in a different availability zone from master, using synchronous replication. (Refer link)
- A second, standby database is deployed and maintained in a different availability zone from master using asynchronous replication.
- A second, standby database is deployed and maintained in a different region from master using asynchronous replication.
- A second, standby database is deployed and maintained in a different region from master using synchronous replication.
- A customer is running an application in US-West (Northern California) region and wants to setup disaster recovery failover to the Asian Pacific (Singapore) region. The customer is interested in achieving a low Recovery Point Objective (RPO) for an Amazon RDS multi-AZ MySQL database instance. Which approach is best suited to this need?
- Synchronous replication
- Asynchronous replication
- Route53 health checks
- Copying of RDS incremental snapshots
- A user is using a small MySQL RDS DB. The user is experiencing high latency due to the Multi AZ feature. Which of the below mentioned options may not help the user in this situation?
- Schedule the automated back up in non-working hours
- Use a large or higher size instance
- Use PIOPS
- Take a snapshot from standby Replica
- Are Reserved Instances available for Multi-AZ Deployments?
- Only for Cluster Compute instances
- Yes for all instance types
- Only for M3 instance types
- My Read Replica appears “stuck” after a Multi-AZ failover and is unable to obtain or apply updates from the source DB Instance. What do I do?
- You will need to delete the Read Replica and create a new one to replace it.
- You will need to disassociate the DB Engine and re-associate it.
- The instance should be deployed to Single AZ and then moved to Multi-AZ once again
- You will need to delete the DB Instance and create a new one to replace it.
- What is the charge for the data transfer incurred in replicating data between your primary and standby?
- No charge. It is free.
- Double the standard data transfer charge
- Same as the standard data transfer charge
- Half of the standard data transfer charge
- A user has enabled the Multi-AZ feature with the MS SQL RDS database server. Which of the below mentioned statements will help the user understand the Multi-AZ feature better?
- In a Multi-AZ, AWS runs two DBs in parallel and copies the data asynchronously to the replica copy
- In a Multi-AZ, AWS runs two DBs in parallel and copies the data synchronously to the replica copy
- In a Multi-AZ, AWS runs just one DB but copies the data synchronously to the standby replica
- AWS MS SQL does not support the Multi-AZ feature
- A company is running a batch analysis every hour on their main transactional DB running on an RDS MySQL instance to populate their central Data Warehouse running on Redshift. During the execution of the batch their transactional applications are very slow. When the batch completes they need to update the top management dashboard with the new data. The dashboard is produced by another system running on-premises that is currently started when a manually sent email notifies that an update is required The on-premises system cannot be modified because is managed by another team. How would you optimize this scenario to solve performance issues and automate the process as much as possible?
- Replace RDS with Redshift for the batch analysis and SNS to notify the on-premises system to update the dashboard
- Replace RDS with Redshift for the batch analysis and SQS to send a message to the on-premises system to update the dashboard
- Create an RDS Read Replica for the batch analysis and SNS to notify me on-premises system to update the dashboard
- Create an RDS Read Replica for the batch analysis and SQS to send a message to the on-premises system to update the dashboard.