AWS Gateway Load Balancer – GWLB
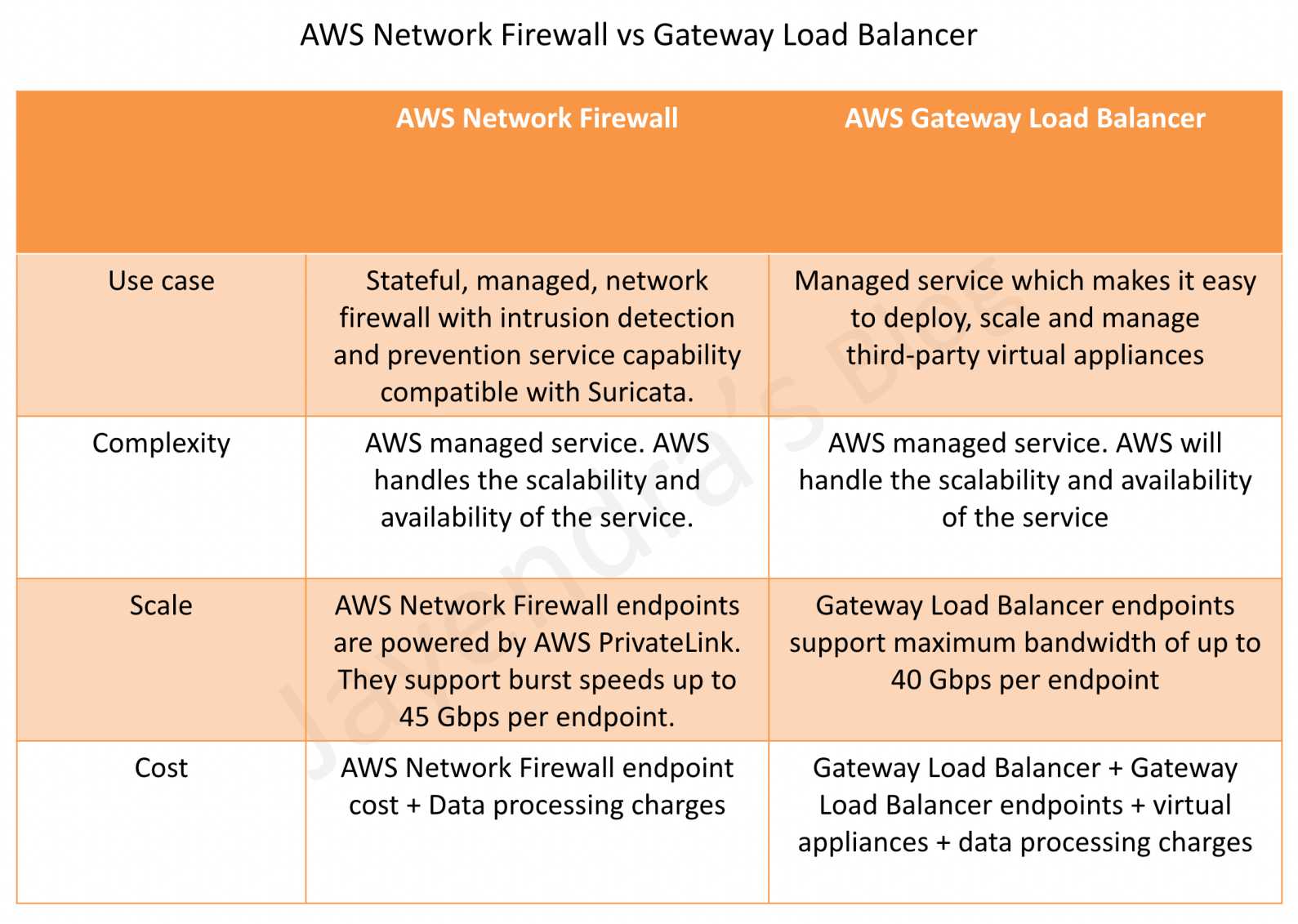
- Gateway Load Balancer helps deploy, scale, and manage virtual appliances, such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and deep packet inspection systems.
- GWLB and its registered virtual appliance instances exchange application traffic using the GENEVE (Generic Network Virtualization Encapsulation) protocol on port 6081.
- operates at Layer 3 of the OSI model, the network layer.
- transparently passes all Layer 3 traffic through third-party virtual appliances, and is invisible to the source and destination of the traffic.
- combines a transparent network gateway (that is, a single entry and exit point for all traffic) and distributes traffic while scaling the virtual appliances with the demand.
- listens for all IP packets across all ports and forwards traffic to the target group that’s specified in the listener rule.
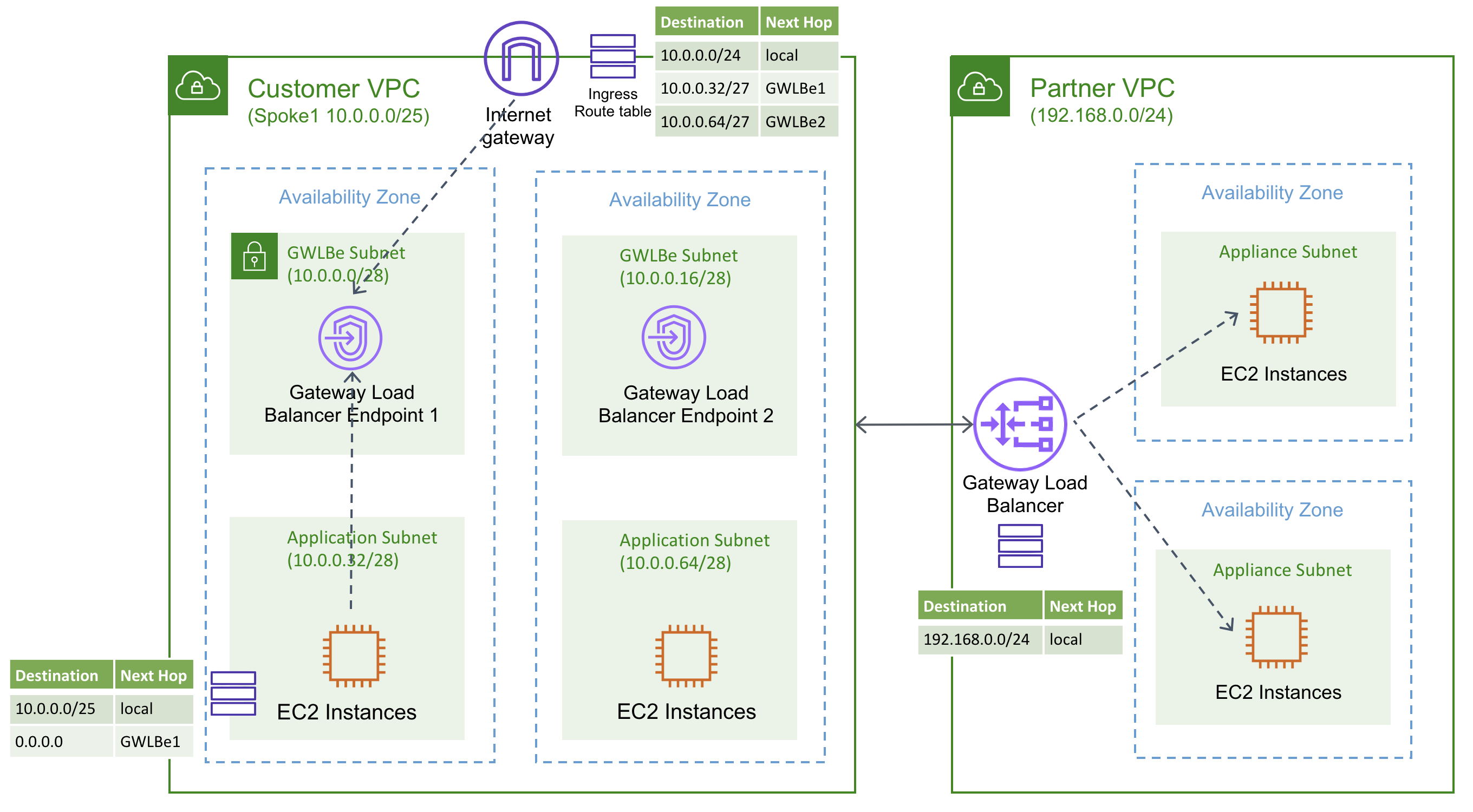
- runs within one AZ and is recommended to be deployed in multiple AZs for greater availability. If all appliances fail in one AZ, scripts can be used to either add new appliances or direct traffic to a GWLB in a different AZ.
- cannot add or remove availability zones after the GWLB is created.
- is architected to handle millions of requests/second, volatile traffic patterns, and introduces extremely low latency.
- does not perform TLS termination and does not maintain any application state. These functions are performed by the third-party virtual appliances it directs traffic to and receives traffic from.
- maintains stickiness of flows to a specific target appliance using 5-tuple (TCP/UDP flows) or 3-tuple (for non-TCP/UDP flows).
- supports a maximum transmission unit (MTU) size of 8500 bytes.
- supports cross-zone load balancing, which is disabled by default. You pay charges for inter-AZ data transfer if enabled.
Gateway Load Balancer Endpoint – GWLBE
- GWLB uses Gateway Load Balancer endpoints – GWLBE to exchange traffic across VPC boundaries securely.
- A Gateway Load Balancer endpoint is a VPC endpoint that provides private connectivity between virtual appliances in the service provider VPC and application servers in the service consumer VPC.
- One GWLB can be connected to many GWLBEs.
- GWLB is deployed in the same VPC as the virtual appliances.
- Virtual appliances are registered with a target group for the GWLB.
- Traffic to and from a GWLBE is configured using route tables.
- Traffic flows from the service consumer VPC over the GWLBE to the GWLB in the service provider VPC, and then returns to the service consumer VPC
- GWLBE and the application servers must be created in different subnets. This enables you to configure the GWLBE as the next hop in the route table for the application subnet.
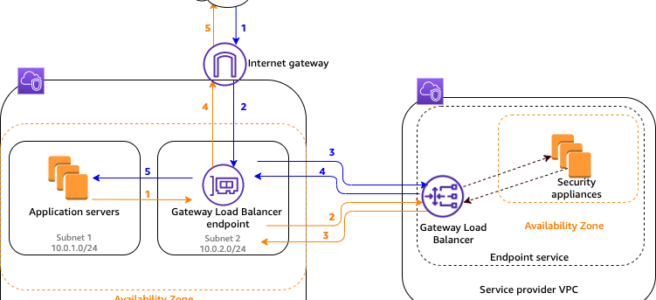
Gateway Load Balancer Flow
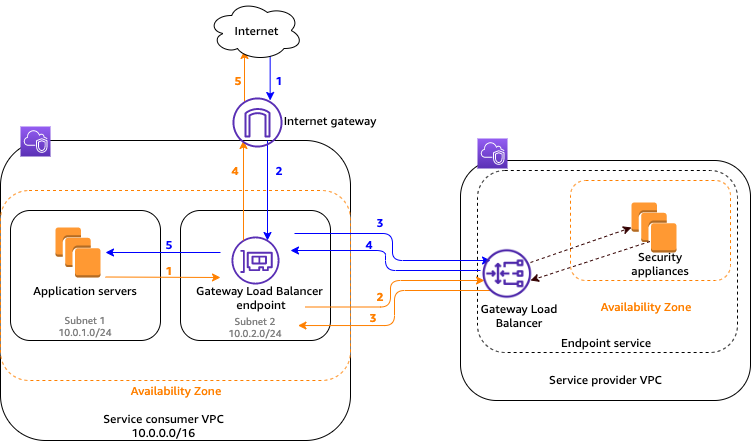
Traffic from the internet to the application (blue arrows)
- Traffic enters the service consumer VPC through the internet gateway.
- Traffic is sent to the GWLBE, as a result of VPC ingress routing.
- Traffic is sent to the GWLB for inspection through the security appliance.
- Traffic is sent back to the GWLBE after inspection.
- Traffic is sent to the application servers (destination subnet).
Traffic from the application to the internet (orange arrows):
- Traffic is sent to the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint due to the default route configured on the application server subnet.
- Traffic is sent to the GWLB for inspection through the security appliance.
- Traffic is sent back to the GWLBE after inspection.
- Traffic is sent to the internet gateway based on the route table configuration.
- Traffic is routed back to the internet.
Gateway Load Balancer High Availability
AWS Certification Exam Practice Questions
- Questions are collected from Internet and the answers are marked as per my knowledge and understanding (which might differ with yours).
- AWS services are updated everyday and both the answers and questions might be outdated soon, so research accordingly.
- AWS exam questions are not updated to keep up the pace with AWS updates, so even if the underlying feature has changed the question might not be updated
- Open to further feedback, discussion and correction.
References
AWS_Gateway_Load_Balancer