Google Cloud App Engine
- App Engine helps build highly scalable applications on a fully managed serverless platform
- App Engine provides PaaS and helps build and deploy apps quickly using popular languages or bring your own language runtimes and frameworks.
- App Engine allows to scale the applications from zero to planet scale without having to manage infrastructure
- Each Cloud project can contain only a single App Engine application
- App Engine is regional, which means the infrastructure that runs the apps is located in a specific region, and Google manages it so that it is available redundantly across all of the zones within that region
- App Engine application location or region cannot be changed once created
- App Engine is well suited to applications that are designed using a microservice architecture
- App Engine creates a default bucket in Cloud Storage for each app creation
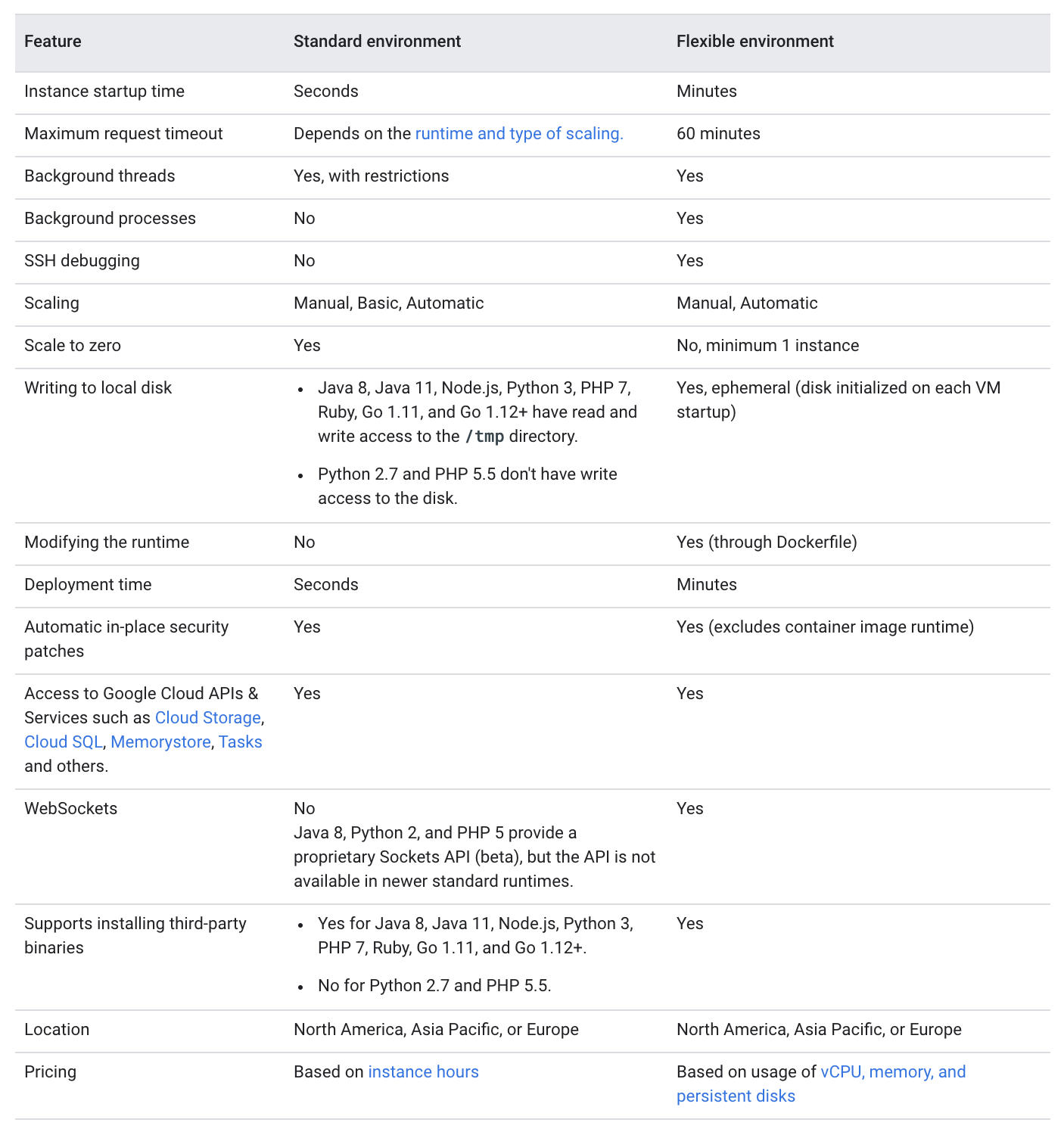
Standard vs Flexible Environment
Refer blog post Standard vs Flexible Environment
App Engine Scaling
- App Engine can automatically create and shut down instances as traffic fluctuates, or a number of instances can be specified to run regardless of the amount of traffic
- App Engine supports the following scaling types, which controls how and when instances are created:
- Basic (Standard Only)
- creates instances when the application receives requests.
- each instance will be shut down when the application becomes idle.
- is ideal for work that is intermittent or driven by user activity.
- Automatic
- creates instances based on request rate, response latencies, and other application metrics.
- thresholds can be specified for each of these metrics, as well as a minimum number instances to keep running at all times.
- Manual
- specifies the number of instances that continuously run regardless of the load level.
- allows tasks such as complex initializations and applications that rely on the state of the memory over time.
Managing Traffic
App engine allows traffic management to an application version by migrating or splitting traffic.
Traffic Migration
- Traffic migration smoothly switches request routing
- Gradually moves traffic from the versions currently receiving traffic to one or more specified versions
- Standard environment allows you to choose to route requests to the target version, either immediately or gradually.
- Flexible environment only allows immediate traffic migration
Traffic Splitting
- Traffic splitting distributes a percentage of traffic to versions of the application.
- Allows canary deployments or conduct A/B testing between the versions and provides control over the pace when rolling out features
- Traffic can be split to move 100% of traffic to a single version or to route percentages of traffic to multiple versions.
- Traffic splitting is applied to URLs that do not explicitly target a version.
- Traffic split is supported by using either an IP address or HTTP cookie.
- Default behaviour for splitting traffic is to do it by IP.
- Setting up IP address traffic split is easier, but a cookie split is more precise
- For traffic splitting, execute
gcloud app deploy --no-promote to make a new version of the application available and then run gcloud app services set-traffic to start sending the new version traffic. Use --splits flag with two versions and weight
GCP Certification Exam Practice Questions
- Questions are collected from Internet and the answers are marked as per my knowledge and understanding (which might differ with yours).
- GCP services are updated everyday and both the answers and questions might be outdated soon, so research accordingly.
- GCP exam questions are not updated to keep up the pace with GCP updates, so even if the underlying feature has changed the question might not be updated
- Open to further feedback, discussion and correction.
- You have a website hosted on App Engine standard environment. You want 1% of your users to see a new test version of the website. You want to minimize complexity. What should you do?
- Deploy the new version in the same application and use the –migrate option.
- Deploy the new version in the same application and use the –splits option to give a weight of 99 to the current version and a weight of 1 to the new version.
- Create a new App Engine application in the same project. Deploy the new version in that application. Use the App Engine library to proxy 1% of the requests to the new version.
- Create a new App Engine application in the same project. Deploy the new version in that application. Configure your network load balancer to send 1% of the traffic to that new application.
- You have created an App engine application in the us-central region. However, you found out the network team has configured all the VPN connections in the asia-east2 region, which are not possible to move. How can you change the location efficiently?
- Change the region in app.yaml and redeploy
- From App Engine console, change the region of the application
- Change the region in application.xml within the application and redeploy
- Create a new project in the asia-east2 region and create app engine in the project