AWS CloudFront vs Global Accelerator
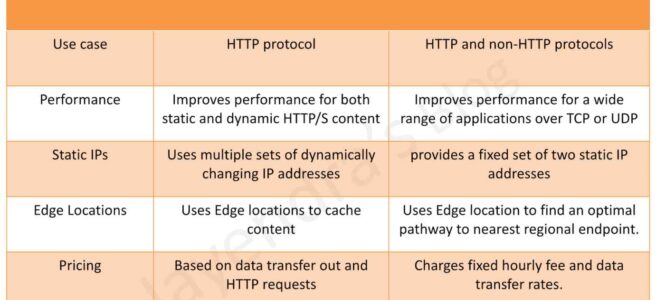
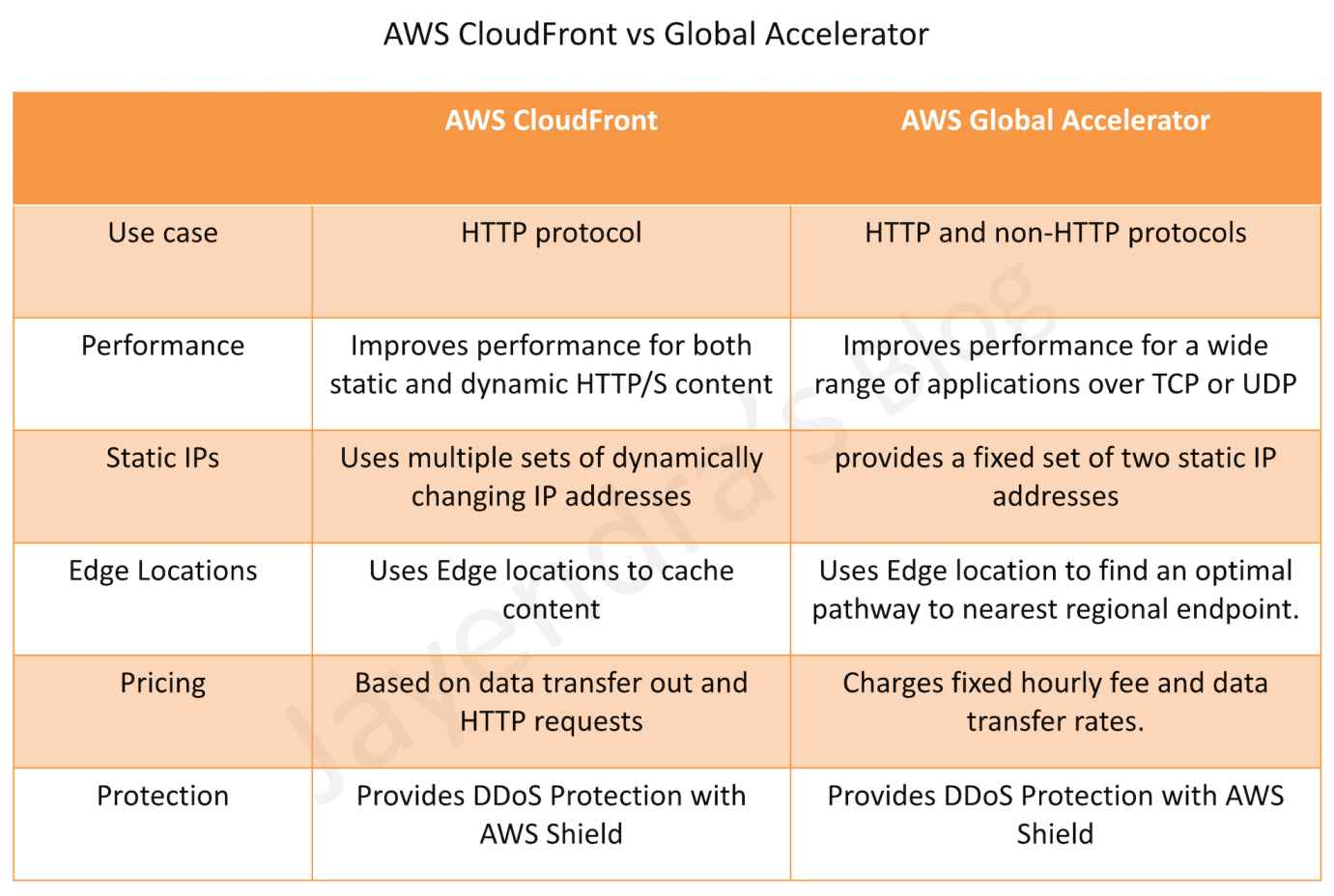
- Global Accelerator and CloudFront both use the AWS global network and its edge locations around the world.
- Both services integrate with AWS Shield for DDoS protection.
- Performance
- CloudFront improves performance for both cacheable content (such as images and videos) and dynamic content (such as API acceleration and dynamic site delivery).
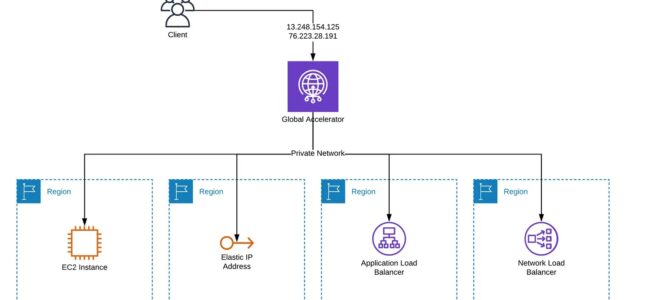
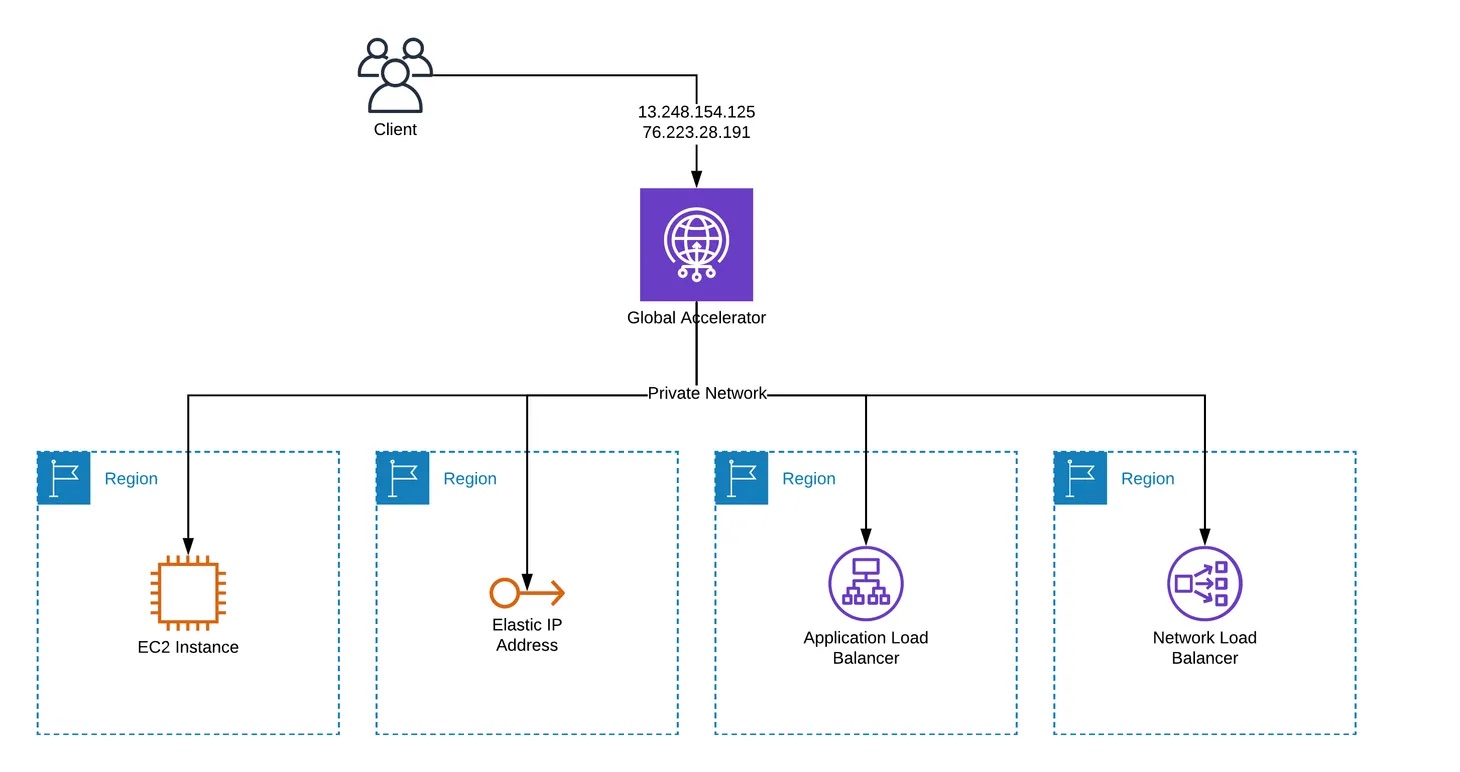
- Global Accelerator improves performance for a wide range of applications over TCP or UDP by proxying packets at the edge to applications running in one or more AWS Regions.
- Use Cases
- CloudFront is a good fit for HTTP use cases
- Global Accelerator is a good fit for non-HTTP use cases, such as gaming (UDP), IoT (MQTT), or VoIP, as well as for HTTP use cases that require static IP addresses or deterministic, fast regional failover.
- Caching
- CloudFront supports Edge caching
- Global Accelerator does not support Edge Caching.
AWS Certification Exam Practice Questions
- Questions are collected from Internet and the answers are marked as per my knowledge and understanding (which might differ with yours).
- AWS services are updated everyday and both the answers and questions might be outdated soon, so research accordingly.
- AWS exam questions are not updated to keep up the pace with AWS updates, so even if the underlying feature has changed the question might not be updated
- Open to further feedback, discussion and correction.
- A company wants to improve the availability and performance of its stateless UDP-based workload. The workload is deployed on Amazon EC2 instances in multiple AWS Regions. What should a solutions architect recommend to accomplish this?
- Place the EC2 instances behind Network Load Balancers (NLBs) in each Region. Create an accelerator using AWS Global Accelerator. Use the NLBs as endpoints for the accelerator.
- Place the EC2 instances behind Application Load Balancers (ALBs) in each Region. Create an accelerator using AWS Global Accelerator. Use the ALBs as endpoints for the accelerator.
- Place the EC2 instances behind Network Load Balancers (NLBs) in each Region. Create a CloudFront distribution with an origin that uses Route 53 latency-based routing to route requests to the NLBs.
- Place the EC2 instances behind Application Load Balancers (ALBs) in each Region. Create a CloudFront distribution with an origin that uses Route 53 latency-based routing to route requests to the ALBs.
References
AWS_Global_Accelerator_FAQs