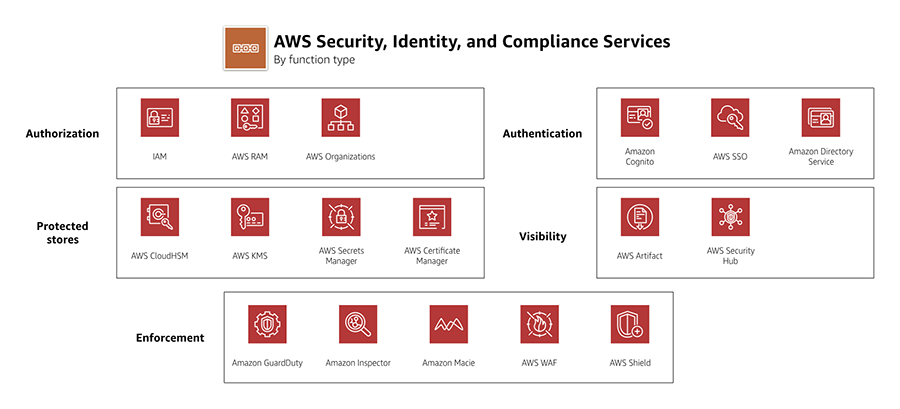
AWS Organizations Service Control Policies
-
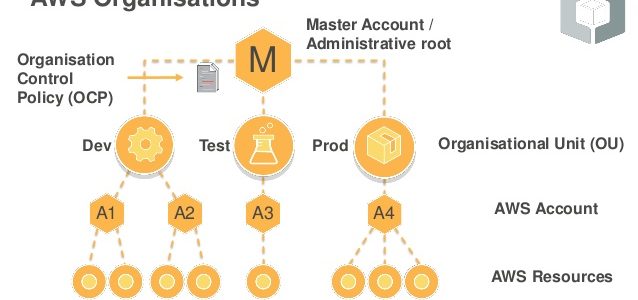
AWS Organizations Service control policies – SCPs offer central control over the maximum available permissions for all of the accounts in the organization, ensuring member accounts stay within the organization’s access control guidelines.
- are one type of policy that help manage the organization.
- are available only in an organization that has all features enabled, and aren’t available if the organization has enabled only the consolidated billing features.
- are NOT sufficient for granting access to the accounts in the organization.
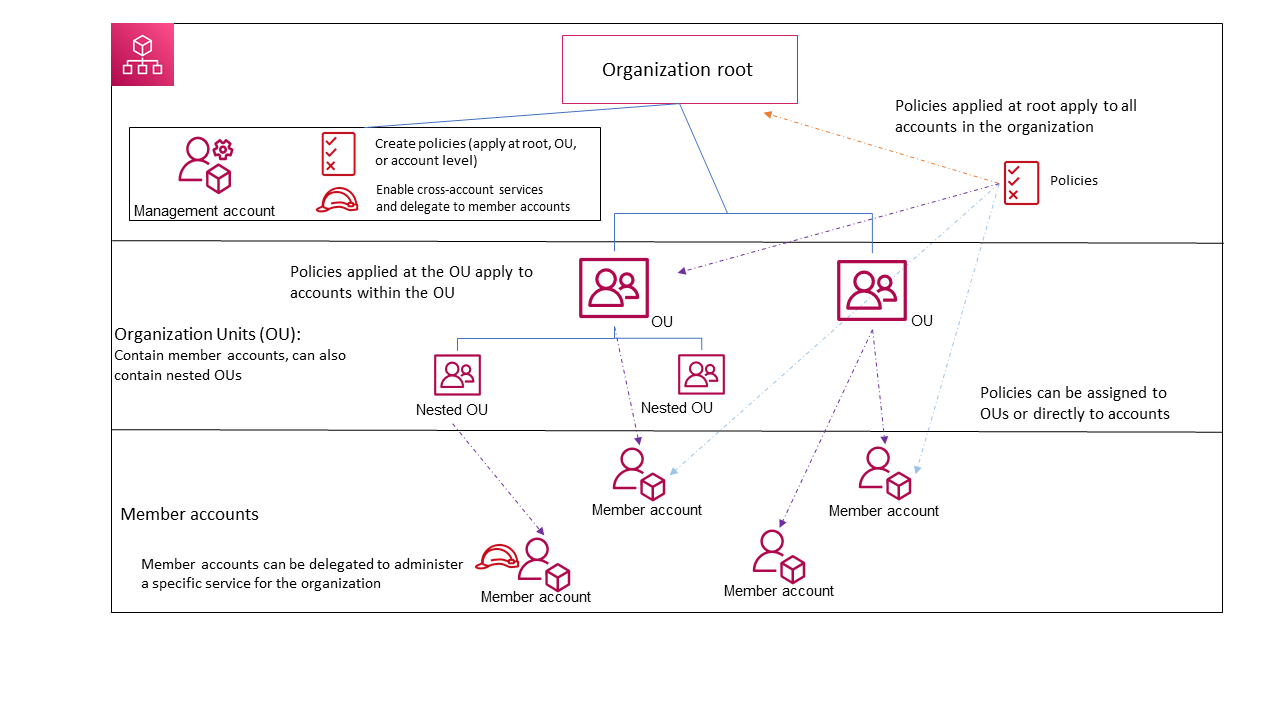
- defines a guardrail for what actions accounts within the organization root or OU can do, but IAM policies need to be attached to the users and roles in the organization’s accounts to grant permissions to them.
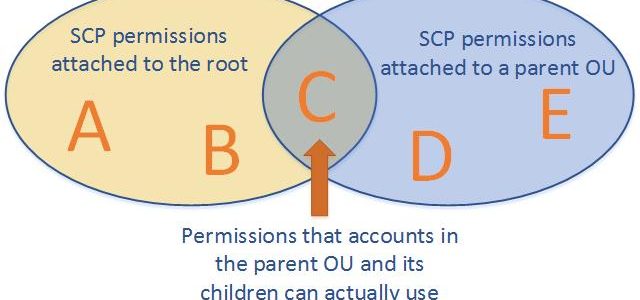
- Effective permissions are the logical intersection between what is allowed by the SCP and what is allowed by the IAM and resource-based policies.
- with an SCP attached to member accounts, identity-based and resource-based policies grant permissions to entities only if those policies and the SCP allow the action.
- don’t affect users or roles in the management account. They affect only the member accounts in your organization.
SCPs Effects on Permissions
- never grant permissions but define the maximum permissions for the affected accounts.
- Users and roles must still be granted permissions with appropriate IAM permission policies. A user without any IAM permission policies has no access at all, even if the applicable SCPs allow all services and all actions.
- limits permissions for entities in member accounts, including each AWS account root user.
- does not limit actions performed by the master or management account.
- does not affect any service-linked role. Service-linked roles enable other AWS services to integrate with AWS Organizations and can’t be restricted by SCPs.
- affect only IAM users or roles that are managed by accounts that are part of the organization. They don’t affect users or roles from accounts outside the organization.
- don’t affect resource-based policies directly.
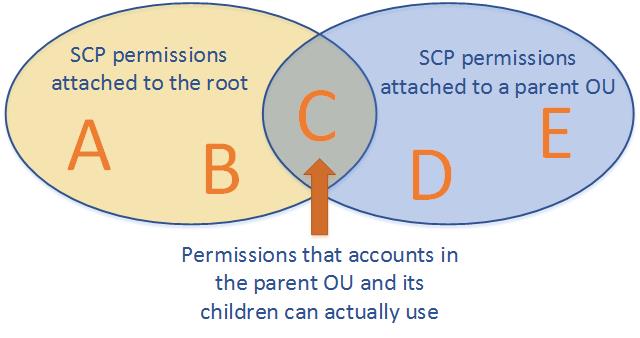
SCPs Strategies
- By default, an SCP named
FullAWSAccessis attached to every root, OU, and account, which allows all actions and all services. - Blacklist or Deny Strategy
- actions are allowed by default and services and actions to be prohibited need to be specified.
- blacklist permissions using deny statements can be assigned in combination with the default
FullAWSAccessSCP. - using deny statements in SCPs require less maintenance because they don’t need to be updated when AWS adds new services.
- deny statements usually use less space, thus making it easier to stay within SCP size limits.
- Whitelist or Allow Strategy
- actions are prohibited by default, and you specify what services and actions are allowed.
- whitelist permissions can be assigned, by removing the default
FullAWSAccessSCP. - allows SCP that explicitly permits only those allowed services and actions
SCPs Testing Effects
- don’t attach SCPs to the root of the organization without thoroughly testing the impact that the policy has on accounts.
- Create an OU that the accounts can be moved into one at a time, or at least in small numbers, to ensure that users are not inadvertently locked out of key services.
AWS Certification Exam Practice Questions
- Questions are collected from Internet and the answers are marked as per my knowledge and understanding (which might differ with yours).
- AWS services are updated everyday and both the answers and questions might be outdated soon, so research accordingly.
- AWS exam questions are not updated to keep up the pace with AWS updates, so even if the underlying feature has changed the question might not be updated
- Open to further feedback, discussion and correction.
- Your company is planning on setting up multiple accounts in AWS. The IT Security department has a requirement to ensure that certain services and actions are not allowed across all accounts. How would the system admin achieve this in the most EFFECTIVE way possible?
- Create a common IAM policy that can be applied across all accounts
- Create an IAM policy per account and apply them accordingly
- Deny the services to be used across accounts by contacting AWS support
- Use AWS Organizations and Service Control Policies
- You are in the process of implementing AWS Organizations for your company. At your previous company, you saw an Organizations implementation go bad when an SCP (Service Control Policy) was applied at the root of the organization before being thoroughly tested. In what way can an SCP be properly tested and implemented?
- Back up your entire Organization to S3 and restore rollback and restore if something goes wrong
- The SCP must be verified with AWS before it is implemented to avoid any problems.
- Mirror your Organizational Unit in another region. Apply the SCP and test it. Once testing is complete, attach the SCP to the root of your organization.
- Create an Organizational Unit (OU). Attach the SCP to this new OU. Move your accounts in one at a time to ensure that you don’t inadvertently lock users out of key services.