Amazon EventBridge
- Amazon EventBridge is a serverless event bus service that makes it easy to connect applications with data from a variety of sources.
- enables building loosely coupled and distributed event-driven architectures.
- provides a simple and consistent way to ingest, filter, transform, and deliver events so you can build new applications quickly.
- delivers a stream of real-time data from applications, SaaS applications, and AWS services, and routes that data to targets such as AWS Lambda.
- supports routing rules to determine where to send the data to build application architectures that react in real-time to all of the data sources.
- supports event buses for many-to-many routing of events between event-driven services.
- provides Pipes for point-to-point integrations between these sources and targets, with support for advanced transformations and enrichment.
- provides schemas, which define the structure of events, for all events that are generated by AWS services.
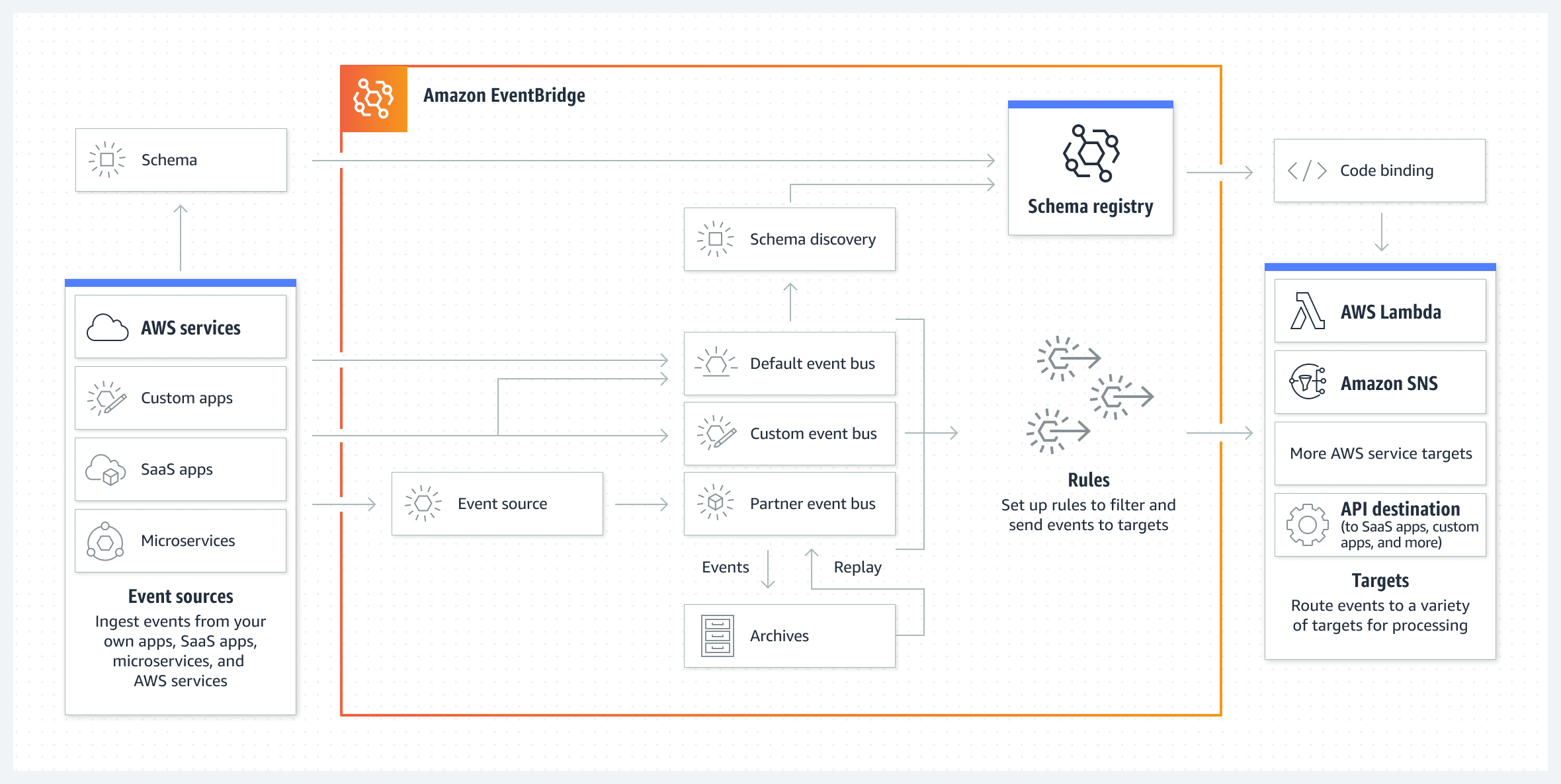
EventBridge Components
- EventBridge receives an event on an event bus and applies a rule to route the event to a target.
- Event sources
- An event source is used to ingest events from AWS Services, applications, or SaaS partners.
- Events
- An event is a real-time indicator of a change in the environment such as an AWS environment, a SaaS partner service or application, or one of your applications or services.
- All events are associated with an event bus.
- Events are represented as JSON objects and they all have a similar structure and the same top-level fields.
- Contents of the detail top-level field are different depending on which service generated the event and what the event is.
- An event pattern defines the event structure and the fields that a rule matches.
- Event buses
- Event bus is a pipeline that receives events.
- Each account has a default event bus that receives events from AWS services. Custom event buses can be created to send or receive events from a different account or Region.
- Rules
- Rules associated with the event bus evaluate events as they arrive.
- Rules match incoming events to targets based either on the structure of the event, called an event pattern, or on a schedule.
- Each rule checks whether an event matches the rule’s criteria.
- A single rule can send an event to multiple targets, which then run in parallel.
- Rules that are based on a schedule perform an action at regular intervals.
- Targets
- A target is a resource or endpoint that EventBridge sends an event to when the event matches the event pattern defined for a rule.
- The rule processes the event data and sends the relevant information to the target.
- EventBridge needs permission to access the target resource to be able to deliver event data to the target.
- Up to five targets can be defined for each rule.
- EventBridge allows events to be archived and replayed later.
AWS Certification Exam Practice Questions
- Questions are collected from Internet and the answers are marked as per my knowledge and understanding (which might differ with yours).
- AWS services are updated everyday and both the answers and questions might be outdated soon, so research accordingly.
- AWS exam questions are not updated to keep up the pace with AWS updates, so even if the underlying feature has changed the question might not be updated
- Open to further feedback, discussion and correction.
- A company wants to be alerted through email when IAM CreateUser API calls are made within its AWS account. Which combination of actions should a SysOps administrator take to meet this requirement? (Choose two.)
- Create an Amazon EventBridge (Amazon CloudWatch Events) rule with AWS CloudTrail as the event source and IAM CreateUser as the specific API call for the event pattern.
- Create an Amazon EventBridge (Amazon CloudWatch Events) rule with Amazon CloudSearch as the event source and IAM CreateUser as the specific API call for the event pattern.
- Create an Amazon EventBridge (Amazon CloudWatch Events) rule with AWS IAM Access Analyzer as the event source and IAM CreateUser as the specific API call for the event pattern.
- Use an Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) topic as an event target with an email subscription.
- Use an Amazon Simple Email Service (Amazon SES) notification as an event target with an email subscription.