EC2 Placement Groups
- EC2 Placement groups determine how the instances are placed on the underlying hardware.
- AWS now provides three types of placement groups
- Cluster – clusters instances into a low-latency group in a single AZ
- Partition – spreads instances across logical partitions, ensuring that instances in one partition do not share underlying hardware with instances in other partitions
- Spread – strictly places a small group of instances across distinct underlying hardware to reduce correlated failures
Cluster Placement Groups
- is a logical grouping of instances within a single Availability Zone
- don’t span across Availability Zones
- can span peered VPCs in the same Region
- impacts High Availability as susceptible to hardware failures for the application
- recommended for
- applications that benefit from low network latency, high network throughput, or both.
- when the majority of the network traffic is between the instances in the group.
- To provide the lowest latency, and the highest packet-per-second network performance for the placement group, choose an instance type that supports enhanced networking
- recommended to launch all group instances with the same instance type at the same time to ensure enough capacity
- instances can be added later, but there are chances of encountering an insufficient capacity error
- for moving an instance into the placement group,
- create an AMI from the existing instance,
- and then launch a new instance from the AMI into a placement group.
- an instance still runs in the same placement group if stopped and started within the placement group.
- in case of a capacity error, stop and start all of the instances in the placement group, and try the launch again. Restarting the instances may migrate them to hardware that has capacity for all requested instances
- is only available within a single AZ either in the same VPC or peered VPCs
- is more of a hint to AWS that the instances need to be launched physically close to each together
- enables applications to participate in a low-latency, 10 Gbps network.
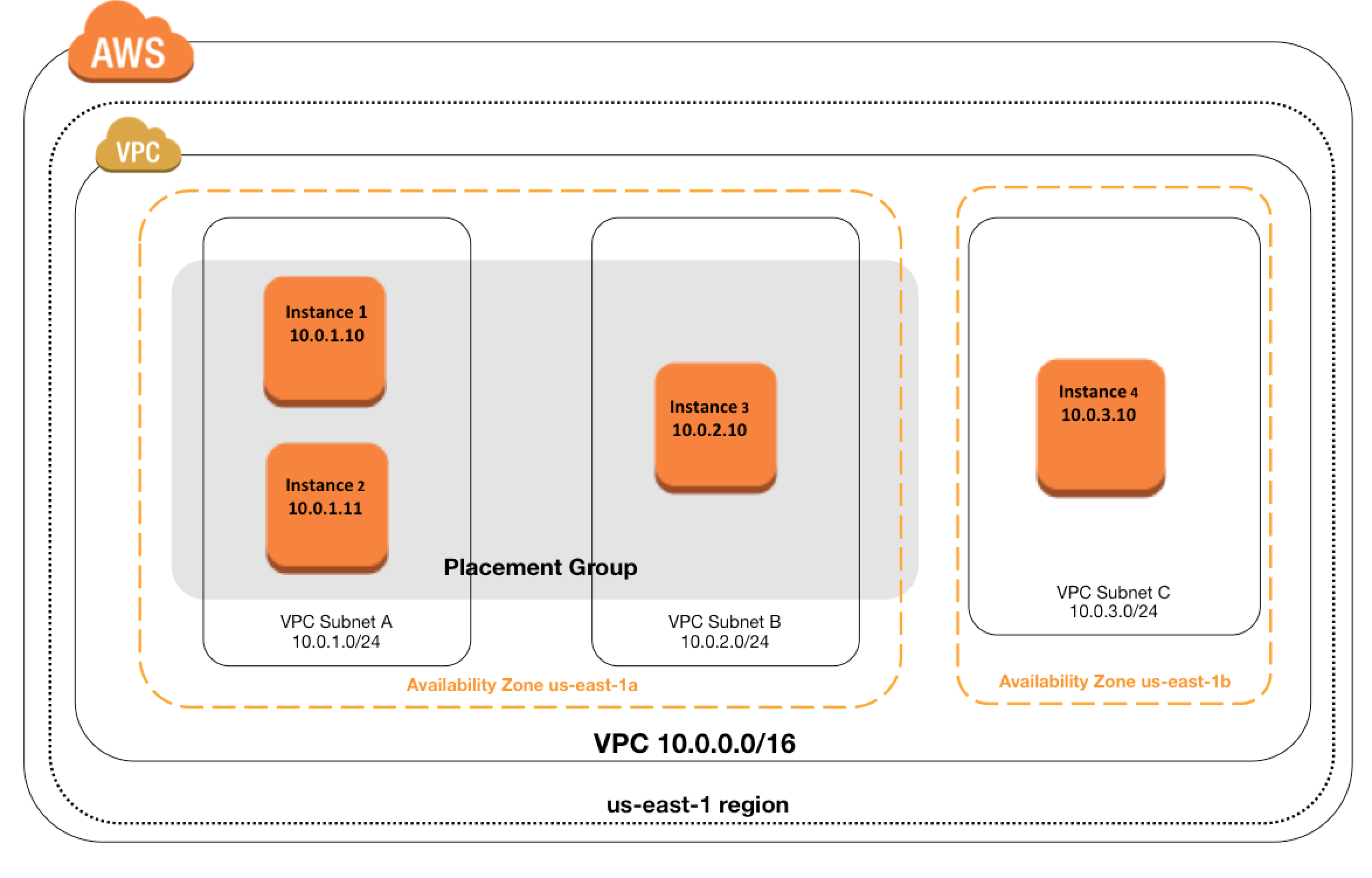
Partition Placement Groups
- is a group of instances spread across partitions i.e. group of instances spread across racks.
- Partitions are logical groupings of instances, where contained instances do not share the same underlying hardware across different partitions.
- EC2 divides each group into logical segments called partitions.
- EC2 ensures that each partition within a placement group has its own set of racks. Each rack has its own network and power source.
- No two partitions within a placement group share the same racks, allowing isolating the impact of a hardware failure within the application.
- reduces the likelihood of correlated hardware failures for the application.
- can have partitions in multiple Availability Zones in the same region
- can have a maximum of seven partitions per Availability Zone
- number of instances that can be launched into a partition placement group is limited only by the limits of the account.
- can be used to spread deployment of large distributed and replicated workloads, such as HDFS, HBase, and Cassandra, across distinct hardware.
- offer visibility into the partitions and the instances to partitions mapping can be seen. This information can be shared with topology-aware applications, such as HDFS, HBase, and Cassandra. These applications use this information to make intelligent data replication decisions for increasing data availability and durability.
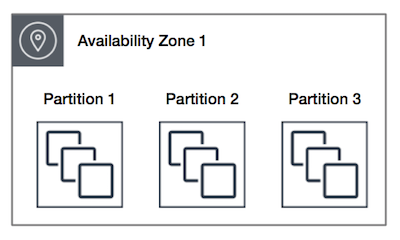
Spread Placement Groups
- is a group of instances that are each placed on distinct underlying hardware i.e. each instance on a distinct rack with each rack having its own network and power source.
- recommended for applications that have a small number of critical instances that should be kept separate from each other.
- reduces the risk of simultaneous failures that might occur when instances share the same underlying hardware.
- provide access to distinct hardware, and are therefore suitable for mixing instance types or launching instances over time.
- can span multiple Availability Zones in the same region.
- can have a maximum of seven running instances per AZ per group
- maximum number of instances = 1 instance per rack * 7 racks * No. of AZs for e.g. in a Region with three AZs, a total of 21 instances in the group (seven per zone) can be launched
- If the start or launch of an instance in a spread placement group fails cause of insufficient unique hardware to fulfil the request, the request can be tried later as EC2 makes more distinct hardware available over time
Placement Group Rules and Limitations
- Ensure unique Placement group name within AWS account for the region.
- Placement groups cannot be merged.
- Instances cannot span multiple placement groups.
- Instances with Dedicated Hosts cannot be launched in placement groups.
- Instances with a tenancy of host cannot be launched in placement groups.
- Cluster Placement groups
- can’t span multiple Availability Zones.
- supported by specific instance types which support 10 Gigabyte network
- maximum network throughput speed of traffic between two instances in a cluster placement group is limited by the slower of the two instances, so choose the instance type properly.
- can use up to 10 Gbps for single-flow traffic.
- Traffic to and from S3 buckets within the same region over the public IP address space or through a VPC endpoint can use all available instance aggregate bandwidth.
- recommended using the same instance type i.e. homogenous instance types. Although multiple instance types can be launched into a cluster placement group. However, this reduces the likelihood that the required capacity will be available for your launch to succeed.
- Network traffic to the internet and over an AWS Direct Connect connection to on-premises resources is limited to 5 Gbps.
- Partition placement groups
- supports a maximum of seven partitions per Availability Zone
- Dedicated Instances can have a maximum of two partitions
- are not supported for Dedicated Hosts
are currently only available through the API or AWS CLI.
- Spread placement groups
- supports a maximum of seven running instances per Availability Zone for e.g., in a region that has three AZs, then a total of 21 running instances in the group (seven per zone).
- are not supported for Dedicated Instances or Dedicated Hosts.
AWS Certification Exam Practice Questions
- Questions are collected from Internet and the answers are marked as per my knowledge and understanding (which might differ with yours).
- AWS services are updated everyday and both the answers and questions might be outdated soon, so research accordingly.
- AWS exam questions are not updated to keep up the pace with AWS updates, so even if the underlying feature has changed the question might not be updated
- Open to further feedback, discussion and correction.
- What is a cluster placement group?
- A collection of Auto Scaling groups in the same Region
- Feature that enables EC2 instances to interact with each other via high bandwidth, low latency connections
- A collection of Elastic Load Balancers in the same Region or Availability Zone
- A collection of authorized Cloud Front edge locations for a distribution
- In order to optimize performance for a compute cluster that requires low inter-node latency, which feature in the following list should you use?
- AWS Direct Connect
- Cluster Placement Groups
- VPC private subnets
- EC2 Dedicated Instances
- Multiple Availability Zones
- What is required to achieve gigabit network throughput on EC2? You already selected cluster-compute, 10GB instances with enhanced networking, and your workload is already network-bound, but you are not seeing 10 gigabit speeds.
- Enable biplex networking on your servers, so packets are non-blocking in both directions and there’s no switching overhead.
- Ensure the instances are in different VPCs so you don’t saturate the Internet Gateway on any one VPC.
- Select PIOPS for your drives and mount several, so you can provision sufficient disk throughput
- Use a Cluster placement group for your instances so the instances are physically near each other in the same Availability Zone. (You are not guaranteed 10 gigabit performance, except within a placement group. Using placement groups enables applications to participate in a low-latency, 10 Gbps network)
- You need the absolute highest possible network performance for a cluster computing application. You already selected homogeneous instance types supporting 10 gigabit enhanced networking, made sure that your workload was network bound, and put the instances in a placement group. What is the last optimization you can make?
- Use 9001 MTU instead of 1500 for Jumbo Frames, to raise packet body to packet overhead ratios. (For instances that are collocated inside a placement group, jumbo frames help to achieve the maximum network throughput possible, and they are recommended in this case)
- Segregate the instances into different peered VPCs while keeping them all in a placement group, so each one has its own Internet Gateway.
- Bake an AMI for the instances and relaunch, so the instances are fresh in the placement group and do not have noisy neighbors
- Turn off SYN/ACK on your TCP stack or begin using UDP for higher throughput.
References
EC2_User_Guide – Placement_Groups


