AWS Certified Developer – Associate Exam Learning Path
NOTE – Refer to AWS Certified Developer – Associate June 2018 Exam for latest Developer Associate Exam learning path.
AWS Developer – Associate exam basically validates the following
- Design, develop and deploy cloud based solutions using AWS
- Understand the core AWS services, uses, and basic architecture best practices
- Develop and maintain applications written for Amazon Simple Storage Services (S3), Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS), Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS), Amazon Simple Workflow Service (SWF), AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and AWS CloudFormation
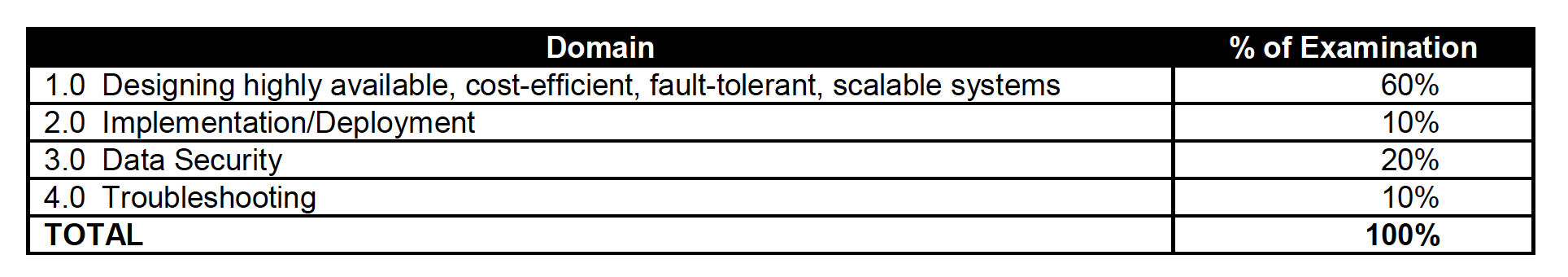
Refer to the AWS Certified Developer – Associate Exam Blue Print

AWS Developer – Associate Exam Contents
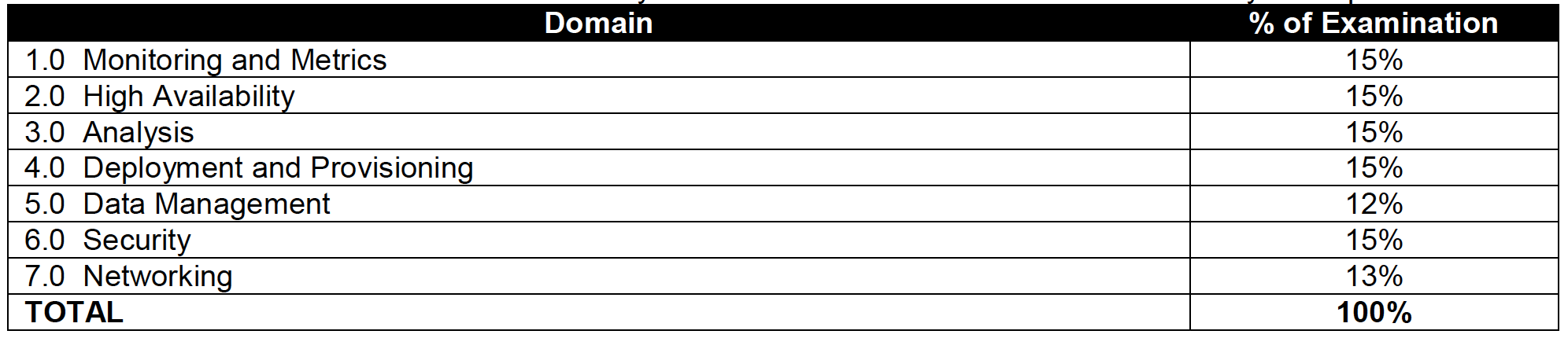
Domain 1.0: AWS Fundamentals
- 1.1 Identify and recognize cloud architecture considerations, such as fundamental components and effective designs.
- How to design cloud services
- Database concepts
- Planning and design
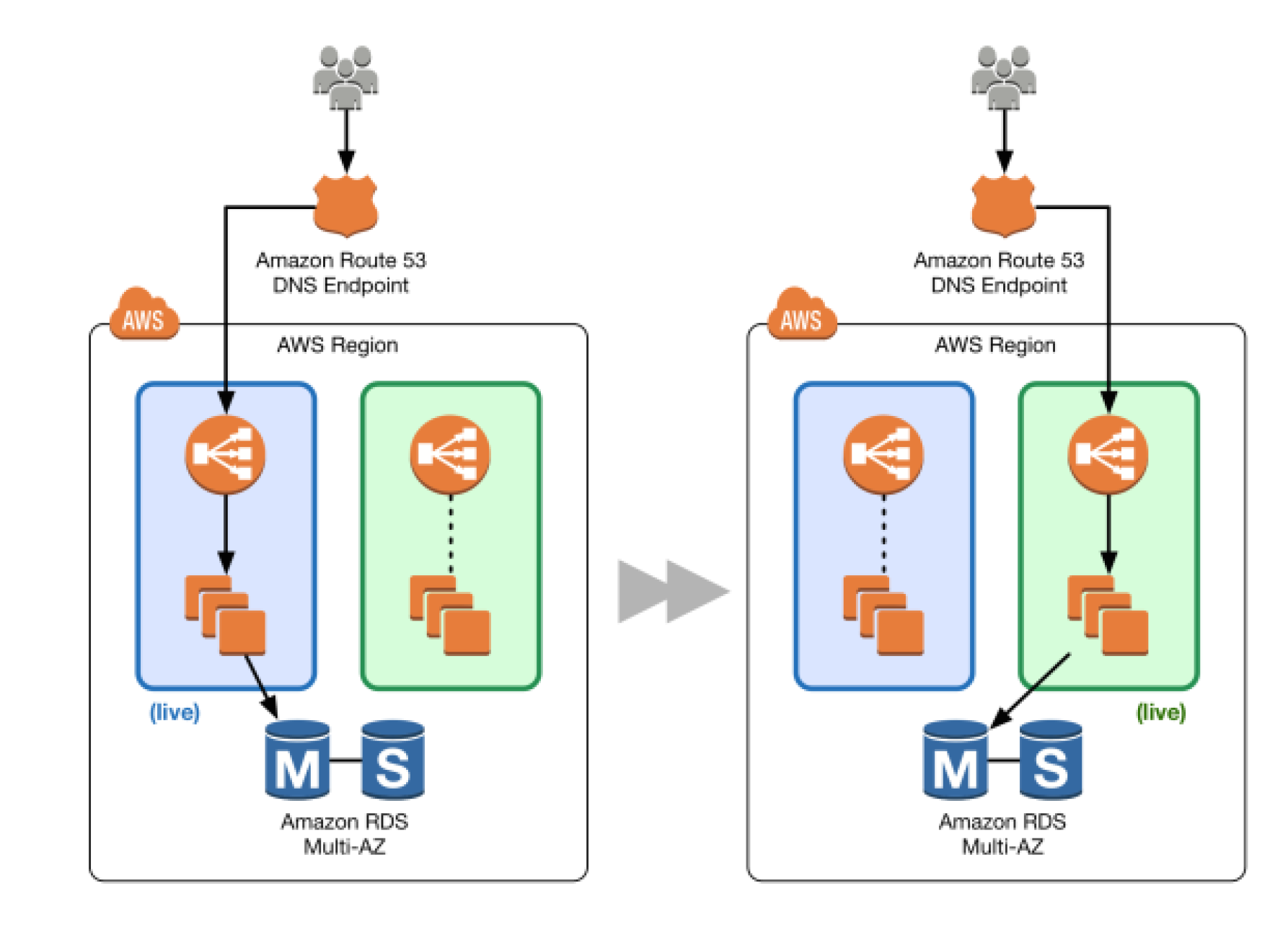
- Familiarity with architectural trade-off decisions (high availability vs. cost, Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) vs. installing your own database on Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2))
- include Storage Options Whitepaper
- Amazon S3, Amazon Simple Workflow Service (SWF), and Messaging
- DynamoDB, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, AWS CloudFormation
- Elasticity and scalability
Domain 2.0: Designing and Developing
- Identify the appropriate techniques to code a cloud solution.
- Configure an Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
- Programming with AWS APIs
- includes AWS Interaction Tools and actual usage of commands and APIs
Domain 3.0: Deployment and Security
- Recognize and implement secure procedures for optimum cloud deployment and maintenance.
- Cloud Security Best Practices
- Demonstrate ability to implement the right architecture for development, testing, and staging environments.
- Shared Security Responsibility Model
- AWS Platform Compliance
- AWS security attributes (customer workloads down to physical layer)
- Security Services
- includes KMS, Encryption techniques
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
- CIA and AAA models, ingress vs. egress filtering, and which AWS services and features fit
- AAA = authentication, authorization, and accounting
- CIA = Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability
- includes Security Groups vs NACLs, IAM Role, IAM Identity Providers and Federation
Domain 4.0: Debugging
- General troubleshooting information and questions
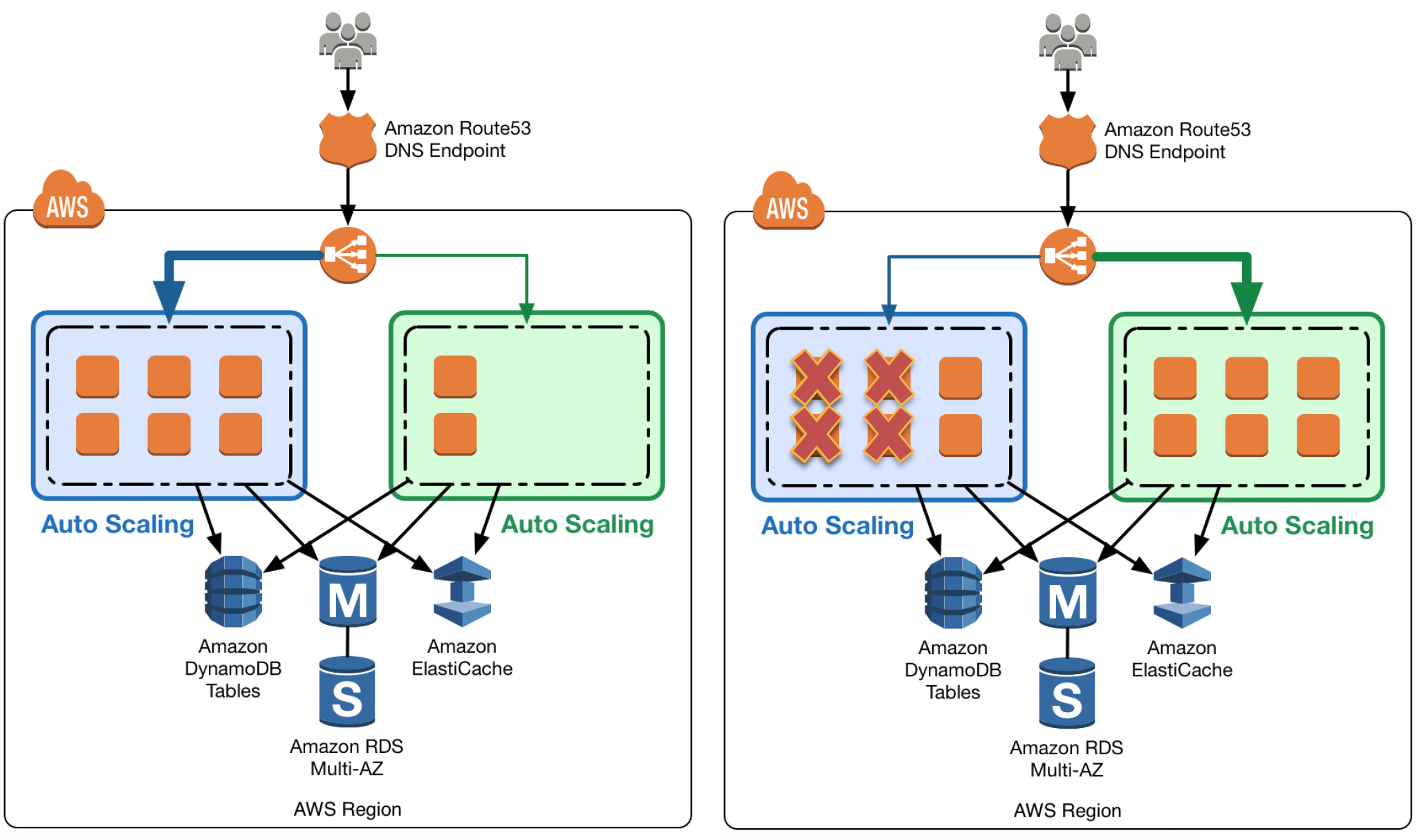
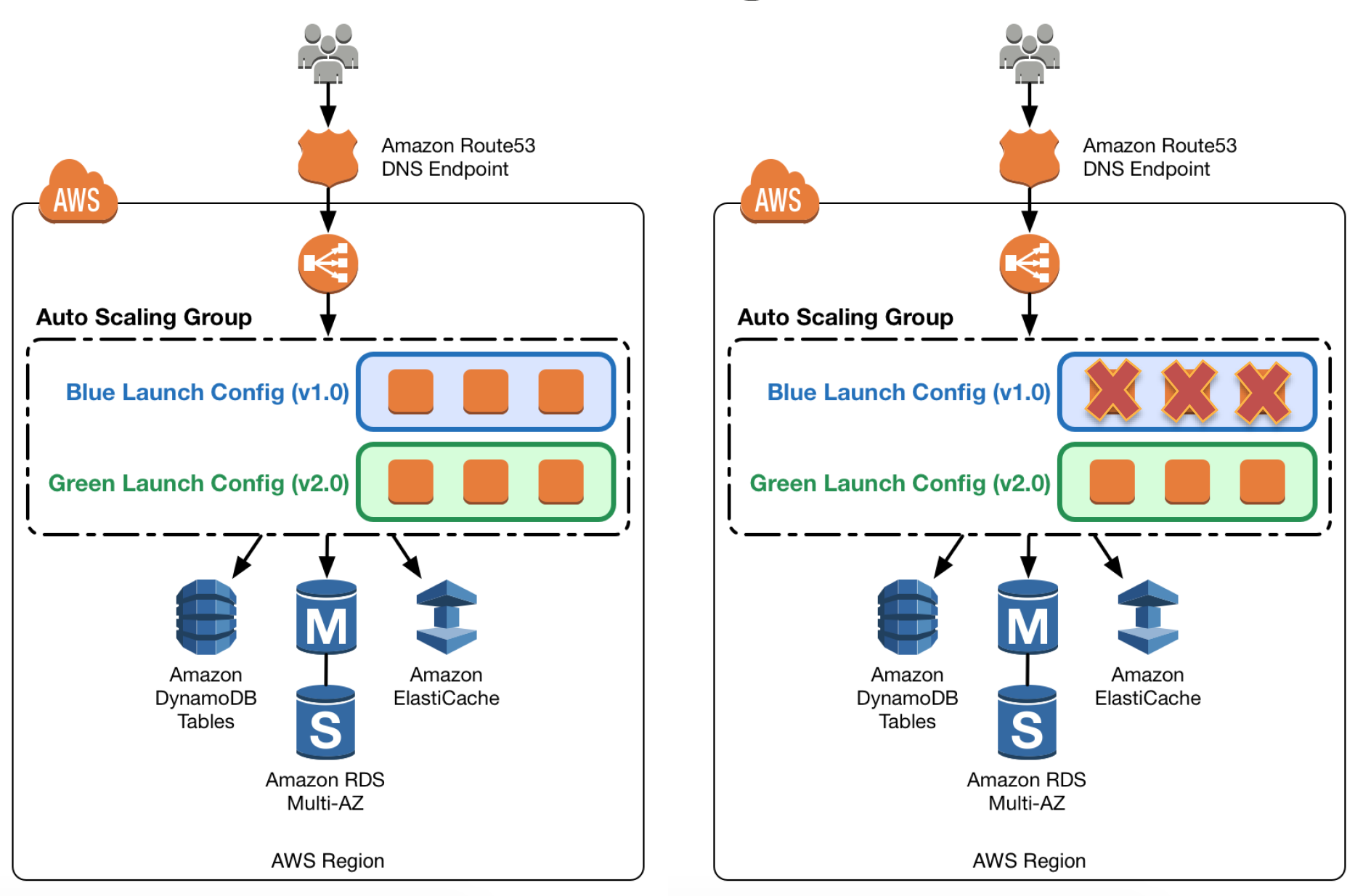
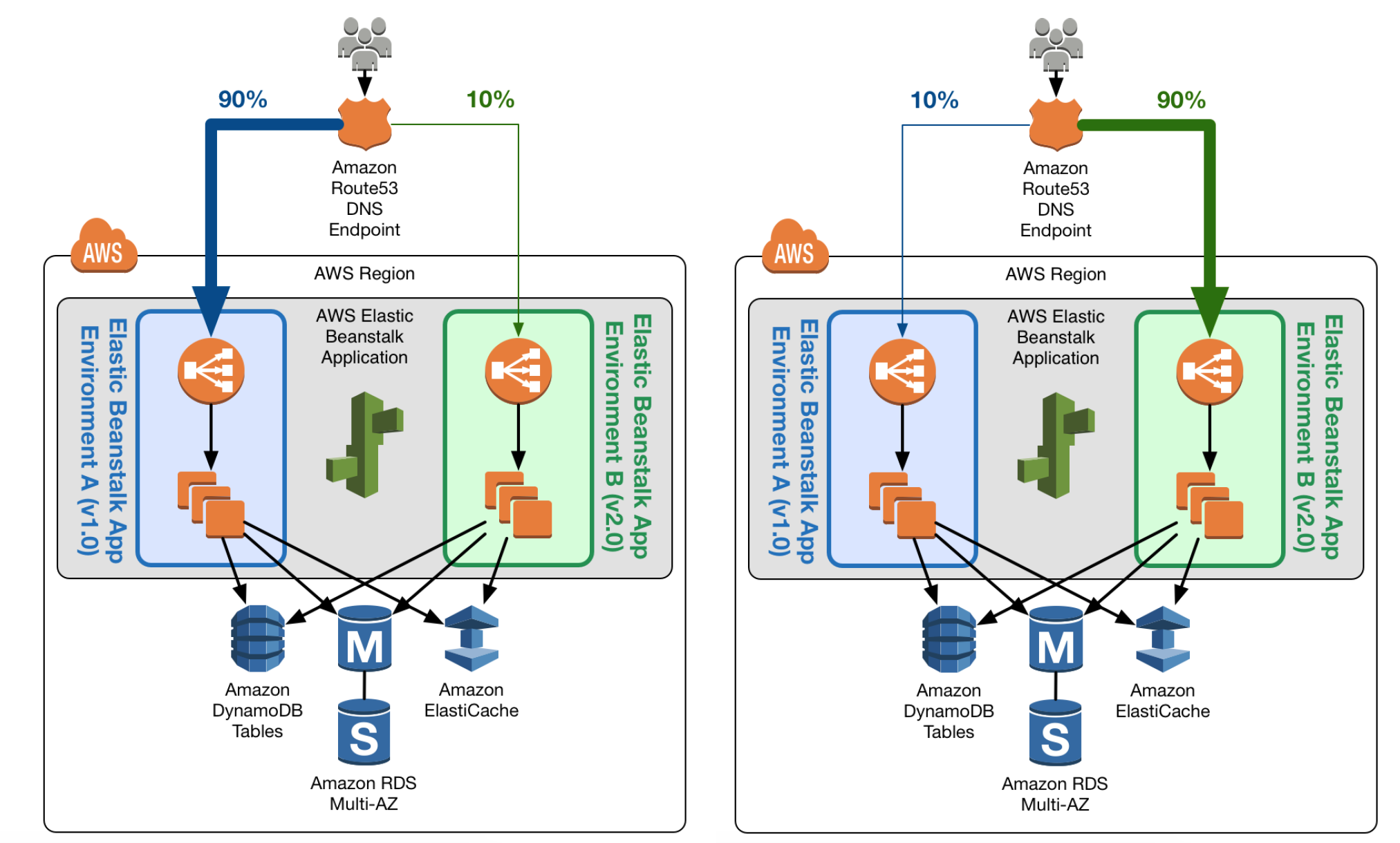
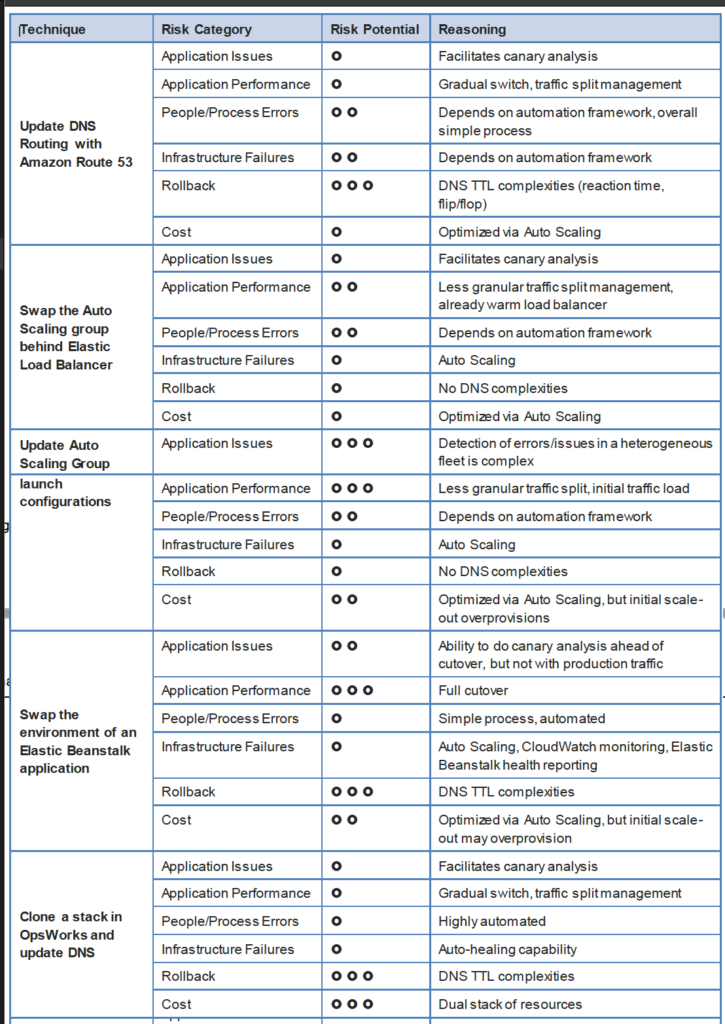
- includes Troubleshooting EC2, Auto Scaling
- Best Practices in debugging
NOTE: I have just marked the topics inline with the AWS Exam Blue Print. So be sure to check the same, as it is updated regularly and go through Whitepapers, FAQs and Re-Invent videos.
AWS Developer – Associate Exam Resources
- Purchased the acloud guru AWS Certified Developer – Associate course from udemy (should get it for $10-$15 on discount) helps to get a clear picture of the the format, topics and relevant sections
- Opinion : acloud guru course are good by itself but is not sufficient to pass the exam but might help to counter about 50-60% of exam questions
- Signed up with AWS for the Free Tier account which provides a lot of the Services to be tried for free with certain limits which are more then enough to get things going. Be sure to decommission anything, if you using any thing beyond the free limits, preventing any surprises 🙂
- Also, used the QwikLabs for all the introductory courses which are free and allow you to try out the services multiple times (I think its max 5, as I got the warnings couple of times)
- Update: Qwiklabs seems to have reduced the free courses quite a lot and now provide targeted labs for AWS Certification exams which are charged
- Read the FAQs atleast for the important topics, as they cover important points and are good for quick review
- Did not purchase the AWS Practice exams, as the questions are available all around. But if you want to check the format, it might be useful.
- You can also check practice tests
- Braincert AWS Certified Developer – Associate Practice Exam
- Set of extensive questions, with very nice, accurate & detailed explanation
- Whizlabs AWS Developer Associate Exam – Practice Test exams which seem to be similar to the actual AWS exam
- A Cloud Guru AWS Certified Developer – Associate (Practice Tests)
- Braincert AWS Certified Developer – Associate Practice Exam